Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase Avi, CF New
Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase Avi, CF Summary
- R&D Systems HEK293-derived Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase Avi (AVI1310)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
Met1-Leu431 with C-terminal 6-His and Avi-tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
AVI1310
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in HEPES, NaCl and CaCl2. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM Tris, 0.01% (v/v) Tween® 20, pH 8.5
- Biotinylated Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase His-tag Avi-tag (rhuPA) (Catalog # AVI1310)
- Substrate: Z-GGR-AMC, 10 mM stock in DMSO
- Black 96-Well Plate
- Plate Reader with Fluorescence Read Capability
- Dilute rhuPA to 0.5 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute Substrate to 400 µM in Assay Buffer.
- Load 50 µL of the 0.5 µg/mL rhuPA into a black well plate and start the reaction by adding 50 µL of 400 µM Substrate. Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 µL Assay Buffer and 50 µL of 400 µM Substrate.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 380 nm and 460 nm (top read), respectively, in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
- Calculate specific activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Vmax* (RFU/min) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| amount of enzyme (µg) |
- rhuPA His Avi: 0.025 µg
- Substrate: 200 µM
Scientific Data
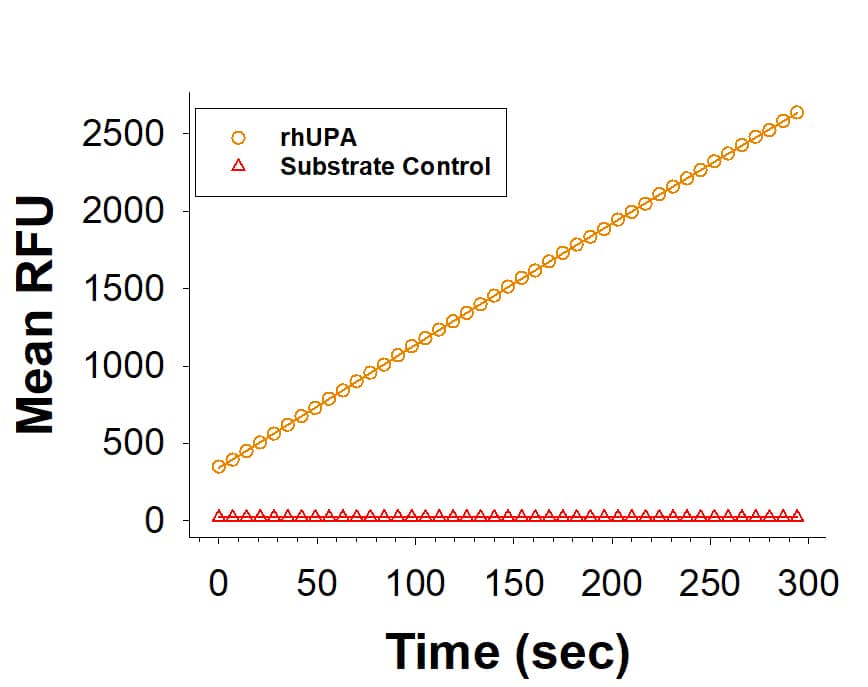 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator (uPA)/Urokinase His-tag Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI1310) is measured by its ability to cleave a peptide substrate, N-carbobenzyloxy-Gly-Gly-Arg-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (Z-GGR-AMC).
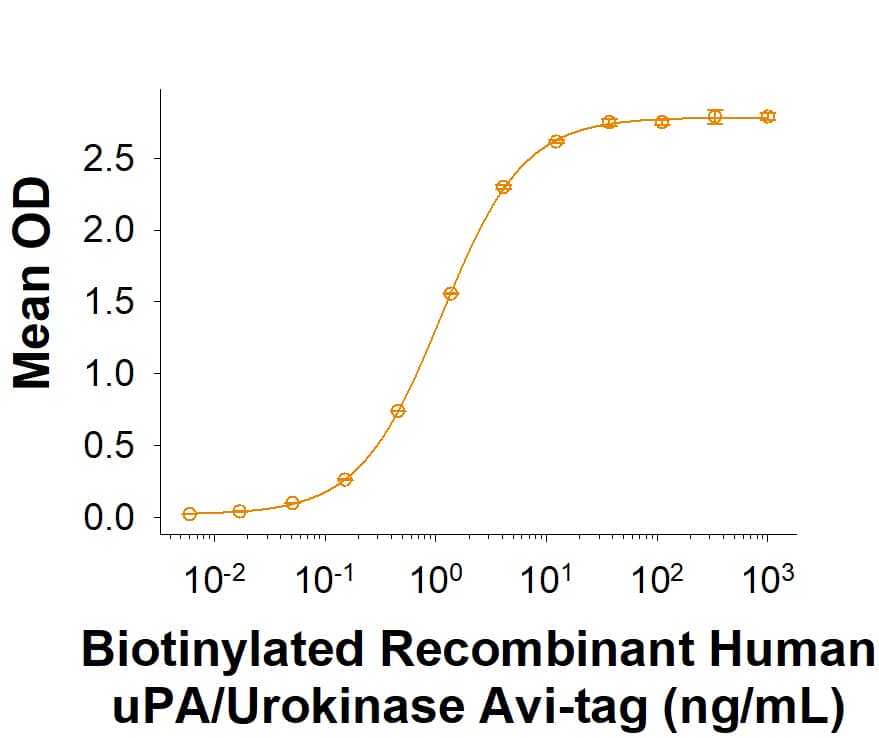 View Larger
View Larger
In a functional ELISA, Biotinylated Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator (uPA)/Urokinase His-tag Avi-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI1310) binds to Human u-Plasminogen Activator (uPA) Antibody (MAB1310) with an ED50 of 0.300-4.50 ng/mL
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: u-Plasminogen Activator (uPA)/Urokinase
Urokinase Plasminogen Activator (uPA), also known as u-plasminogen activator or urokinase, is a highly-specific serine protease from the peptidase S1 family that cleaves plasminogen to form plasmin making it a key player in the plasminogen activator (PA) system (1, 2). In cancer, the PA system plays a commanding role in tumor growth, angiogenesis, tumor cell invasion, migration, and metastasis. Expression of uPA is minimal in normal cells but is increased several fold in tumor cells by extracellular stimuli elevated in cancer (3) and corresponds to poor outcomes in several types of cancer (2, 4-7). Therefore, uPA has been identified as an excellent target for therapeutic development through inhibition of protease activity or though inhibition of uPA-dependent signaling while in complex with uPA receptor (uPAR) (2, 7). The pro-enzyme of uPA is synthesized with a N-terminal signal peptide and processed into an active disulfide-linked two-chain molecule (2, 7-10). For human uPA, the B chain starting at Ile179 corresponds to the catalytic domain. Two forms of the A chain exist, one starting at Ser21 (the long form) and the other at Lys156 (the short form). While the B chain is common for both forms, the long and short A chains are unique to expected 49 kDa and 34 kDa two-chain forms, respectively. The long A chain contains an EGF-like domain and the kringle domain. The long A domain is reportedly responsible for the binding of the uPA receptor (uPAR) (2,7).
- Ellis, V. (2004) in Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Barrett, A.J. et. al. eds., Academic Press, San Diego, pp.1677.
- Mahmood, N. et. al. (2018) Front Oncol. 8:24.
- Nagamine, Y. et. al. (2005) Thromb. Haemost. 93:661.
- Duffy, M. and C. Duggan. (2004) Clin. Biochem. 37:541.
- Pappot, H. et. al. (2006) Lung Cancer 51:193.
- Taubert, H. et. al. (2010) Br. J. Cancer 102:731.
- Masucci, M.T. et. al. (2022) Cancers. 14:498.
- Riccio, A. et. al. (1985) Nucleic Acids Res. 13:2759.
- Nagai, M. et. al. (1985) Gene 36:183.
- Jacobs, P. et. al. (1985) DNA 4:139.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase Avi, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase Avi, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human u-Plasminogen Activator/Urokinase Avi, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image

