Immuno-Oncology Research
Immuno-oncology research is providing the foundation for the development of more effective cancer therapies. To support these studies, we are focused on providing the highest quality reagents to simplify and advance your research. From proteins and antibodies to single and multianalyte immunoassays, our products undergo extensive in-house validation to ensure performance, consistency, and specificity, so you can have confidence in your results from one experiment to the next.
Immune Checkpoint Targets
Immune checkpoint molecules can either promote or inhibit immune cell functions. Ligand binding to stimulatory receptors promotes immune cell activation, while ligand binding to inhibitory receptors suppresses immune cell activation.
Tumor cells frequently exploit immune checkpoint pathways by up-regulating the expression of ligands that bind to inhibitory receptors, allowing them to evade immune detection. To prevent this, researchers have targeted immune checkpoint molecules for cancer immunotherapy using either agonists of immune cell stimulatory receptors to drive immune cell activation, or antagonists of inhibitory receptors to prevent down-regulation of anti-tumor immune responses. Use the links below to browse our selection of products for immune checkpoint research.

Immune Checkpoint Proteins
Rely on the performance and consistency of our immune checkpoint proteins to optimize your inhibitor screening assays. Multiple species and tags are available.
Immune Checkpoint Blocking Antibodies
Explore our wide selection of blocking antibodies for key ligand- receptor pairs involved in regulating immune cell activity.
ELISAs for Immune Checkpoint Research
Quantitatively assess the presence and abundance of disease markers with immune checkpoint immunoassays.
Immune Cell Phenotyping in the Tumor Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complex network of different cell types that can either suppress or promote tumor growth. Use the links below to find the markers that are commonly used to distinguish different immune cell types or cell type-specific subsets in the tumor microenvironment.


Natural Killer Cells
NK cells provide the first line of defense against tumor cells by exerting direct cytotoxic effects and secreting IFN-γ. Learn more about NK cell activation and markers.
CD4+ Th1 Cells
CD4+ Th1 cells secrete high levels of IFN-γ and promote the functions of M1 macrophages, NK cells, and CD8+ T cells to drive tumor rejection. Discover more about Th1 cells.
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells regulate T cell activation and promote the differentiation of effector T cell subsets. Learn about different DC subsets.

Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs)
TAMs are typically the most abundant immune cell type in the TME. Explore macrophage phenotypes and functions.
Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs)
MDSCs are immature myeloid cells that accumulate in the TME and promote tumor growth. Learn about the two major MDSC subsets.
Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
Tregs produce cytokines that inhibit the activities of effector T cells in the TME. See the markers used to identify Tregs.
Cell-Mediated Mechanisms of Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment
Regulatory T cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and tumor-associated M2 macrophages are immune cells with immunosuppressive properties that are thought to play key roles in inhibiting anti-tumor immune responses. Explore the interactive pathways linked below to learn about the different mechanisms that these cell types use to negatively regulate anti-tumor immune responses.
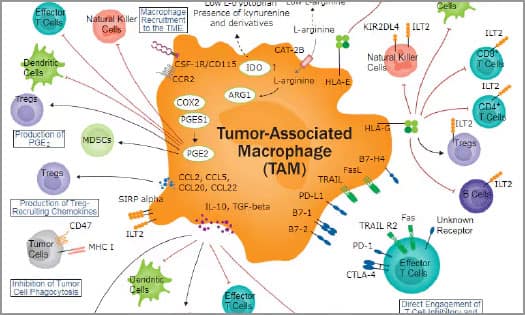
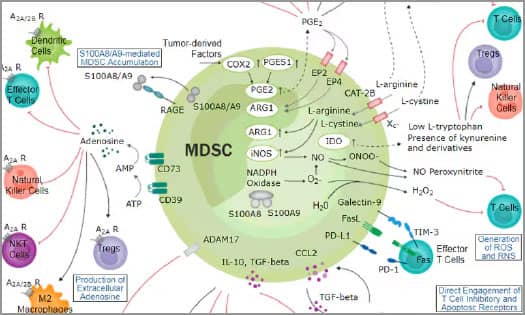
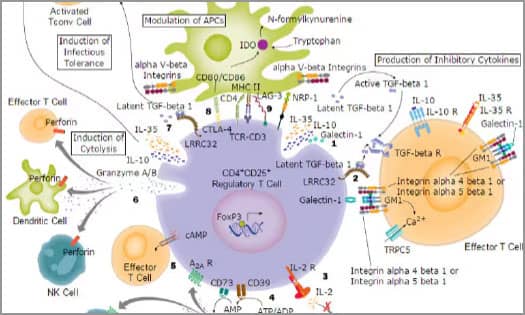
Tumor-Associated Macrophages
TAMs inhibit anti-tumor immune responses through multiple mechanisms. Discover how TAMs drive tumor progression.
Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells
MDSCs accumulate during cancer and inhibit anti-tumor immune responses. Learn about MDSC-mediated mechanisms of immunosuppression.
Regulatory T Cells
Tregs inhibit anti-tumor immune responses and promote tumor growth. Read about Treg-mediated immune suppression.
Cancer Signaling Pathways
Signaling pathways that regulate cell survival, proliferation, and growth are frequently altered in tumor cells and can contribute to immune suppression and resistance to immune checkpoint blockade strategies. View these pathways to see how they may promote tumor escape and gain a better understanding of why simultaneous blockade of these pathways is being investigated to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint therapies.
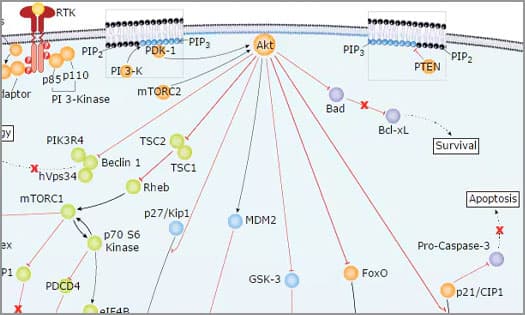
Akt Signaling Pathways
Akt signaling is frequently up-regulated in cancer, promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Explore Akt signaling pathways.
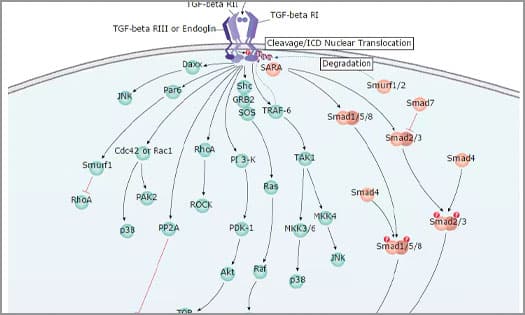
TGF-β Signaling Pathways
TGF-β signaling has tumor-suppressing or tumor-promoting effects, that is context-dependent. Learn more about TGF-β signaling.
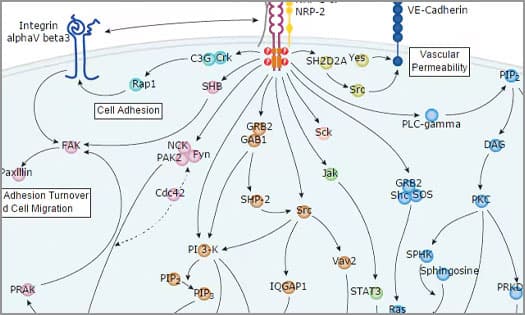
VEGF R2 Signaling Pathways
VEGF signaling can contribute to immune suppression in the TME. Discover the pathways activated by VEGF and its biological effects.

Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines are intended to train the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Learn more about cancer vaccines.
Immune Cell Therapy
Seamlessly transition the development of immune cell therapies from research to the clinic with our solutions for cell therapy.
Biosimilar Antibodies
Biosimilar antibodies serve as critical controls to benchmark novel treatments. Read more about biosimilar antibodies.
Expedite Your Research with Analytical Instruments
Accelerate your immuno-oncology research using our automated analytical platforms. From Luminex® multiplex panels designed to maximize biomarker detection to our Simple Plex and Simple Western platforms, our solutions ensure accurate, consistent results in minimal time.

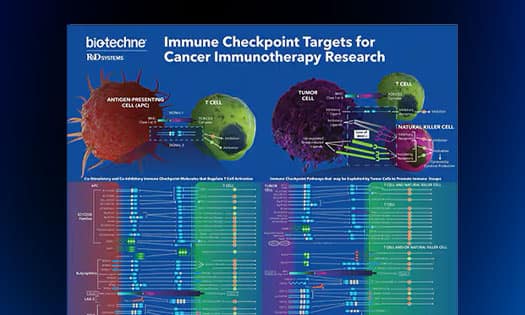

Immune Checkpoint Targets For Cancer Immunotherapy Poster
Request this poster to explore the current and emerging immune checkpoint molecules being investigated as potential cancer immunotherapy targets.
Immune Checkpoint Targets eBook
Request this eBook to learn about the latest research on some of the most promising targets for cancer immunotherapy.
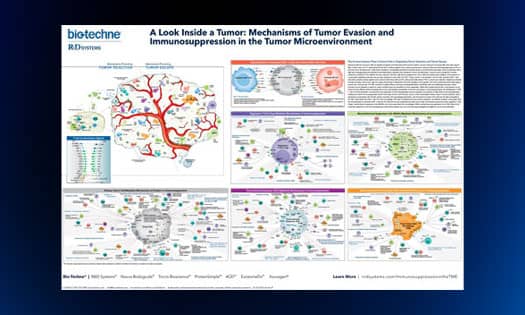
A Look Inside a Tumor Poster
Request this poster to learn about the key mechanisms used by Tregs, MDSCs, TAMs, and tumor-derived exosomes that drive immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment.

Immuno-Oncology Webinars
How Cancer Circumvents the Immune System (Bio-Techne)
Exploiting Tumor Hypoxia for Targeted Immunotherapy (Bio-Techne)
The CAR Toolkit: Progress and Challenges in CAR T/NK Cell R&D and Manufacture (Bio-Techne)
