Recombinant Human Epiregulin Protein Summary
- R&D Systems E. coli-derived Recombinant Human Epiregulin Protein (1195-EP)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
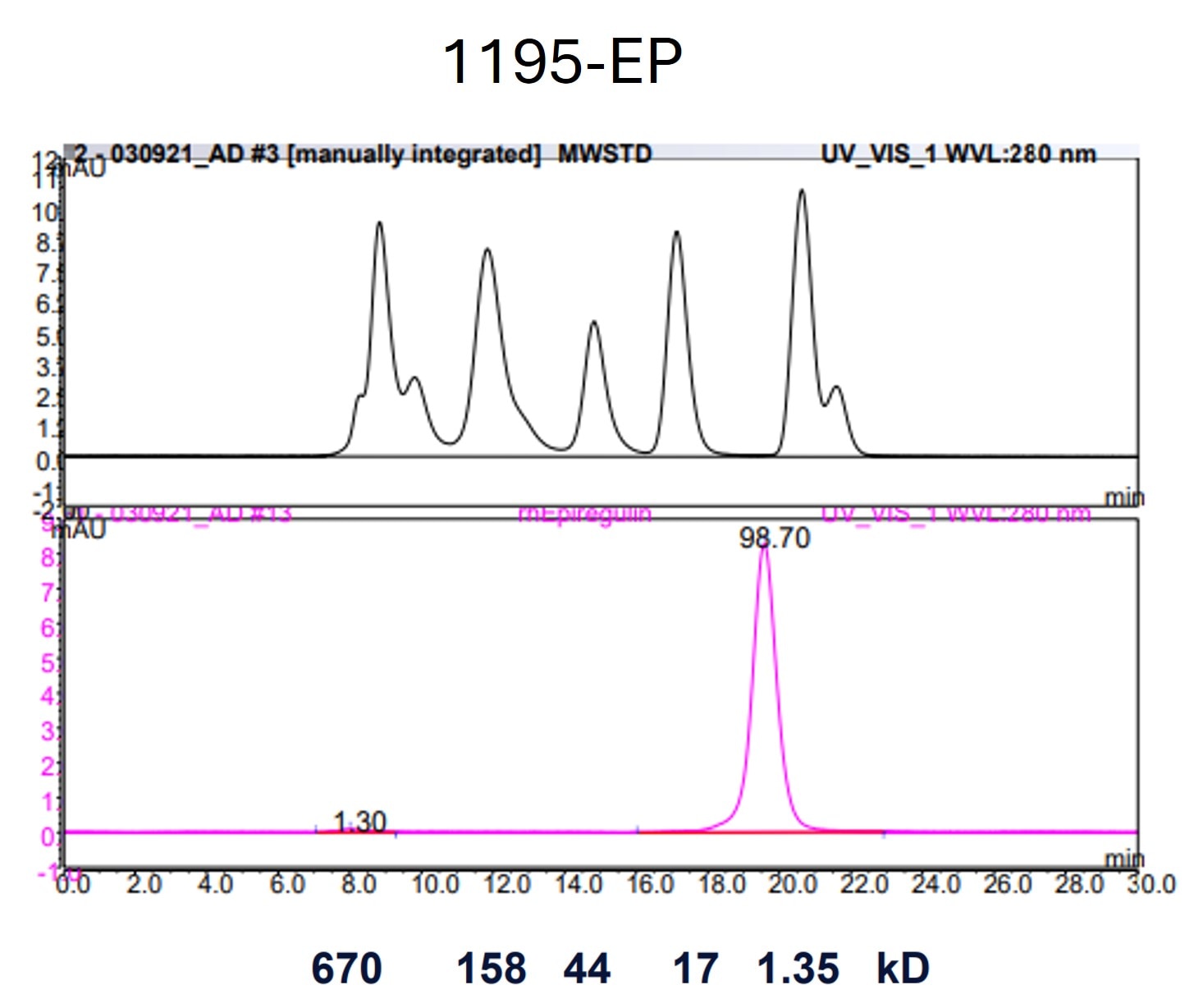
Val63-Leu108, with an N-terminal Met
Analysis
Product Datasheets
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
1195-EP
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
1195-EP/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Recombinant Human Epiregulin (Catalog # 1195-EP) stimulates proliferation in the Balb/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line. The ED50 is 0.125-0.75 ng/mL.
 View Larger
View Larger
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Human Epiregulin was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing a single band at 5 kDa.
Reconstitution Calculator
Background: Epiregulin
Epiregulin is a member of the EGF family of growth factors which includes, among others, epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha, amphiregulin (ARG), HB (heparin-binding)-EGF, betacellulin, and the various heregulins. All EGF family members are synthesized as transmembrane precursors and are converted to soluble forms by proteolytic cleavage. Epiregulin was originally purified from the mouse fibroblast-derived tumor cell line NIH3T3/T7 (1). The human epiregulin cDNA encodes a 169 amino acid (aa) residues transmembrane precursor with a 29 aa signal peptide, a 21 aa transmembrane domain and a 21 aa cytoplasmic domain. The putative soluble mature Epiregulin comprising the EGF-like domain (aa residues 64-104) is formed by proteolytic removal of the propeptide regions (2). There is 85% aa sequence homology between human and mouse epiregulins. Epiregulin is expressed primarily in the placenta and macrophages (3). High level expression has also been detected in various carcinomas. Epiregulin specifically binds EGFR (ErbB1) and ErbB4 but not ErbB2 and ErbB3. It activates the homodimers of both ErbB1 and ErbB4. In addition, epiregulin can also activate all possible heteromeric combinations of the four ErbB family members (4). Epiregulin stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and hepatocytes. It has been shown to be an autocrine growth factor for epidermal keratinocytes as well as mesangial cells (5, 6). Epiregulin has also been shown to inhibit growth of several epithelial tumor cells. In addition, Epiregulin has been implicated in the implantation process during pregnancy (7).
- Toyoda, H. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:7495.
- Toyoda, H. et al. (1997) Biochem. J. 326:69.
- Komurasaki, T. et al. (1997) Oncogene 15:2841.
- Shelly, M. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:10496.
- Shirakata, Y. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:5748.
- Mishre, R. et al. (2002) Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 283:F1151.
- Das, S.K. et al. (1997) Dev. Biol. 190:178.
Citations for Recombinant Human Epiregulin Protein
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
11
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the EGFR Ligand Epiregulin Elicit Robust Anti-Tumor Activity in Colorectal Cancer
Authors: Jacob, J;Anami, Y;High, P;Liang, Z;Subramanian, S;Ghosh, SC;AghaAmiri, S;Guernsey-Biddle, C;Tran, H;Rowe, JH;Azhdarinia, A;Tsuchikama, K;Carmon, KS;
bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Quantification of ligand and mutation-induced bias in EGFR phosphorylation in direct response to ligand binding
Authors: Wirth, D;Özdemir, E;Hristova, K;
Nature communications
Species: Chinese Hamster
Sample Types: Vesicles
Applications: Bioassay -
pYtags enable spatiotemporal measurements of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in living cells
Authors: Farahani, PE;Yang, X;Mesev, EV;Fomby, KA;Brumbaugh-Reed, EH;Bashor, CJ;Nelson, CM;Toettcher, JE;
eLife
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Transfected Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Fibroblast-derived EGF ligand Neuregulin-1 induces fetal-like reprogramming of the intestinal epithelium without supporting tumorigenic growth
Authors: TT Lemmetyine, EW Viitala, L Wartiovaar, T Kaprio, J Hagström, C Haglund, P Katajisto, TC Wang, E Domènech-M, S Ollila
Disease Models & Mechanisms, 2023-04-03;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Organoid
Applications: Bioassay -
Epiregulin as an Alternative Ligand for Leptin Receptor Alleviates Glucose Intolerance without Change in Obesity
Authors: NJ Song, A Lee, R Yasmeen, Q Shen, K Yang, SB Kumar, D Muhanna, S Arnipalli, SF Noria, BJ Needleman, JW Hazey, DJ Mikami, J Ortega-Ana, R Jiménez-Fl, J Prokop, O Ziouzenkov
Cells, 2022-01-26;11(3):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
EREG-driven oncogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma exhibits higher sensitivity to Erlotinib therapy
Authors: S Liu, Y Wang, Y Han, W Xia, L Zhang, S Xu, H Ju, X Zhang, G Ren, L Liu, W Ye, Z Zhang, J Hu
Theranostics, 2020-08-25;10(23):10589-10605.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Epiregulin-blocking antibody inhibits epiregulin-dependent EGFR signaling
Authors: M Iijima, M Anai, T Kodama, Y Shibasaki
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, 2017-03-06;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Epiregulin contributes to breast tumorigenesis through regulating matrix metalloproteinase 1 and promoting cell survival
Authors: Mariya Farooqui, Laura R. Bohrer, Nicholas J. Brady, Pavlina Chuntova, Sarah E. Kemp, C. Taylor Wardwell et al.
Molecular Cancer
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Gene expression analysis of pig cumulus-oocyte complexes stimulated in vitro with follicle stimulating hormone or epidermal growth factor-like peptides.
Authors: Blaha M, Nemcova L, Kepkova K, Vodicka P, Prochazka R
Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2015-10-06;13(0):113.
Species: Porcine
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
High epiregulin expression in human U87 glioma cells relies on IRE1alpha and promotes autocrine growth through EGF receptor.
Authors: Auf G, Jabouille A, Delugin M, Guerit S, Pineau R, North S, Platonova N, Maitre M, Favereaux A, Vajkoczy P, Seno M, Bikfalvi A, Minchenko D, Minchenko O, Moenner M
BMC Cancer, 2013-12-13;13(0):597.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay -
Human trophoblast survival at low oxygen concentrations requires metalloproteinase-mediated shedding of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor.
Authors: Armant DR, Kilburn BA, Petkova A, Edwin SS, Duniec-Dmuchowski ZM, Edwards HJ, Romero R, Leach RE
Development, 2006-01-11;133(4):751-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Bioassay
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Proteins and Enzyme FAQsReviews for Recombinant Human Epiregulin Protein
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Recombinant Human Epiregulin Protein?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: