Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
Immunocytochemistry (ICC), often referred to as immunofluorescence (IF), is an immunostaining technique that detects antigens in cultured or primary cells via light microscopy. Fluorescent conjugated antibodies are used in multicolor ICC experiments.
Featured ICC Products
Verify Stemness of iPSCs
Analyzing human stem pluripotency using marker antibodies allows the identification and expansion of high quality, undifferentiated stem cell populations. Provides increased confidence in pluripotent status through the use of multiple markers.
Signal Transduction in Focus
Visualize intracellular signaling events with antibodies validated for ICC. Whether its synapse formation and subsequent signalling cascade or the watching the inner workings of the mitochondria, we have a range of antibodies for signal transduction.
Get Clearer Organoid Images
Visualize intracellular signalling events with antibodies validated for ICC. Whether its synapse formation and subsequent signalling cascade or the watching the inner workings of the mitochondria, we have a range of antibodies for signal transduction.
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Primary Antibodies
Successful ICC experiments start with specific and validated primary antibodies. Factors like species reactivity, clonality, and host species are critical considerations for antibody selection. To maximize your ICC staining signal, it is important to ensure antibody specificity while minimizing cross-reactivity. Bio-Techne’s extensive data image library showcases the performance of our ICC/IF validated antibodies across different cell types and species.
For ICC tips and guidance see our ICC Protocols.
ICC Primary Antibodies by Species Reactivity
| All Primary Antibodies | Mouse Primary Antibodies |
| Human Primary Antibodies | Rat Primary Antibodies |
Antibodies for Multicolor ICC
Bio-Techne is here to meet your multicolor ICC needs. We offer an unparalleled catalog of fluorescent conjugated antibodies, including primary antibodies conjugated to photostable dyes such as Alexa Fluor® 647 and Alexa Fluor® 488.
Find pre-conjugated primary antibodies below:
| Alexa Fluor® 488 | Janelia Fluor® 549 | DyLightTM 550 |
| Alexa Fluor® 647 | Janelia Fluor® 646 | Biotin |
Secondary Antibodies and Detection Reagents
ICC staining can be visualized using direct staining with a conjugated primary antibody or indirect detection using a secondary conjugated antibody. In indirect IF detection, a fluorochrome-labeled secondary antibody is required to detect the primary antibody-antigen complex. If you are using indirect detection methods, it is important to ensure the primary antibodies have different host species during primary antibody selection. Other considerations for secondary antibody selection include primary antibody subclass (eg, IgG, IgM, IgA) and targeting the Heavy Chain (Hc) only, Light Chain (Lc) only, or both Heavy and Light Chain (H+L).
Indirect detection methods can improve detection of low abundance targets due to multiple secondary antibodies binding to one primary antibody. Learn more about the differences between direct and indirect detection.
ICC Secondary Antibodies by Reactivity
| Anti-Goat | Anti-Mouse | Anti-Rat |
| Anti-Human | Anti-Rabbit | Anti-Sheep |
Detection Reagents
In addition to antibody staining, fluorescent dyes and probes can be used to further investigate cellular structures and visualize cellular morphology.
| Cellular Structure | Reagents | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | DAPI, DRAQ5TM | Live or fixed cells; membrane permeable |
| Nucleus | DRAQ7TM | Live or fixed cells; will not stain intact live cells, can be used for viability |
| Cytoplasm | DRAQ9TM | Live or fixed cells; membrane permeable |
| Mitochondria | MitoBrilliantTM 646 | Live or fixed cells |
| Mitochondria | MitoBrilliantTM Live 646, MitoBrilliantTM Live 549 | Live cells; activity dependent on membrane potential (Δψm) |
ICC Controls
Proper experimental controls are critical to ensuring accurate interpretation of your ICC data. ICC controls include background staining controls and antibody specificity controls.
Antibody Specificity Controls
Bio-Techne performs rigorous testing on all ICC validated antibodies. Our extensive data image library showcases our dedicate to antibody quality. Some common methods to verify antibody specificity are outlined below, including knockout (KO) cell line, positive and negative cell lines, protein stimulation, and RNA-protein codetection. Bio-Techne also offers controls such as blocking peptides.
Background Staining Controls
Background staining can be a confounding factor when visualizing ICC images. If using an indirect detection method, it’s important to include a no primary antibody control. This can be accomplished by leaving one sample out of the primary antibody incubation step and then continuing to treat that sample with secondary antibody and any additional detection reagents.
Isotype controls are used as negative controls to help differentiate non-specific background signal from specific antibody signal. Isotype controls are primary antibodies that lack specificity to the target, but match the class and type of the primary antibody used in the application.

Knockout ICC Control. Detection of KRT18 in wild-type HeLa cells (positive) control and in HeLa cells in which KRT18 was knocked out (negative control). Notice lack of staining in KO cells which is indicative for the specificity of primary antibodies. Cells were counterstained with DAPI (NBP2-31156).

Positive and Negative Cell Line Control. Detection of neuron-specific β-III Tubulin in SH-SY5Y cells known to express this protein. No staining was observed in HEL92.1.7 cells which do not express this protein. Cells were counterstained with DAPI (NBP2-31156).

Protein Stimulation Control. HeLa cells underwent hypoxia treatment leading to upregulation of HIF-1α protein in cell nuclei (left), whereas no signal was detected in untreated cells. Cells were counterstained with DAPI (NBP2-31156).
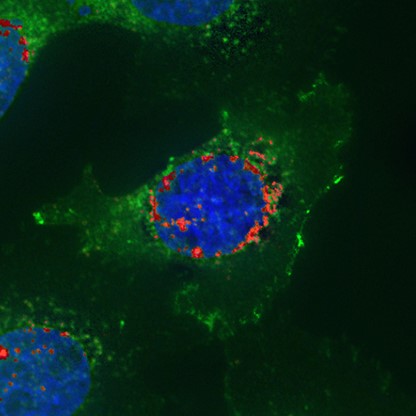
RNA-Protein Co-detection Control. Co-detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mRNA (red) using RNAscopeTM protocol and EGFR protein (green) by ICC in the same cells. Co-localization of mRNA and its protein within the same cells confirms specificity of antibodies.

HepG2 cells were incubated either with mouse anti-human AFP antibody (MAB1368) IgG1 isotype or with non-immune IgG1 antibody (MAB002) both at 25 μg/mL working dilution. Strong specific cell labeling in the cytoplasm can be seen with MAB1368 antibody, whereas there was no staining in cells incubates with IgG1 isotype control.
Support Products for ICC
| Normal Serum | Pap Pen | Mounting Media |
| PBS Buffer Tablets | BSA |
Protocols
- ICC Protocol
- ICC Video Protocol
- Multicolor ICC/IF Protocols
- ICC Troubleshooting Guide
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips
- Antigen Retrieval Methods
Application Support
- Sample Preparation for ICC/IF Experiments
- Fixation and Permeabilization in Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence (ICC/IF)
- IHC/ICC Sample Fixation (Formalin vs. Alcohol)
- Blocking ICC/IF
- Cytosolic and Nuclear Staining
- Counterstaining and Mounting in ICC/IF
- Controls for ICC/IF Experiments
- Selection of Fluorochromes for Multicolor ICC/IF
- Immunocytochemistry Troubleshooting
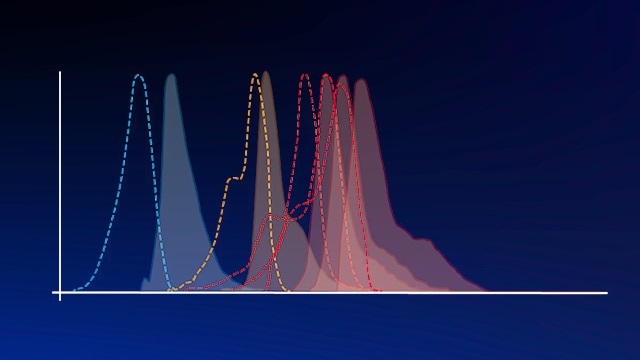
Spectra Viewer
Use our spectra viewer to interactively plan your experiments, assessing multiplexing options. View the excitation and emission spectra for our fluorescent dye range and other commonly used dyes.
Fluorescent Dyes and Probes Brochure

Providing a background to the use of fluorescent dyes, probes and stains and listing our extensive product range, our brochure can help you to select the most appropriate dye or probe to obtain the best results for your experiment.
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Handbook

This Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Handbook offers an introduction to ICC focusing on multicolor ICC/IF, including detailed protocols and troubleshooting tips. It is a great resource for researchers new to ICC/IF as well as experienced users looking to brush up on their skills.
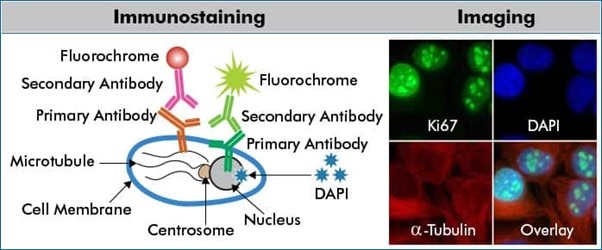
ICC is a widely used form of immunostaining, for visualizing specific proteins in cells, using labeled antibodies that selectively bind the target protein in situ. Visualization is via fluorescence microscopy and enables assessment of whether and where a cell expresses a particular protein. The ICC technique uses cells that are isolated from tissue, such as cells in culture, whereas immunohistochemistry (IHC) uses sections of tissue. Learn more about the difference between ICC and IHC.
The illustration above depicts a multicolor ICC/IF scheme for indirect protein detection. HeLa cells were probed with anti-Ki67 (nuclear protein; NBP2-54791) and anti-α-tubulin (microtubular protein; NB100-690) followed by detection with DyLight 488 (green) and DyLight 550 (red) conjugated secondary antibodies, respectively. Fixed cells were counterstained with the nuclear dye, DAPI (blue; NBP2-31156).
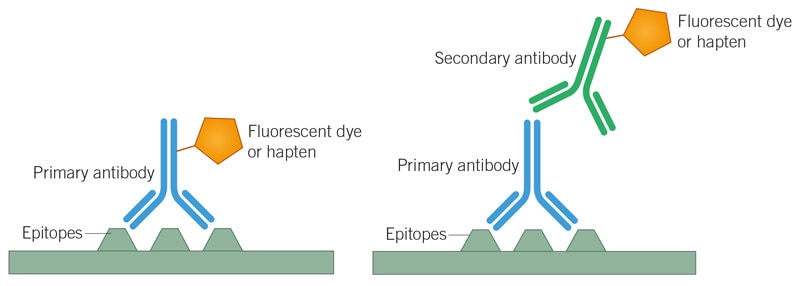
In fluorescence-based immunodetection, antibodies are conjugated to fluorochromes which emit light upon excitation with light at a specific wavelength. While detection typically involves either a labeled primary or secondary antibody, using a biotinylated antibody followed by fluorochrome-labeled streptavidin improves assay sensitivity.
Direct and Indirect Detection
Direct detection in multicolor ICC/IF uses primary antibodies that are conjugated to a fluorochrome. Indirect detection, however, uses an unlabeled primary antibody targeting the molecule of interest and a labeled secondary antibody that is directed against the constant region of the primary antibody.
Which Detection Method is Better – Direct or Indirect?
The optimal detection method may vary from experiment to experiment. The factors and considerations listed in the table below can help determine which method is best suited for your experiment.
| Direct Detection Method | Indirect Detection Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | The direct method of detection is less sensitive because the amplification of signal afforded by the secondary antibody is lost. | The indirect method of detection is highly sensitive as more than one secondary antibody can bind to a single primary antibody molecule. |
| Assay Time | The direct method protocol is shorter due to the elimination of the secondary antibody incubation steps. | The indirect method protocol is longer due to secondary antibody incubation and the resistent wash steps. |
| Multiplexing | Multiplexing is easier with direct detection because multiple primary antibodies from the same host species can be used together. | Indirect method multiplexing is more complicated due to secondary antibody cross-reactivity. |
| Background | Nonspecific background signal is lower in the direct method as secondary antibody mediated cross-reactivity is eliminated. | Nonspecific background staining is generally higher in the indirect method due to secondary antibody cross-reactivity. |
| Flexibility | The direct method is less flexible since the selection of directly conjugated antibodies can be limited. | The indirect method is more flexible because it is possible to use different conjugated secondary antibodies depending on your experiment. |
DRAQ5™ is a registered trademark of BioStatus Limited.
