Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Protein, CF New
Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Protein, CF Summary
- R&D Systems HEK293-derived Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Protein (11649-AV)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
| Human ITGAV (Phe31-Val992) Accession # AAA36808.1 | IEGR | Human IgG1 (Glu99-Lys330) (with modifications) |
| Human ITGB6 (Gly22-Asn707) Accession # P18564.2 | HHPIEGR | Human IgG1 (Glu99-Lys330) (with modifications) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
11649-AV
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 250 μg/mL in water. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
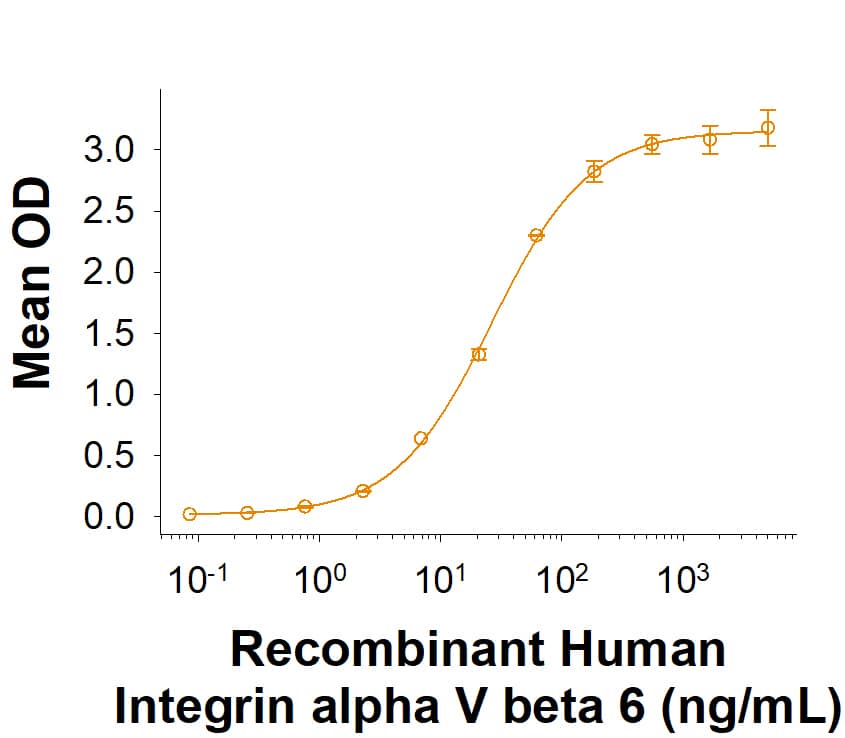 View Larger
View Larger
In a functional ELISA, Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11649-AV) binds to Recombinant Human LAP (TGF-beta 1) (246-LP) with an ED50 of 9.00‑96.0 ng/mL.
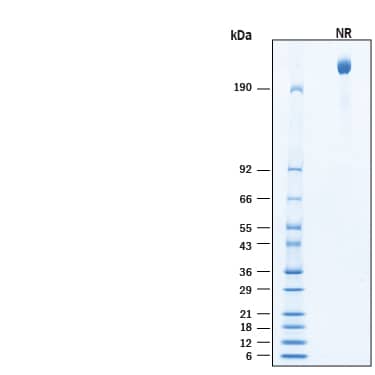 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11649-AV) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under non-reducing (NR) condition and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at >190 kDa.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Integrin alpha V beta 6
Integrin alpha V beta 6 is one of five alpha V integrins and the sole beta 6 integrin (1, 2). The non-covalent heterodimer of 170 kDa alpha V/CD51 and 95 kDa beta 6 integrin subunits is expressed exclusively on subsets of epithelial cells, especially during development, after injury or inflammation, or on many carcinomas (2-5). The ligand interaction site of alpha V beta 6 is in the N-terminal head region formed by an interaction of the beta 6 vWFA domain with the alpha V beta-propeller structure (2). The alpha V subunit contains domains termed thigh, calf, and calf-2 with a divalent cation-binding site found at a position equivalent to the “knee”. The 962 aa human alpha V ECD (4), which is cleaved at aa 890 but remains associated, shares 92-95% aa sequence identity with mouse and bovine alpha V, while the 685 aa human beta 6 ECD (5) shares 90-93% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat, bovine, ovine, and porcine beta 6. Each subunit has a transmembrane sequence and a short cytoplasmic tail connected to the cytoskeleton. The beta 6 C-terminal 11 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic sequence transduces a signal, enhancing proliferation and inducing MMP-9 expression (6). Either “inside-out” signaling or Mg2+ or Mn2+ binding unfolds and activates the integrin (1). Active alpha V beta 6 binds matrix proteins fibronectin and tenascin C (2). It also binds the TGF-beta latency‑associated peptide (LAP) and activates TGF-beta 1 or TGF-beta 3 from large latent complexes (7). This activation requires interaction with LTBP-1 and fibronectin, and is enhanced by PAR-1 (8, 9). Deletion of beta 6 ablates tonic inhibition of alveolar macrophages by TGF-beta, inhibits intestinal regulatory T cell production, and predisposes mice to inflammatory reactions in the skin, lungs, and intestines where irritations and microbial challenges are frequent (10-12). High alpha V beta 6 expression in carcinomas may contribute to progression through its effects on TGF-beta and MMP activity (3). The foot-and-mouth disease virus and several other viruses can use alpha V beta 6 as a receptor, and soluble alpha V beta 6 may block virus infectivity in vitro (13, 14).
- Hynes, R.O. (2002) Cell 110:673.
- Sheppard, D. (2004) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16:552.
- Bandyopadhyay, A. and S. Raghavan (2009) Curr. Drug Targets 10:645.
- Suzuki, S. et al. (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 262:14080.
- Sheppard, D. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265:11502.
- Dixit, R.B. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:25976.
- Munger, J.S. et al. (1999) Cell 96:319.
- Fontana, L. et al. (2005) FASEB J. 19:1798.
- Jenkins, R.G. et al. (2006) J. Clin. Invest. 116:1606.
- Huang, X.Z. et al. (1996) J. Cell Biol. 133:921.
- Morris, D.G. et al. (2003) Nature 422:169.
- Chen, X. et al. (2011) J. Leukoc. Biol. 90:751.
- Berryman, S. et al. (2005) J. Virol. 79:8519.
- Heikkila, O. et al. (2009) J. Gen. Virol. 90:197.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 Fc Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
