Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini, Pack of 4
Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini, Pack of 4 Summary
Kit Summary
For the isolation of mouse CD4+ T cells.
Key Benefits
- Yields a highly pure (86-92%) population of CD4+ T cells
- Separates cells based on gravitational flow
- Negative selection reduces sources of experimental variation
Why Isolate CD4+ T cells?
CD4+ T cells develop in the thymus and differentiate into subsets of specialized effector T lymphocytes in response to distinct environmental cues and the activation of specific transcription factors. The isolation of CD4+ T cells is an important step in the preparation of multiple subsets including Th1, Th2, Th17, Th9, Th22, and regulatory T cells. CD4+ T cell subsets secrete characteristic combinations of cytokines which enables them to exert diverse functions including the recruitment and activation of additional immune cells, the dampening of ongoing immune responses, and the maintenance of immunologic memory.
The Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column Kit, Mini contains the following components to isolate mouse CD4+ T cells.
- Mouse CD4+ T Cell Subset Columns
- Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail
- Column Buffer Concentrate (10X)
Specifications
Product Datasheets
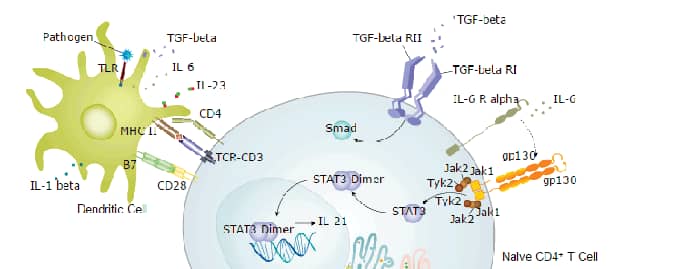
Background: CD4
CD4 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed predominantly on thymocytes and a subset of mature T lymphocytes. It is a standard phenotype marker for the identification of T cell populations. CD4 is expressed along with CD8 on double positive T cells during their development in the thymus. Either CD4 or CD8 expression is then lost, giving rise to single positive (SP) CD4+ or CD8+ mature T cells. CD4+ SP cells, also known as T helper cells, further differentiate into multiple subsets of CD4+ cells including Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17,Th22, Tfh, and Treg cells which regulate humoral and cellular immunity. In human, CD4 is additionally expressed on macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes, NK cells, and neurons and glial cells in the brain. CD4 binds directly to MHC class II molecules on antigen presenting cells. This interaction contributes to the formation of the immunological synapse which is focused around the TCR-MHC class II-antigenic peptide interaction. CD4 also functions as a chemotactic receptor for IL-16 and, in human, as a coreceptor for the gp120 surface glycoprotein of HIV-1.
Assay Procedure
Refer to the product datasheet for complete product details.
Briefly, mouse CD4+ T cells can be isolated using the following procedure:
- Incubate a single-cell suspension of leukocytes with the Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail
- Apply antibody-treated cell suspension to the CD4+ T Cell Subset Column
- Elute CD4+ T cells with 1X Column Buffer
Kit Contents
The Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column Kit, Mini (Catalog #MCD43) contains the following components to allow for the isolation of mouse CD4+ T cells.
- Mouse CD4+ T Cell Subset Columns
- Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail
- Column Buffer Concentrate (10X)
Other Supplies Required
Technical notes
- In order to best determine column performance, we advise that users retain a small portion of the starting cell population. Following cell selection with the column, it is then possible to perform immunophenotyping analysis on both starting and eluted cells. This information, when combined with the actual number of cells loaded and recovered, can then be used to calculate the percentage recovery of the target cell population.
- Care should be taken during cell preparation to reduce the number of platelets before loading the cells onto the column. Platelet contamination can be reduced by performing a final wash centrifugation of the cells at a reduced speed (150 - 200 x g).
- Some of the salts in the 10X column buffer solution may precipitate after storage at 4 °C. Should this be the case, do not carry out the 1:10 buffer dilution until all salts are in solution. This may be achieved by warming the 10X column buffer bottle in a 37 °C water bath for 5 - 10 minutes. Once there is no longer evidence of precipitates, the 10X column buffer may be diluted 1:10 to prepare the 1X column buffer for column processing.
Helpful Hints in Running T Cell Enrichment Columns
- Remove as many clumps as possible from the cell suspension before loading cells onto the column. Although the column is designed to filter out larger clumps of cells, too many clumps on the filter will reduce the column flow rate and cell recovery. In addition, leaving a large number of cells in a small volume of buffer for more than 30 minutes may promote cell clumping.
- If cells do not move into column after 15 minutes, the filter may have become clogged. If this occurs, move the white filter at the top of the column to the side with a sterile pipette. The cells should migrate into the column more easily.
- The column is designed so that the white filter at the top of the column bed will stop buffer flow and prevent the column from drying out. However leaving the open column exposed to air for more than 1 hour may cause the column bed to dry out and the CD4+ T cell enrichment to be compromised.
- Cell recovery after column processing is largely dependent on the total number of cells loaded. Optimal column performance is achieved by loading approximately 75 x106 cells. Loading fewer cells will negatively affect total cell recovery.
- If buffer does not drip out of column after initial removal of the bottom cap, try tapping the side of the column to remove any air locks that may be preventing the flow of buffer.
- The white filter at the top of the column bed may be found floating as a result of being dislodged during shipping. The column can still be used for cell processing after pushing the white filter onto the column bed with the back end of a sterile 2 mL pipette. The white filter should be positioned close to the column bed.
Procedure Overview
R&D Systems Protocol for Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini
Prepare a single cell suspension of mononuclear cells.
Wash the cells with excess sterile PBS.
Remove the red blood cells if necessary (e.g., using R&D Systems Mouse Erythrocyte Lysing Kit Catalog # WL2000)
Resuspend the cells in a small volume of 1X Column Wash Buffer.
Perform a cell count.
Adjust the cell concentration to 1 x 108 cells/mL with 1X Column Wash Buffer.

Mix 1 x 108 suspended cells with the contents of one vial of Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail.
Incubate for 15 minutes at room temperature.
Wash cells twice with 10 mL 1X Column Wash Buffer.
Resuspend cells in 1 mL of 1X Column Wash Buffer.
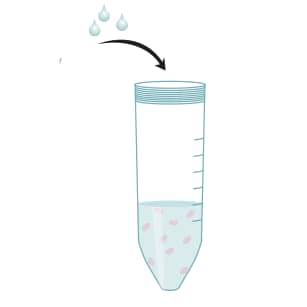
Load cell suspension onto the prepared column.
Incubate for 10 minutes at room temperature.
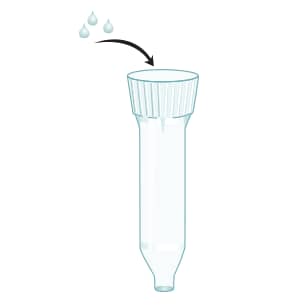
Elute CD4+ T cells with 8 mL of 1X Column Wash Buffer.
Collect the cells in a sterile 50 mL centrifuge tube.
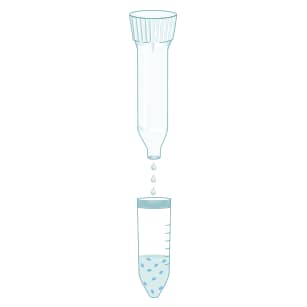
Pellet the cells using centrifugation.
Resuspend CD4+ T cells in the appropriate buffer or culture medium for downstream applications.
Citations for Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini, Pack of 4
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
13
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Immethridine, histamine H3-receptor (H3R) agonist, alleviated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via inhibiting the function of dendritic cells
Authors: Y Shi, Z Li, R Chen, J Zhang, X Hu, C He, Q Su, H Ma, H Ren, M Qian, S Cui, W Jiang
Oncotarget, 2017-08-24;8(43):75038-75049. 2017-08-24
-
LPS-treated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells induce immune tolerance through modulating differentiation of CD4(+) regulatory T cell subpopulations mediated by 3G11 and CD127
Authors: Fang Zhou
Immunol. Res, 2017-06-01;0(0):. 2017-06-01
-
Induction and characterization of anti-tumor endothelium immunity elicited by ValloVax therapeutic cancer vaccine
Authors: SC Wagner, TE Ichim, V Bogin, WP Min, F Silva, AN Patel, S Kesari
Oncotarget, 2017-04-25;8(17):28595-28613. 2017-04-25
-
Characterisation of a K390R ITK kinase dead transgenic mouse--implications for ITK as a therapeutic target.
Authors: Deakin A, Duddy G, Wilson S, Harrison S, Latcham J, Fulleylove M, Fung S, Smith J, Pedrick M, McKevitt T, Felton L, Morley J, Quint D, Fattah D, Hayes B, Gough J, Solari R
PLoS ONE, 2014-09-24;9(9):e107490. 2014-09-24
-
An artificial antigen-presenting cell with paracrine delivery of IL-2 impacts the magnitude and direction of the T cell response.
Authors: Steenblock ER, Fadel T, Labowsky M, Pober JS, Fahmy TM
J. Biol. Chem., 2011-08-17;286(40):34883-92. 2011-08-17
-
Impaired basophil induction leads to an age-dependent innate defect in type 2 immunity during helminth infection in mice.
Authors: Nel HJ, Hams E, Saunders SP
J. Immunol., 2011-03-11;186(8):4631-9. 2011-03-11
-
The role of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in regulating IFN-beta-mediated IL-10 production.
Authors: Wang H, Brown J, Garcia CA, Tang Y, Benakanakere MR, Greenway T, Alard P, Kinane DF, Martin M
J. Immunol., 2010-12-15;186(2):675-84. 2010-12-15
-
Systemic autoimmunity and defective Fas ligand secretion in the absence of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein.
Authors: Nikolov NP, Shimizu M, Cleland S
Blood, 2010-05-10;116(5):740-7. 2010-05-10
-
Functional Th1 cells are required for surgical adhesion formation in a murine model.
Authors: Tzianabos AO, Holsti MA, Zheng XX, Stucchi AF, Kuchroo VK, Strom TB, Glimcher LH, Cruikshank WW
J. Immunol., 2008-05-15;180(10):6970-6. 2008-05-15
-
Reversion of immune tolerance in advanced malignancy: modulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cell development by blockade of stem-cell factor function.
Authors: Pan PY, Wang GX, Yin B, Ozao J, Ku T, Divino CM, Chen SH
Blood, 2007-09-20;111(1):219-28. 2007-09-20
-
Relative importance of T-cell subsets in monocytotropic ehrlichiosis: a novel effector mechanism involved in Ehrlichia-induced immunopathology in murine ehrlichiosis.
Authors: Ismail N, Crossley EC, Stevenson HL, Walker DH
Infect. Immun., 2007-06-11;75(9):4608-20. 2007-06-11
-
Interleukin-23 and interleukin-27 exert quite different antitumor and vaccine effects on poorly immunogenic melanoma.
Authors: Oniki S, Nagai H, Horikawa T, Furukawa J, Belladonna ML, Yoshimoto T, Hara I, Nishigori C
Cancer Res., 2006-06-15;66(12):6395-404. 2006-06-15
-
TGF-beta 1 plays an important role in the mechanism of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell activity in both humans and mice.
Authors: Kitani A, Fuss I, Pedersen A, Nawata H
J. Immunol., 2004-01-15;172(2):834-42. 2004-01-15
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Cell Selection and Detection Kit FAQsReviews for Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini, Pack of 4
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini, Pack of 4 and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Column, Mini, Pack of 4?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image