CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
Novus Biologicals | Catalog # NBP1-19371

![Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NBP1-19371-img0017.jpg)
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Format
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Reactivity Notes
Localization
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Description
Scientific Data Images for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Increased CD3+ and CD4+ T-cell occurrence in the brainstem of SHR-72 transgenic rat model for tauopathies. (A-D) Immunofluorescence staining showed CD4+ T-cells in SHR-72 transgenic animals. (E- H) Immunofluorescence staining showed more perivascular than brain parenchyma infiltrating CD4+ T-cells in SHR-72 transgenic animals. PLoS One. 2019 May 23;14(5):e0217216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217216.Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - DBZ inhibits the accumulation of CD4+ T cells and Th2 differentiation in the AAAs. (B) The representation of immunohistochemical staining for CD4+ in abdominal aorta from four groups (left). Bar graphs show the percentage of CD4+ positive cell areas (right; n=3 per group). Bar: 50 um.Western Blot: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Western Blot: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - CD4 antibody was tested in the following cell lysates: 1) human spleen 2) human tonsil 3) human placenta 4) human kidney 5) human liver 6) mouse spleen 7) mouse placenta 8) rat placenta.Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - CD4 antibody was tested in Jurkat cells with DyLight 488 (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] - An intracellular stain was performed on U-251 MG cells with CD4 Antibody NBP1-19371AF594 (blue) and a matched isotype control NBP2-24891 (orange). Cells were fixed with 4% PFA and then permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. Cells were incubated in an antibody dilution of 2.5 ug/mL for 30 minutes at room temperature. Both antibodies were conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594.Western Blot: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Western Blot: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Mouse spleen, 25ug total protein. Image from verified customer review.Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Staining of paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue. Photo courtesy of product review by verified customer.Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Analysis of a FFPE tissue section of mouse brain using CD4 antibody at 1:300 dilution with HRP-DAB detection and hematoxylin counterstaining. The antibody primarily generated a strong signal in the membranes of a subset of cells in the tested section.Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Analysis of a FFPE section of mouse spleen using CD4 antibody at 1:300 dilution with HRP-DAB detection and hematoxylin counterstaining. The antibody generated a strong signal in the membranes of a subset of cells in the spleen section and the staining showed punctate appearance in some cells.Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Staining in mouse liver tissue.Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Alcohol-fixed paraffin-embedded rat spleen tissue. Dilution 1:150. Image from verified customer review.Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - An intracellular stain was performed on Jurkat cells with CD4 Antibody NBP1-19371R (blue) and a matched isotype control (orange). Cells were fixed with 4% PFA and then permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. Cells were incubated in an antibody dilution of 5 ug/mL for 30 minutes at room temperature. Both antibodies were conjugated to DyLight 550.Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - An intracellular stain was performed on Jurkat cells with CD4 Antibody NBP1-19371AF488 (blue) and a matched isotype control (orange). Cells were fixed with 4% PFA and then permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. Cells were incubated in an antibody dilution of 10 ug/mL for 30 minutes at room temperature. Both antibodies were conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488.Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - An intracellular stain was performed on U937 cells with CD4 Antibody NBP1-19371AF594 (blue) and a matched isotype control (orange). Cells were fixed with 4% PFA and then permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. Cells were incubated in an antibody dilution of 2.5 ug/mL for 30 minutes at room temperature. Both antibodies were conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594.Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - An intracellular stain was performed on U937 cells with CD4 Antibody NBP1-19371G (blue) and a matched isotype control (orange). Cells were fixed with 4% PFA and then permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. Cells were incubated in an antibody dilution of 5 ug/mL for 30 minutes at room temperature. Both antibodies were conjugated to DyLight 488.Simple Western: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371]
Simple Western: CD4 Antibody [NBP1-19371] - Lane view shows a specific band for CD4 in 0.5 mg/ml of HeLa lysate. This experiment was performed under reducing conditions using the 12-230 kDa separation system.Western Blot: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] -
ATM activation by chloroquine alleviates senescence.(a) Immunoblots showing protein levels of ATM, NBS1, and RAP80 in human skin fibroblasts (HSFs). A gradually increased level of p16 indicates cellular senescence, while elevated gamma H2AX level indicates accumulated DNA damage. (b) Immunoblots showing protein levels of ATM, NBS1, and RAP80 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). (c) Immunoblots showing protein levels of ATM, NBS1, and RAP80 in brain tissues isolated from 3-, 10-, and 18-month-old male mice. (d) SA-beta -Gal staining in HSFs treated with sh-ATM or scramble shRNA. Scale bar, 100 µm. (e) Quantification of SA-beta -Gal-positive staining of (d) from five views randomly captured for each group. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.001. (f) Immunoblots showing increased gamma H2AX and unaffected LC3I/II in HSFs treated with sh-ATM or scramble shRNA. (g) Immunoblots showing protein levels of pS1981 ATM, gamma H2AX, and cleaved caspase-3 in HSFs treated with 10 μM of CQ for indicated time. (h) SA-beta -Gal staining in HSFs expressing either scramble or ATM shRNA treated with 1 μM CQ or DMSO (12 hr). Scale bar, 100 µm. (i) Quantification of SA-beta -Gal-positive staining of (h) from five views randomly captured for each group. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.001; ‘N.S.’ indicates no significant difference. (j) HSFs at passage 20 were continuously cultured with 1 μM CQ or DMSO, and cell number was calculated at each passage. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.01. (k) Immunoblots showing protein levels of gamma H2AX, p62, and LC3 in MEFs treated with 1 μM CQ or DMSO. Note that CQ had little effect on the expression levels of p62 and LC3. (l) MEFs at passage one were continuously cultured in 20% O2 with 1 μM CQ or DMSO, and cell number was determined at each passage. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.01.10.7554/eLife.34836.006Figure 1—source data 1.Statistical analysis for SA-beta -Gal positive staining.10.7554/eLife.34836.007Figure 1—source data 2.Statistical analysis for EdU positive staining.Statistical analysis for SA-beta -Gal positive staining.Statistical analysis for EdU positive staining.Decline of ATM-centered DNA repair machinery during senescence.(a) Real-time PCR analysis showing progressively elevated mRNA level of p21 in continuously cultured human endothelial cells (HUVEC). **p<0.01. (b) SA-beta -Gal staining of HUVEC cells at indicated passages. Scale bar, 100 µm. (c) HUVEC cells at P21, P18, P12, and P7 were subjected to transcriptome analysis. A minimum average rpkm value of 1.0 and maximum 10% fluctuation in young cells (P7 Vs P12) was set as the threshold. Genes were downregulated by more than 20% in pre-senescent, and senescent cells compared with young cells (P21/P18 Vs P12/P7) were selected. (d) Pathway analysis of genes identified in (c) by STRING v10. (e) Downregulation of ATM-related DNA repair genes during senescence.ATM regulates replicative senescence.(a) Representative images showing cells treated with Scramble (sh-NC) or sh-ATM. (b) Percent EdU-positive cells in sh-NC or sh-ATM treated HSFs. Views were randomly captured and at least 100 cells were included in each group. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.001. (c) Immunoblots showing protein levels of pS1981 ATM and gamma H2AX in HSFs treated with 10 μM chloroquine (CQ) or 0.4 μM CPT (4 hr). Note that CQ activated ATM (pS1981) without increasing gamma H2AX, while CPT activated ATM accompanied by increased gamma H2AX. (d) SA-beta -Gal staining in primary MEFs treated with 1 μM CQ or DMSO. Scale bar, 100 µm. (e) Quantification of SA-beta -Gal-positive staining of (d) from five views randomly captured for each group. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.001. (f) Percent EdU-positive cells in HSFs treated with DMSO, 1 μM or 10 μM CQ. Views were randomly captured and at least 100 cells were included in each group. Data represent means ± SEM. ***p<0.001. (g) Representative images showing proliferative HSFs treated with different doses of CQ for the indicated time points. (h) Immunoblots showing LC3B levels in HSFs treated with indicated dose of CQ for indicated period of time. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29717979), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] - Rats with mild liver damage show immune cells infiltration in cerebellum at 4 weeks, which is prevented by rifaximin. Analysis of immune cells infiltration in cerebellum was performed at 4 weeks by immunohistochemistry using antibodies against (A) CD4, a marker of T lymphocytes (F(3,8) = 4.511, p < 0.01) & (B) IBA1, a marker of meningeal & perivascular macrophages (K-W(4,10) = 27.76, p < 0.0001). (C) Double immunofluorescence with anti-CD4 & anti-CX3CR1 as markers of autoreactive CD4+CD28− T lymphocytes was performed & quantified (K-W(4,5) = 8.711, p < 0.05). (D) Double immunofluorescence with anti-CD4 & anti-CCR6 as marker of Th17 lymphocytes was performed & quantified (K-W(4,7) = 8.858, p < 0.05). Number of animals in each group was added under group names. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test (CD4+) & nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis (K-W statistic) with Dunn’s test (Iba1, CD4+/CX3CR1+ & CD4+/CCR6+) was performed to compare all groups. Values significantly different from control rats are indicated by asterisks & from CCl4 rats by a. * p < 0.05, a p < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34440206), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.Applications for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
Flow Cytometry
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
Simple Western
Western Blot
This CD4 antibody is useful for ICC, Western Blot, and IHC-paraffin embedded sections. In WB, a band is seen ~45 kDa. In ICC/IF, membrane staining was observed in human brain cells. Prior to immunostaining paraffin tissues, antigen retrieval with sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) is recommended. In ICC/IF, membrane staining was observed in Jurkat cells.
In Simple Western only 10 - 15 uL of the recommended dilution is used per data point.
See Simple Western Antibody Database for Simple Western validation: Tested in HeLa lysate 0.5 mg/mL, separated by Size, antibody dilution of 1:100. Separated by Size-Wes, Sally Sue/Peggy Sue.
Reviewed Applications
Read 9 reviews rated 4.1 using NBP1-19371 in the following applications:
Flow Cytometry Panel Builder
Bio-Techne Knows Flow Cytometry
Save time and reduce costly mistakes by quickly finding compatible reagents using the Panel Builder Tool.
Advanced Features
- Spectra Viewer - Custom analysis of spectra from multiple fluorochromes
- Spillover Popups - Visualize the spectra of individual fluorochromes
- Antigen Density Selector - Match fluorochrome brightness with antigen density
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Format
Preservative
Concentration
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: CD4
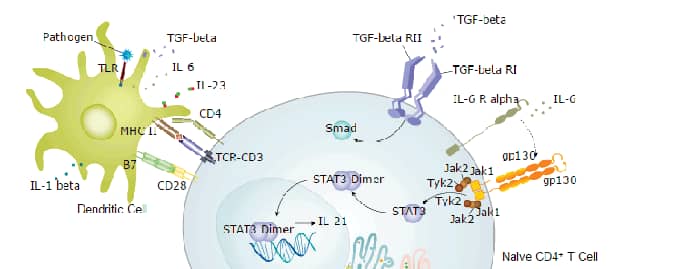
Given its critical role in T cell development, CD4 also has diverse immunology-related functions. CD4 acts as a coreceptor with the T-cell receptor (TCR) during T cell activation and thymic differentiation by binding directly to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigens and associating with the protein tyrosine kinase, Lck (4). This interaction contributes to the formation of the immunological synapse (5). Defects in antigen presentation cause dysfunction of CD4+ T cells and the almost complete loss of MHC II expression on B cells in peripheral blood, as observed in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) (6). CD4 also functions as a receptor for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) by binding to gp120, the envelope glycoprotein of HIV-1. It has been shown that the V-like domains are critical for binding to gp120 (7). In immune mediated and infectious diseases of the central nervous system, CD4 functions as an indirect mediator of neuronal damage (8).
References
1. Omri, B., Crisanti, P., Alliot, F., Marty, M., Rutin, J., Levallois, C.,... Pessac, B. (1994). CD4 expression in neurons of the central nervous system. International Immunology, 6(3), 377-385. doi:10.1093/intimm/6.3.377
2. Wan, Y. Y., & Flavell, R. A. (2009). How diverse-CD4 effector T cells and their functions. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, 1(1), 20-36. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjp001
3. Wu, H., Myszka, D. G., Tendian, S. W., Brouillette, C. G., Sweet, R. W., Chaiken, I. M., & Hendrickson, W. A. (1996). Kinetic and structural analysis of mutant CD4 receptors that are defective in HIV gp120 binding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 93(26), 15030-15035. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.26.15030
4. Doyle, C., & Strominger, J. L. (1987). Interaction between CD4 and class II MHC molecules mediates cell adhesion. Nature, 330, 256-259. doi:10.1038/330256a0
5. Vignali, D. A. (2010). CD4 on the road to coreceptor status. The Journal of Immunology, 184(11), 5933-5934. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1090037
6. Tasher, D., & Dalal, I. (2012). The genetic basis of severe combined immunodeficiency and its variants. The Application of Clinical Genetics, 5, 67-80. doi:10.2147/tacg.s18693
7. Arthos, J., Deen, K. C., Chaikin, M. A., Fornwald, J. A., Sathe, G., Sattentau, Q. J.,... Sweet, R. W. (1989). Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell, 57(3), 469-481. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7
8. Buttini, M., Westland, C. E., Masliah, E., Yafeh, A. M., Wyss-Coray, T., Mucke, L. (1998). Novel role of human cd4 molecule identified in neurodegeneration. Nature Medicine, 4(4), 441-446. doi:10.1038/nm0498-441
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional CD4 Products
Product Documents for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Citations for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
Customer Reviews for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free (9)
Have you used CD4 Antibody - BSA Free?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card!
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10CAN/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Submit a review
Customer Images
-
Application: Immunohistochemistry-ParaffinSample Tested: Spleen tissueSpecies: Sprague-Dawley ratVerified Customer | Posted 01/04/2019Alcohol-fixed paraffin-embedded rat spleen tissue. Dilution: 1:150
-
Application: Immunohistochemistry-FrozenSample Tested: LiverSpecies: MouseVerified Customer | Posted 06/05/2018
-
Application: Immunohistochemistry-FrozenSample Tested: Mouse SpleenSpecies: MouseVerified Customer | Posted 03/16/2017Double staining of CD4 (green) and CD20 (red) on OCT frozen spleen sections from 3 weeks CCl4 treated mouse. 1ry CD4 Ab is the NBP1-19371 CD4 Ab from Novus Biologicals. 2ry Ab is A647.
-
Application: Immunohistochemistry-ParaffinSample Tested: Mouse SpleenSpecies: MouseVerified Customer | Posted 10/06/2015Mouse spleen, cells in red pulp
-
Application: Immunohistochemistry-ParaffinVerified Customer | Posted 10/04/2014Synovium
-
Application: Western BlotSample Tested: Dog Spleen HomogenateSpecies: OtherVerified Customer | Posted 09/19/2014Dog Spleen Homogenate; Dual-Probed with Anti-CD4 and Anti-CD8
-
Application: Western BlotVerified Customer | Posted 08/28/2014Mouse spleen, 25ug total protein
-
Application: Flow CytometrySample Tested: Human peripheral blood cellsSpecies: HumanVerified Customer | Posted 04/24/2010
-
Application: Immunohistochemistry-ParaffinSample Tested: Mouse Brain TissueSpecies: MouseVerified Customer | Posted 04/22/2010
There are no reviews that match your criteria.
Protocols
View specific protocols for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free (NBP1-19371):
Immunocytochemistry Protocol
Culture cells to appropriate density in 35 mm culture dishes or 6-well plates.
1. Remove culture medium and add 10% formalin to the dish. Fix at room temperature for 30 minutes.
2. Remove the formalin and add ice cold methanol. Incubate for 5-10 minutes.
3. Remove methanol and add washing solution (i.e. PBS). Be sure to not let the specimen dry out. Wash three times for 10 minutes.
4. To block nonspecific antibody binding incubate in 10% normal goat serum from 1 hour to overnight at room temperature.
5. Add primary antibody at appropriate dilution and incubate at room temperature from 2 hours to overnight at room temperature.
6. Remove primary antibody and replace with washing solution. Wash three times for 10 minutes.
7. Add secondary antibody at appropriate dilution. Incubate for 1 hour at room temperature.
8. Remove antibody and replace with wash solution, then wash for 10 minutes. Add Hoechst 33258 to wash solution at 1:25,0000 and incubate for 10 minutes. Wash a third time for 10 minutes.
9. Cells can be viewed directly after washing. The plates can also be stored in PBS containing Azide covered in Parafilm (TM). Cells can also be cover-slipped using Fluoromount, with appropriate sealing.
*The above information is only intended as a guide. The researcher should determine what protocol best meets their needs. Please follow safe laboratory procedures.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin Embedded Sections
Antigen Unmasking:
Bring slides to a boil in 10 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) then maintain at a sub-boiling temperature for 10 minutes. Cool slides on bench-top for 30 minutes.
Staining:
1. Wash sections in deionized water three times for 5 minutes each.
2. Wash sections in wash buffer for 5 minutes.
3. Block each section with 100-400 ul blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature.
4. Remove blocking solution and add 100-400 ul diluted primary antibody. Incubate overnight at 4C.
5. Remove antibody solution and wash sections in wash buffer three times for 5 minutes each.
6. Add 100-400 ul biotinylated diluted secondary antibody. Incubate 30 minutes at room temperature.
7. Remove secondary antibody solution and wash sections three times with wash buffer for 5 minutes each.
8. Add 100-400 ul Streptavidin-HRP reagent to each section and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature.
9. Wash sections three times in wash buffer for 5 minutes each.
10. Add 100-400 ul DAB substrate to each section and monitor staining closely.
11. As soon as the sections develop, immerse slides in deionized water.
12. Counterstain sections in hematoxylin.
13. Wash sections in deionized water two times for 5 minutes each.
14. Dehydrate sections.
15. Mount coverslips.
1. Perform SDS-PAGE on samples to be analyzed, loading 25 ug of total protein per lane.
2. Transfer proteins to membrane according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the membrane and transfer apparatus.
3. Stain according to standard Ponceau S procedure (or similar product) to assess transfer success, and mark molecular weight standards where appropriate.
4. Rinse the blot.
5. Block the membrane using standard blocking buffer for at least 1 hour.
6. Wash the membrane in wash buffer three times for 10 minutes each.
7. Dilute primary antibody in blocking buffer and incubate 1 hour at room temperature.
8. Wash the membrane in wash buffer three times for 10 minutes each.
9. Apply the diluted HRP conjugated secondary antibody in blocking buffer (as per manufacturers instructions) and incubate 1 hour at room temperature.
10. Wash the blot in wash buffer three times for 10 minutes each (this step can be repeated as required to reduce background).
11. Apply the detection reagent of choice in accordance with the manufacturers instructions.
*Note: Tween-20 can be added to the blocking or antibody dilution buffer at a final concentration of 0.05-0.2%.
Find general support by application which include: protocols, troubleshooting, illustrated assays, videos and webinars.
- 7-Amino Actinomycin D (7-AAD) Cell Viability Flow Cytometry Protocol
- Antigen Retrieval Protocol (PIER)
- Antigen Retrieval for Frozen Sections Protocol
- Appropriate Fixation of IHC/ICC Samples
- Cellular Response to Hypoxia Protocols
- Chromogenic IHC Staining of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Protocol
- Chromogenic Immunohistochemistry Staining of Frozen Tissue
- Detection & Visualization of Antibody Binding
- Extracellular Membrane Flow Cytometry Protocol
- Flow Cytometry Protocol for Cell Surface Markers
- Flow Cytometry Protocol for Staining Membrane Associated Proteins
- Flow Cytometry Staining Protocols
- Flow Cytometry Troubleshooting Guide
- Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Protocol
- Graphic Protocol for Heat-induced Epitope Retrieval
- Graphic Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections
- Graphic Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections
- Graphic Protocol for the Preparation of Gelatin-coated Slides for Histological Tissue Sections
- ICC Cell Smear Protocol for Suspension Cells
- ICC Immunocytochemistry Protocol Videos
- ICC for Adherent Cells
- IHC Sample Preparation (Frozen sections vs Paraffin)
- ISH-IHC Protocol for Chromogenic Detection on Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) Tissue
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Protocol
- Immunocytochemistry Troubleshooting
- Immunofluorescence of Organoids Embedded in Cultrex Basement Membrane Extract
- Immunofluorescent IHC Staining of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Protocol
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Protocols
- Immunohistochemistry Frozen Troubleshooting
- Immunohistochemistry Paraffin Troubleshooting
- Intracellular Flow Cytometry Protocol Using Alcohol (Methanol)
- Intracellular Flow Cytometry Protocol Using Detergents
- Intracellular Nuclear Staining Flow Cytometry Protocol Using Detergents
- Intracellular Staining Flow Cytometry Protocol Using Alcohol Permeabilization
- Intracellular Staining Flow Cytometry Protocol Using Detergents to Permeabilize Cells
- Preparing Samples for IHC/ICC Experiments
- Preventing Non-Specific Staining (Non-Specific Binding)
- Primary Antibody Selection & Optimization
- Propidium Iodide Cell Viability Flow Cytometry Protocol
- Protocol for Heat-Induced Epitope Retrieval (HIER)
- Protocol for Making a 4% Formaldehyde Solution in PBS
- Protocol for VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Detection Reagent
- Protocol for the Characterization of Human Th22 Cells
- Protocol for the Characterization of Human Th9 Cells
- Protocol for the Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cell Smears - Graphic
- Protocol for the Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cultured Cells on Coverslips - Graphic
- Protocol for the Preparation & Fixation of Cells on Coverslips
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections - Graphic
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections - Graphic
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation of Gelatin-coated Slides for Histological Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation of a Cell Smear for Non-adherent Cell ICC - Graphic
- Protocol: Annexin V and PI Staining by Flow Cytometry
- Protocol: Annexin V and PI Staining for Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
- R&D Systems Quality Control Western Blot Protocol
- TUNEL and Active Caspase-3 Detection by IHC/ICC Protocol
- The Importance of IHC/ICC Controls
- Troubleshooting Guide: Fluorokine Flow Cytometry Kits
- Troubleshooting Guide: Immunohistochemistry
- Troubleshooting Guide: Western Blot Figures
- Western Blot Conditions
- Western Blot Protocol
- Western Blot Protocol for Cell Lysates
- Western Blot Troubleshooting
- Western Blot Troubleshooting Guide
- View all Protocols, Troubleshooting, Illustrated assays and Webinars
FAQs for CD4 Antibody - BSA Free
-
A: I just had a look at our QC records and I do not see any mention on using this antibody without antigen retrieval. Moreover, the inclusion or exclusion of antigen retrieval step in protocol depends primarily on the time allowed for tissues fixation (if the tissues were left in fixative for longer time, say more than 14 hours, I would not suggest you to omit the antigen retrieval step). The IHC use of our above mentioned antibody has been cited in couple of recent peer reviewed publications (Immunol Lett. 2011 Aug 30;138:169-78; Cryobiology. 2012 Feb;64:27-32) and you may follow the same for comparison of your IHC outcome.
-
Q: I want to stain some T cell subsets (Th17 and Th1), do you have antibodies for that? I need for flow cytometer in sheep or goat.
A: Unfortunately, we have neither a CD4 antibody nor an IL-17 antibody that has been validated in sheep or goat, although if you would like to try one you would again be eligible for our Innovators Reward Program. Please contact us at innovators@novusbio.com with any questions regarding this program. -
Q: Unmasking method used for detection of Mouse CD4 cells in FFPE tissue secitons with NBP1-19371. HIER with citrate buffer pH6 or enzyme digestion. Details would be very much appreciated. I have this Ab and need some information before I begin to use it on mouse FFPE tissues.
A: I would recommend antigen retrieval using citrate buffer at pH6. Please see this link for our antigen retrieval protocol. -
A: We have only designated that it is IgG and have not isotyped it further.

![Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NBP1-19371-img0018.jpg)
![Western Blot: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371] Western Blot: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-19371-img0002.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP1-19371-img0005.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody---BSA-Free-Flow-Cytometry-NBP1-19371-img0023.jpg)
![Western Blot: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371] Western Blot: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-19371-img0007.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-19371-img0006.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-19371-img0011.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-19371-img0012.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Frozen-NBP1-19371-img0013.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-19371-img0014.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Flow-Cytometry-NBP1-19371-img0015.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Flow-Cytometry-NBP1-19371-img0016.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Flow-Cytometry-NBP1-19371-img0021.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] Flow Cytometry: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Flow-Cytometry-NBP1-19371-img0022.jpg)
![Simple Western: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371] Simple Western: CD4 AntibodyBSA Free [NBP1-19371]](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/CD4-Antibody-Simple-Western-NBP1-19371-img0009.jpg)


![Western Blot: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] - CD4 Antibody - BSA Free](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/nbp1-19371_rabbit-polyclonal-cd4-antibody-23220248151443.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CD4 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-19371] - CD4 Antibody - BSA Free](https://beta-resources.rndsystems.com/images/products/nbp1-19371_rabbit-polyclonal-cd4-antibody-310202416163759.jpg)





-(01-ml)_NBP1-19371_10846.jpg)
-(01-ml)_NBP1-19371_10246.png)
-(01-ml)_NBP1-19371_9666.png)