Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Antibody Summary
Ala27-Arg192
Accession # P07321
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Cell Proliferation Induced by Erythropoietin/EPO and Neutralization by Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Antibody. Recombinant Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO (Catalog # 959-ME) stimulates proliferation in the TF-1 human erythroleukemic cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO (40 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB959). The ND50 is typically 0.2-0.8 µg/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
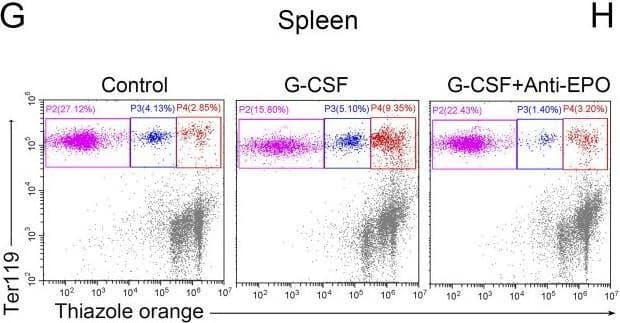
Detection of Erythropoietin/EPO by Flow Cytometry EPO mediates G-CSF–induced splenic erythropoiesis.(G) Representative flow cytometric plots of Ter119-APC and thiazole orange-stained splenocytes from control mice, G-CSF–treated mice, and G-CSF–treated mice with anti-EPO treatment. (H) Flow cytometric quantification of reticulocytes (Ter119+ Thiazole orange+) in the spleens from different treatment groups. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33234677), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
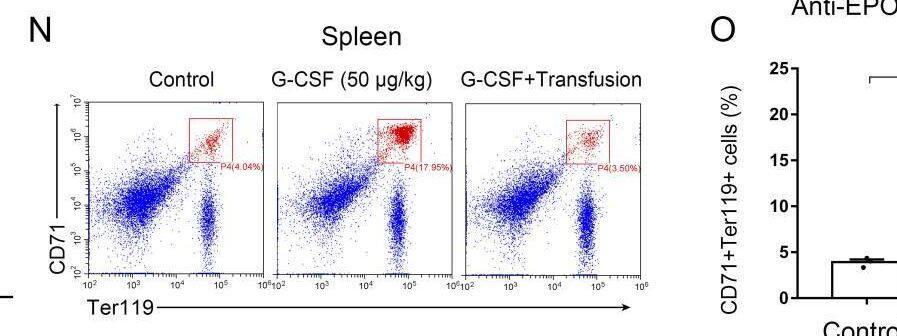
Detection of Erythropoietin/EPO by Flow Cytometry EPO mediates G-CSF–induced splenic erythropoiesis. (N) Representative flow cytometric plots of CD71+Ter119+ cells in the spleens. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33234677), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Erythropoietin/EPO
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a 34 kDa glycoprotein hormone in the type I cytokine family and is related to thrombopoietin (1). Its three N-glycosylation sites, four alpha helices, and N- to C-terminal disulfide bond are conserved across species (2, 3). Glycosylation of EPO is required for biological activities in vivo (4). Mature mouse EPO shares 95% amino acid sequence identity with rat EPO and 73-82% with bovine, canine, equine, feline, human, ovine, and porcine EPO. EPO is primarily produced in the kidney by a population of fibroblast-like cortical interstitial cells adjacent to the proximal tubules (5). It is also produced in much lower, but functionally significant amounts by fetal hepatocytes and in adult liver and brain (6-8). EPO promotes erythrocyte formation by preventing the apoptosis of early erythroid precursors which express the EPO receptor (EPO R) (8, 9). EPO R has also been described in brain, retina, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, endothelial cells, and a variety of tumor cells (7, 8, 10, 11). Ligand induced dimerization of EPO R triggers JAK2-mediated signaling pathways followed by receptor/ligand endocytosis and degradation (1, 12). Rapid regulation of circulating EPO allows tight control of erythrocyte production and hemoglobin concentrations. Anemia or other causes of low tissue oxygen tension induce EPO production by stabilizing the hypoxia-induceable transcription factors HIF-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha (1, 6). EPO additionally plays a tissue-protective role in ischemia by blocking apoptosis and inducing angiogenesis (7, 8, 13).
- Koury, M.J. (2005) Exp. Hematol. 33:1263.
- Shoemaker, C.B. and L.D. Mitsock (1986) Mol. Cell. Biol 6:849.
- Wen, D. et al. (1993) Blood 82:1507.
- Tsuda E. et al. (1990) Eur. J. Biochem. 188:405.
- Lacombe, C. et al. (1988) J. Clin. Invest. 81:620.
- Eckardt, K.U. and A. Kurtz (2005) Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 35 Suppl. 3:13.
- Sharples, E.J. et al. (2006) Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 6:184.
- Rossert, J. and K. Eckardt (2005) Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 20:1025.
- Koury, M.J. and M.C. Bondurant (1990) Science 248:378.
- Acs, G. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:3561.
- Hardee, M.E. et al. (2006) Clin. Cancer Res. 12:332.
- Verdier, F. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:18375.
- Kertesz, N. et al. (2004) Dev. Biol. 276:101.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The Innate Immune Response to Infection Induces Erythropoietin-Dependent Replenishment of the Dendritic Cell Compartment
Authors: Henrik Einwächter, Alexander Heiseke, Andreas Schlitzer, Georg Gasteiger, Heiko Adler, David Voehringer et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibition protects skeletal muscle from eccentric contraction-induced injury
Authors: AN Billin, SE Honeycutt, AV McDougal, JP Kerr, Z Chen, JM Freudenber, DK Rajpal, G Luo, HF Kramer, RS Geske, F Fang, B Yao, RV Clark, J Lepore, A Cobitz, R Miller, K Nosaka, AC Hinken, AJ Russell
Skelet Muscle, 2018-11-13;8(1):35.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Stress-associated erythropoiesis initiation is regulated by type 1 conventional dendritic cells.
Authors: Kim T, Hanak M, Trampont P, Braciale T
J Clin Invest, 2015-09-21;125(10):3965-80.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Transforming growth factor-beta superfamily ligand trap ACE-536 corrects anemia by promoting late-stage erythropoiesis.
Authors: Suragani R, Cadena S, Cawley S, Sako D, Mitchell D, Li R, Davies M, Alexander M, Devine M, Loveday K, Underwood K, Grinberg A, Quisel J, Chopra R, Pearsall R, Seehra J, Kumar R
Nat Med, 2014-03-23;20(4):408-14.
Species: Mouse, Primate - Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating Monkey or Cynomolgus Macaque), Rat
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
Testosterone administration inhibits hepcidin transcription and is associated with increased iron incorporation into red blood cells
Authors: Wen Guo, Eric Bachman, Michelle Li, Cindy N. Roy, Jerzy Blusztajn, Siu Wong et al.
Aging Cell
-
Innate immune activation during Salmonella infection initiates extramedullary erythropoiesis and splenomegaly.
Authors: Jackson A, Nanton MR, O'Donnell H
J. Immunol., 2010-10-15;185(10):6198-204.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse Erythropoietin/EPO Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


