Integrin beta 4/CD104 Recombinant Protein Antigen
Novus Biologicals | Catalog # NBP2-38298PEP

Key Product Details
Source
Applications
Product Specifications
Description
Source: E. coli
Amino Acid Sequence: IVDTVLMAPRSAKPALLKLTEKQVEQRAFHDLKVAPGYYTLTADQDARGMVEFQEGVELVDVRVPLFIRPEDDDEKQLLVEAIDVPAGTATLGRRLVNITIIKEQAR
Fusion Tag: N-terminal His6ABP (ABP = Albumin Binding Protein derived from Streptococcal Protein G)
This product is intended to be used as a blocking antigen for antibody competition assays. Any other use of this antigen is done at the risk of the user. The use of this product for commercial production is strictly prohibited. Please contact technical support if you have any questions.
Purity
Predicted Molecular Mass
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Applications
Application Notes
It is purified by IMAC chromatography, and the expected concentration is greater than 0.5 mg/ml.
For current lot information, including availability, please contact our technical support team click nb-technical@bio-techne.com
Protein / Peptide Type
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
NBP2-38298PEP
| Formulation | PBS and 1M Urea, pH 7.4. |
| Preservative | No Preservative |
| Concentration | Please see the vial label for concentration. If unlisted please contact technical services. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
Background: Integrin beta 4/CD104
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional Integrin beta 4/CD104 Products
Product Documents for Integrin beta 4/CD104 Recombinant Protein Antigen
Product Specific Notices for Integrin beta 4/CD104 Recombinant Protein Antigen
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. This product is guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Related Research Areas
Customer Reviews for Integrin beta 4/CD104 Recombinant Protein Antigen
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Integrin beta 4/CD104 Recombinant Protein Antigen and earn rewards!
Have you used Integrin beta 4/CD104 Recombinant Protein Antigen?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card!
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10CAN/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Submit a review
Associated Pathways
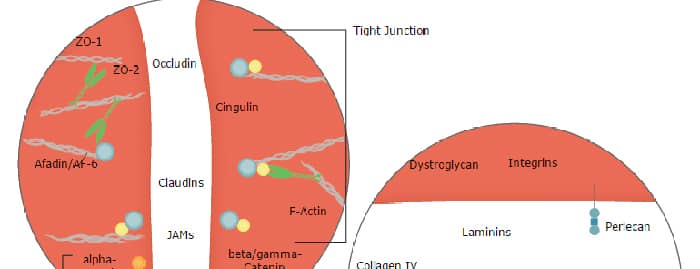
 Blood-Brain Barrier Pathway: Anatomy
Blood-Brain Barrier Pathway: Anatomy