Human NPRA/NPR1 Antibody Summary
Gly33-Glu473
Accession # P16066
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
NPRA/NPR1 in Human Kidney. NPRA/NPR1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using Mouse Anti-Human NPRA/NPR1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB48601) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to epithelial cell membranes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
 View Larger
View Larger
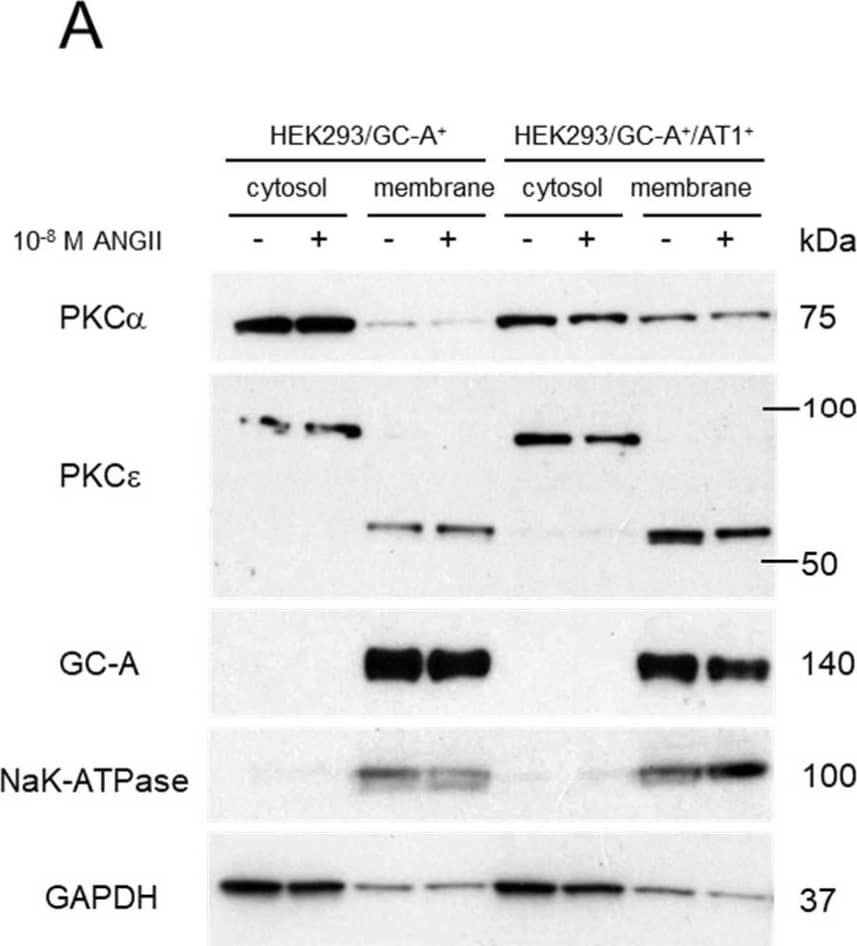
Detection of NPRA/NPR1 by Western Blot Involvement of PKC Signaling in the Crosstalk between ANGII and GC-A. (A) Protein expression of different human PKC isoforms in the membrane and cytosol fractions of different HEK293 cell lines (with or without treatment of ANGII). GC-A and NaK-ATPase serve as quality control for the separation of membrane and cytosol fractions. GAPDH serves as an additional control as it is primarily expressed in the cytosol fraction compared to membrane fraction. (B) Protein expression of phosphorylated PKC substrates, phosphorylated p38 MAPK, and p38 MAPK in HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+ cells treated with different PKC modulators. GAPDH serves as a loading control and 50 µg of total protein (determined using BCA method) was loaded in each lane. PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. (C) In vitro cGMP generation in HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+ in response to ANP (10−8 M) with or without ANGII (10−8 M) and valsartan (10−6 M) or Go6983 (5 µM). Values of cGMP were normalized to vehicle group (blue) under ANP treatment. * indicates p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons test. (D) Hypothetical mechanism underlying the crosstalk between ANGII and GC-A derived from our in vitro studies: (1) ANGII naturally suppresses GC-A mediated cGMP production via AT1 receptor, but not the AT2 receptor nor direct effect on GC-A; (2) PKC is a critical downstream target of AT1 mediating this RAAS/NPS interaction. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37239899), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
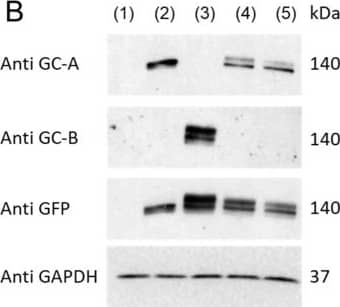
Detection of NPRA/NPR1 by Western Blot ANGII Attenuates GC-A Mediated cGMP Generation via AT1 Receptor. (A) Construction and nomenclature of three different HEK293 transfected cells. (B) Protein expression of human GC-A and GC-B in HEK293 parental and transfected cells by western blotting. 1, HEK293 parental cells; 2, HEK293/GC-A+; 3, HEK293/GC-B+; 4, HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+; 5, HEK293/GC-A+/AT2+. Each lane was loaded with 40 µg total protein. Antibody against GFP detected protein expression incurred by either GC-A or GC-B transfection. HEK293/GC-B+ cells served as a negative control for GC-A specific overexpression in other transfected cells. (C) mRNA expression of human AGTR1 (AT1 coding gene) in HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+ cells and human AGTR2 (AT2 coding gene) in HEK293/GC-A+/AT2+ cells, compared to HEK293/GC-A+ cells. Expression levels were normalized to human GAPDH. (D) In vitro cGMP generation in HEK293 transfected cells in response to different doses of ANP with or without ANGII (10−8 M). Values of cGMP in ANGII treated group (red) were normalized to corresponding vehicle group (blue) under each dose of ANP. Absolute values of cGMP are shown in Supplementary Figure S3. * indicates p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Sidak multiple comparisons test. N = 3 biological replicates (defined as cells grown in 3 independent plates) in each designed group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37239899), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
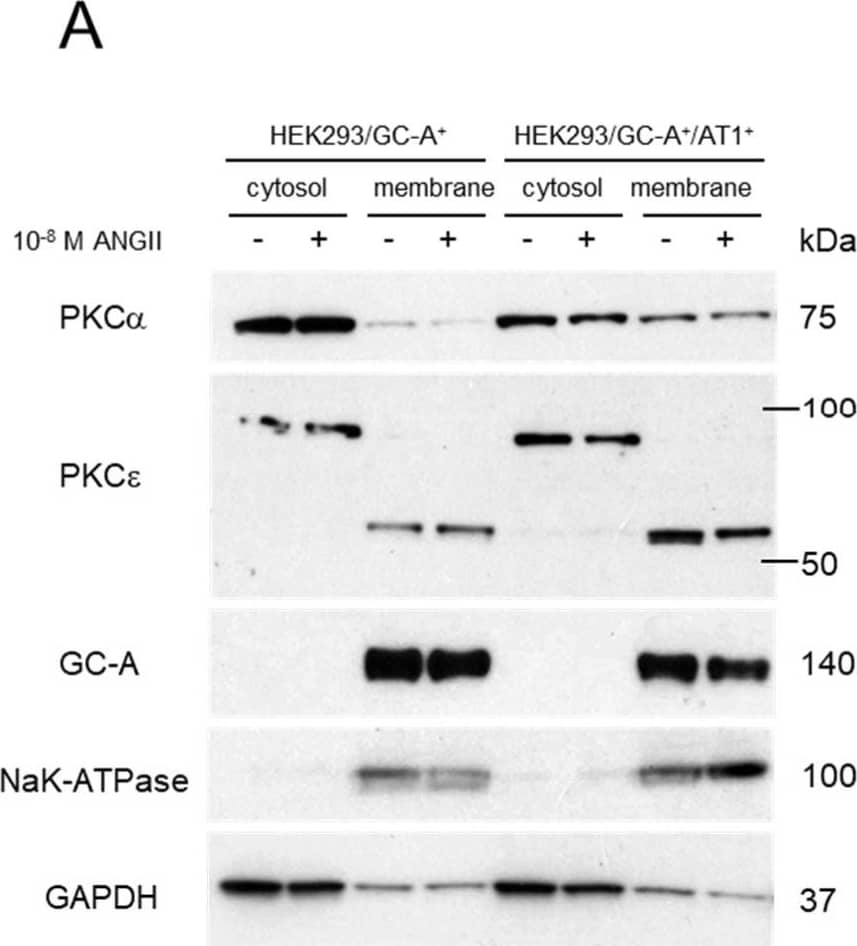
Detection of NPRA/NPR1 by Western Blot Involvement of PKC Signaling in the Crosstalk between ANGII and GC-A. (A) Protein expression of different human PKC isoforms in the membrane and cytosol fractions of different HEK293 cell lines (with or without treatment of ANGII). GC-A and NaK-ATPase serve as quality control for the separation of membrane and cytosol fractions. GAPDH serves as an additional control as it is primarily expressed in the cytosol fraction compared to membrane fraction. (B) Protein expression of phosphorylated PKC substrates, phosphorylated p38 MAPK, and p38 MAPK in HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+ cells treated with different PKC modulators. GAPDH serves as a loading control and 50 µg of total protein (determined using BCA method) was loaded in each lane. PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. (C) In vitro cGMP generation in HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+ in response to ANP (10−8 M) with or without ANGII (10−8 M) and valsartan (10−6 M) or Go6983 (5 µM). Values of cGMP were normalized to vehicle group (blue) under ANP treatment. * indicates p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons test. (D) Hypothetical mechanism underlying the crosstalk between ANGII and GC-A derived from our in vitro studies: (1) ANGII naturally suppresses GC-A mediated cGMP production via AT1 receptor, but not the AT2 receptor nor direct effect on GC-A; (2) PKC is a critical downstream target of AT1 mediating this RAAS/NPS interaction. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37239899), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
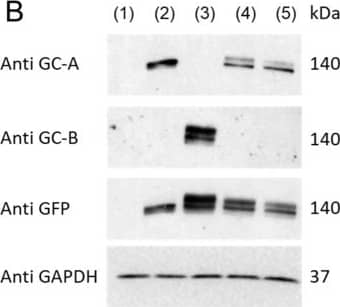
Detection of NPRA/NPR1 by Western Blot ANGII Attenuates GC-A Mediated cGMP Generation via AT1 Receptor. (A) Construction and nomenclature of three different HEK293 transfected cells. (B) Protein expression of human GC-A and GC-B in HEK293 parental and transfected cells by western blotting. 1, HEK293 parental cells; 2, HEK293/GC-A+; 3, HEK293/GC-B+; 4, HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+; 5, HEK293/GC-A+/AT2+. Each lane was loaded with 40 µg total protein. Antibody against GFP detected protein expression incurred by either GC-A or GC-B transfection. HEK293/GC-B+ cells served as a negative control for GC-A specific overexpression in other transfected cells. (C) mRNA expression of human AGTR1 (AT1 coding gene) in HEK293/GC-A+/AT1+ cells and human AGTR2 (AT2 coding gene) in HEK293/GC-A+/AT2+ cells, compared to HEK293/GC-A+ cells. Expression levels were normalized to human GAPDH. (D) In vitro cGMP generation in HEK293 transfected cells in response to different doses of ANP with or without ANGII (10−8 M). Values of cGMP in ANGII treated group (red) were normalized to corresponding vehicle group (blue) under each dose of ANP. Absolute values of cGMP are shown in Supplementary Figure S3. * indicates p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Sidak multiple comparisons test. N = 3 biological replicates (defined as cells grown in 3 independent plates) in each designed group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37239899), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: NPRA/NPR1
Natriuretic peptide receptor A/guanylate cyclase A (NPR1), also called NPRA or GC-A, is a 120‑140 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is the primary receptor for natrietic peptides ANP and BNP. Binding of ANP to the extracellular ligand binding domain (aa 54‑415), plus ATP to the intracellular kinase homology domain (aa 528‑805) activates a cytoplasmic guanylate cyclase (aa 840‑1023). NPR1 is expressed most highly in kidney, adrenal and adipose tissue. Human NPR1 extracellular domain shows 86%, 44% and 34% aa identity with mouse NPR1, human NPRB and human NPRC, respectively.
Product Datasheets
Citation for Human NPRA/NPR1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
1 Citation: Showing 1 - 1
-
Evidence for Angiotensin II as a Naturally Existing Suppressor for the Guanylyl Cyclase A Receptor and Cyclic GMP Generation
Authors: Ma, X;Iyer, SR;Ma, X;Reginauld, SH;Chen, Y;Pan, S;Zheng, Y;Moroni, DG;Yu, Y;Zhang, L;Cannone, V;Chen, HH;Ferrario, CM;Sangaralingham, SJ;Burnett, JC;
International journal of molecular sciences
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human NPRA/NPR1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human NPRA/NPR1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human NPRA/NPR1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
