Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag Protein, CF Summary
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag Protein (11633-LA)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
Gly24-Gln399 with N-terminal HA (YPYDVPDYA) and 6-His tags
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
11633-LA
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MES, NaCl and TCEP. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Assay Procedure
- Assay Buffer: 25 mM MES, 1% Triton X-100, pH 5.5
- Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag (rhLIPA) (Catalog # 11633-LA)
- Substrate: 4-Methylumbelliferyl oleate (4-MUO), 100 mM stock in DMSO
- Black 96-well Plate
- Plate Reader with Fluorescence Read Capability
- Dilute rhLIPA to 2 µg/mL in Assay Buffer.
- Dilute Substrate to 1.2 mM in Assay Buffer.
- Load into a plate 50 µL of 2 µg/mL rhLIPA and start the reaction by adding 50 µL of 1.2 mM Substrate. Include a Substrate Blank containing 50 µL of Assay Buffer and 50 µL of 1.2 mM Substrate.
- Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 365 nm and 445 nm (top read), respectively, in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
- Calculate specific activity:
Specific Activity (pmol/min/µg) = | Adjusted Vmax* (RFU/min) x Conversion Factor** (pmol/RFU) |
| amount of enzyme (µg) |
- rhLIPA: 0.1 µg
- Substrate: 600 µM
Scientific Data
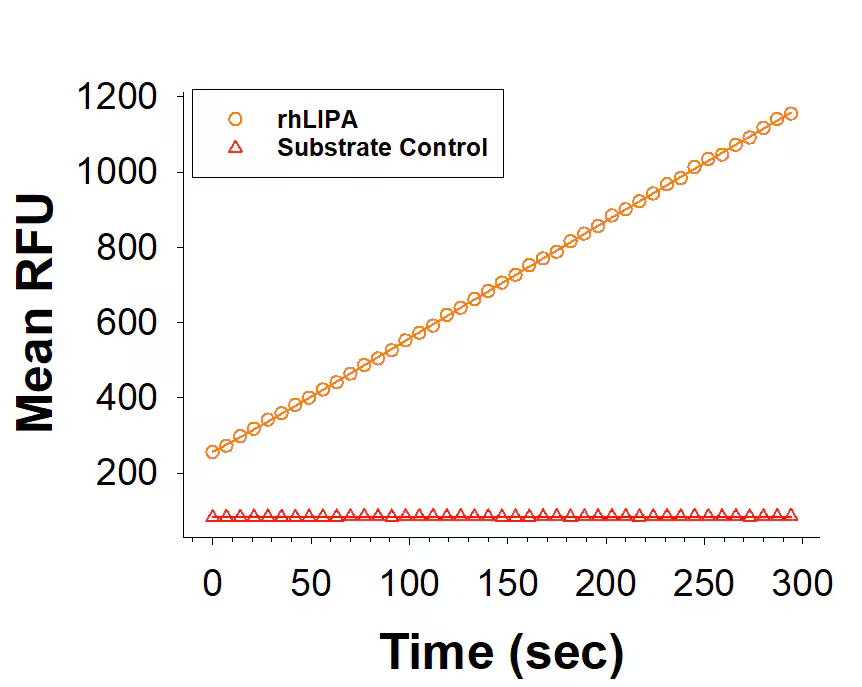 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag (Catalog # 11633-LA) is measured by its ability to cleave a fluorogenic peptide substrate, 4-Methylumbelliferyl oleate (4-MUO).
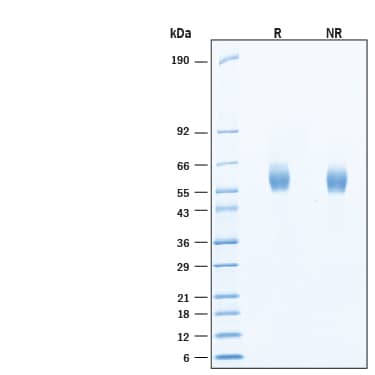 View Larger
View Larger
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag (Catalog # 11633-LA) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 55-67 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: LIPA
Recombinant human Lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) or Lipase A (LIPA), also known as acid cholesteryl ester hydrolase, is a 378 residue mature, glycosylated, lysosomal serine hydrolase of a family of three mammalian acid lipases. Mature LIPA contains a globular core domain typical of a/b hydrolase-fold family members and a cap domain. Beneath the cap region, the core domain contains the catalytic triad surrounded by a hydrophobic surface that promotes lipid substrate binding (1). Except for erythrocytes, LIPA is broadly expressed in cells (1) and is found in the lysozyme where it is required for hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides from low density lipoproteins (LDL) to generate fatty acids and cholesterol (2). LIPA deficiency from over 40 reported loss-of-function mutations leads to accumulation of cholesterol and triglyceride in the lysosome with resulting dysfunctional cholesterol homeostasis (1, 3). Lysosomal acid deficiency (LAL-D) is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease with two phenotypes including early-onset Wolman disease (WD) and later-onset cholesteryl ester storage disease (CESD) (3, 4). Supplementation of LIPA through enzyme replacement therapy has been shown to be effective and is the standard therapy for LAL-deficiency although additional treatments are being explored (3, 4-6). Due to its central role in lipid regulation, altered function and variants of LIPA have also been implicated in development of atherosclerotic disease and coronary artery disease (1, 3, 7, 8). LIPA has additionally been reported as a therapeutic target for cancer and solid tumors through its role in induction of ER stress (9), its association with specific binding partner of interest (10), and its ability to modulate lipid metabolism in cancer cells (11).
- Rajamohan, F. et al. (2020) J. Lipid Res. 61:1192.
- Anderson, R.A. and G.N. Sando (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:22479.
- Maciejko, J.J. (2017) Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 17:217.
- Korbelius, M. et al. (2023) Trends Mol. Med. 29:425.
- Burton, B.K. et al. (2015) N. Engl. J. Med. 373:1010.
- Rader, D.J. (2015) N. Engl. J. Med. 373:1071.
- Wild, P.S. et al. (2011) Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 4:403.
- Li, F. and H. Zhang (2019) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 39:850.
- Liu, X. et al. (2022) Nat. Cancer 3:866.
- Collier, A.B. (2024) Cancers 16:500.
- Jin, Z. et al. (2024) Cancer Res. Commun. 4:2242.
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag Protein, CF
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag Protein, CF and earn rewards!
Have you used Recombinant Human LIPA HA-tag His-tag Protein, CF?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
