Recombinant Human DPEP1 His-tag Protein, CF Summary
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human DPEP1 His-tag Protein (11524-DP)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
Asp17-Ser384, with C-terminal 6-His tag
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
11524-DP
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris and NaCl. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5
- Recombinant Human DPEP1 (rhDEP1) (Catalog # 11524-DP)
- Substrate: L-Carnosine, 100 mM stock in deionized water
- Trichloroacetic acid (TCA), 10% stock in deionized water
- o-Phthaldialdehyde (OPA), 50 mg/mL stock in DMSO
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH), 2 M stock in deionized water
- Black 96-well plate
- Plate Reader with Fluorescence Read Capability
- Dilute rhDPEP1 to 20 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute Substrate to 4 mM in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute 10% TCA to 1% in Assay Buffer (prepare right before adding to Substrate Blank(s) in step 4).
- Mix 60 μL of 20 µg/mL rhDPEP1 and 60 μL 4 mM Substrate for a final concentration of 10 µg/mL and 2 mM respectively. Include a Substrate Blank containing 60 μL of 20 µg/mL rhDPEP1, 60 μL 1% TCA added 1 minute prior to substrate addition, and 60 μL Substrate.
- Incubate reactions for 1 hour at 37 °C.
- Dilute 10% TCA to 1% in Assay Buffer (prepare right before adding to reactions in step 7).
- Stop reactions by adding 60 μL of 1% TCA (do not add to Substrate Blank(s)) and incubate for 10 minutes at room temperature.
- Dilute OPA to 5 mg/mL in 2 M NaOH.
- Add 60 μL of 5 mg/mL OPA to each reaction.
- Incubate for 1 hour at room temperature.
- Load 200 µL of each incubated sample into the plate.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 360 nm and 460 nm (top read), respectively, in endpoint mode.
- Calculate Specific Activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Fluorescence* (RFU) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| Incubation time (min) x amount of enzyme (µg) |
- rhDPEP1: 1.0 µg
- Substrate: 1 mM
Scientific Data
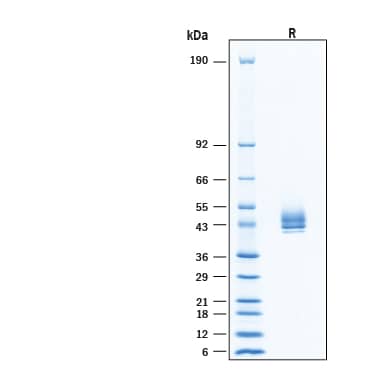 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human DPEP1 His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11524-DP) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 39-49 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: DPEP1
Dipeptidase 1 (DPEP1), also referred to as renal peptidase or beta-lactamase, is a zinc-dependent, glycosylated member of the M19 peptidase metallo-dependent hydrolase superfamily that lacks a sequence commonly found in zinc proteases and has poor homology to other metallopeptiases (1). DPEP1 is a homodimeric elongated ellipsoid with a single disulfide bond between the subunits (1) and GPI-anchored to the cell membrane at the brush border of epithelial cells (2). Each DPEP1 monomer contains a zinc-dependent active site, a propeptide, and a GPI anchor at the c-terminus (1). DPEP1 has activity towards several dipeptides and is critical in glutathione and leukotriene metabolism as well as mammalian metabolism of the B-lactam ring of antibiotics (1, 3). DPEP1 expression is upregulated or associated as a marker in various cancers including colon, kidney, and prostate cancer (4-6). It is also upregulated in renal tubular epithelial cells and associated with iron-related ferroptotic cell death in diabetic retinopathy (2, 7) where it may mediate proinflammatory cancer mediatory leukotrienes or serve as a receptor as an adhesion receptor for neutrophil recruitment and impact inflammation (8-10). DPEP1 has been noted as a potential therapeutic marker or target for mestastasis, cancer progression, and disease in the liver and lungs with acute or chronic inflammation (2, 4, 9, 11).
- Nitanai, Y. et. al. (2002) J. Mol. Biol. 321:177.
- Li, Y. et. al. (2024) Int. Immunopharmacol. 133:111955.
- Campbell, B.J. et. al. (1988) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 956:110.
- Tachibana, K. et. al. (2017) Biomed. Rep. 6:423.
- Xiang, C. et. al. (2023) J. Cell Mol. Med. 27:1947.
- Zhu, W. et. al. (2023) Heliyon 9:e18870.
- Allison, S.J. (2021) Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 17:707.
- Satoh, S. et. al. (1993) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1172:181.
- Choudhury, S.R. et. al. (2019) Cell 178:1205.
- Wang, M. (2022) Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18:199.
- Tutanov. O.S. et. al. (2023) Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids. 4:195.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human DPEP1 His-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human DPEP1 His-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human DPEP1 His-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
