Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Antibody Summary
Leu18-Ser502
Accession # P05186
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line, BG01V human embryonic stem cells, and NTera-2 human testicular embryonic carcinoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.25 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB29092) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF018). A specific band was detected for Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL at approximately 80 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL in Human Liver. Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver using Mouse Anti-Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB29092) at 0.3 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS002) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to bile canaliculi. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cells, Saos‑2 human osteosarcoma cells and BG01V human embryonic stem cells, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL at approximately 115 kDa (as indicated) using 5 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB29092). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12‑230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
View Larger
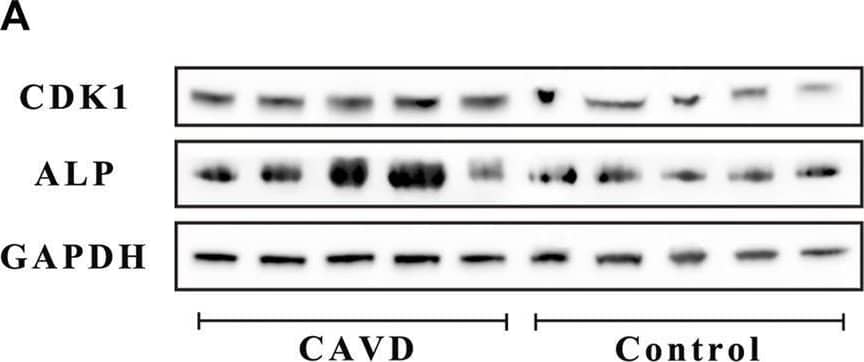
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot Analysis of the control and CAVD aortic valve samples (n = 5 and 5, respectively). (A) Western blotting for CDK1 and ALP proteins on valve tissues. (B) Semi-quantitative analysis of protein expression. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of CDK1 and Ki-67 on valve tissues. (D) Semi-quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity. (E) PCR test for cell proliferation genes on valve tissues. (*) p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35571082), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
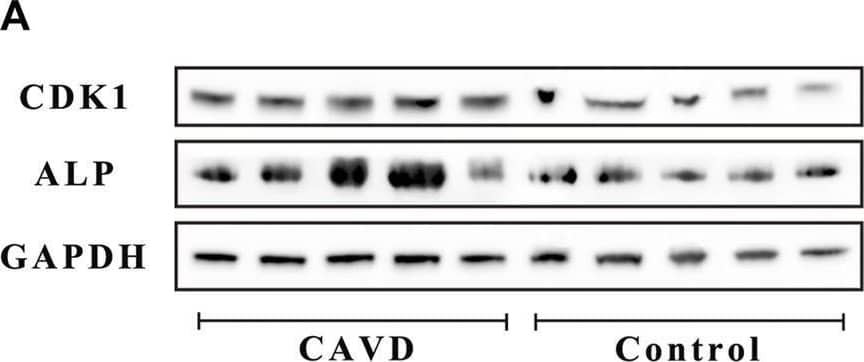
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot Analysis of the control and CAVD aortic valve samples (n = 5 and 5, respectively). (A) Western blotting for CDK1 and ALP proteins on valve tissues. (B) Semi-quantitative analysis of protein expression. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of CDK1 and Ki-67 on valve tissues. (D) Semi-quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity. (E) PCR test for cell proliferation genes on valve tissues. (*) p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35571082), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
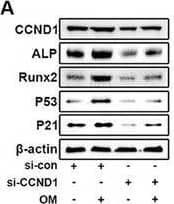
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot CCND1 participates in the osteogenic differentiation of VICs following OM. A–F) VICs were transfected with CCND1 siRNA or scrambled siRNA, and then stimulated with OM for 7 days. Immunoblot analysis of CCND1, ALP, Runx2 P53, and P21 expression in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Bar plots showing the semiquantitative analysis of indicated genes expression. G,H) With OM induction for 7 days, representative ALP staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. I–K) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Alizarin red staining showed the calcific nodules in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. L–M) Representative SA‐ beta ‐gal staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Bar plot showing the percentage of SA‐ beta ‐gal staining positive cells. Scale bar 50 µm. Data are means ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38502885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
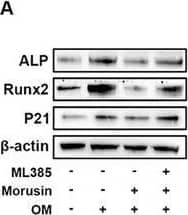
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot Morusin attenuates VIC calcification by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway. A–D) ML385 was used to inhibit the activation of Nrf2 in VICs. Representative immunoblot images and quantification of the levels of ALP, Runx2, and P21 in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). E,F) With OM induction for 7 days, representative ALP staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. G–I) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Alizarin red staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. Data are means ± SD. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38502885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
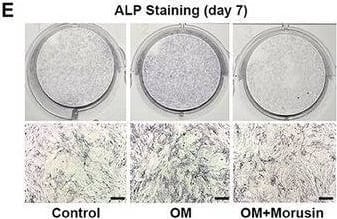
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Immunohistochemistry Morusin inhibits OM‐induced osteogenic differentiation of VICs. A) Immunoblot analysis of Runx2 and ALP expression in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). B) Bar plot showing the fold change of Runx2 expression over control. C) Bar plot showing the fold change of ALP expression over control. D) Immunofluorescent staining of ALP (green), Runx2 (red), and DAPI (blue) in the VICs from indicated groups. Scale bar 50 µm. E,F) With OM induction for 7 days, representative ALP staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. G–I) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Alizarin red staining showed the calcific nodules in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. J) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Von Kossa and Alizarin Red staining of aortic valve leaflets. K) Bar plot showing the percentage of Von Kossa positive staining area of indicated groups (n = 3, each group). L) Bar plot showing the percentage of Alizarin Red positive staining area of indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Data are mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38502885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot Morusin inhibits OM‐induced osteogenic differentiation of VICs. A) Immunoblot analysis of Runx2 and ALP expression in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). B) Bar plot showing the fold change of Runx2 expression over control. C) Bar plot showing the fold change of ALP expression over control. D) Immunofluorescent staining of ALP (green), Runx2 (red), and DAPI (blue) in the VICs from indicated groups. Scale bar 50 µm. E,F) With OM induction for 7 days, representative ALP staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. G–I) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Alizarin red staining showed the calcific nodules in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. J) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Von Kossa and Alizarin Red staining of aortic valve leaflets. K) Bar plot showing the percentage of Von Kossa positive staining area of indicated groups (n = 3, each group). L) Bar plot showing the percentage of Alizarin Red positive staining area of indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Data are mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38502885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Morusin inhibits OM‐induced osteogenic differentiation of VICs. A) Immunoblot analysis of Runx2 and ALP expression in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). B) Bar plot showing the fold change of Runx2 expression over control. C) Bar plot showing the fold change of ALP expression over control. D) Immunofluorescent staining of ALP (green), Runx2 (red), and DAPI (blue) in the VICs from indicated groups. Scale bar 50 µm. E,F) With OM induction for 7 days, representative ALP staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. G–I) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Alizarin red staining showed the calcific nodules in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. J) With OM induction for 21 days, representative Von Kossa and Alizarin Red staining of aortic valve leaflets. K) Bar plot showing the percentage of Von Kossa positive staining area of indicated groups (n = 3, each group). L) Bar plot showing the percentage of Alizarin Red positive staining area of indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Data are mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38502885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
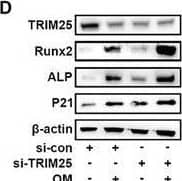
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot Morusin attenuates VIC calcification depending on Trim25. A,B) VICs were transfected with CCND1 siRNA or scrambled siRNA, immunoblot analysis of Trim25 expression in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Bar plots showing the semiquantitative analysis of Trim25 expression. C) VICs were transfected with Trim25 siRNA or scrambled siRNA. Co‐IP analysis of the Keap1 ubiquitination level in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). D–M) Representative immunoblot images and quantification of the levels of Trim25, ALP, Runx2, and P21 in VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). N,S) VICs were transfected with Trim25 siRNA or scrambled siRNA, representative ALP staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). P,U) VICs were transfected with Trim25 siRNA or scrambled siRNA, representative Alizarin red staining of VICs from indicated groups (n = 3, each group). Scale bar 50 µm. Data are means ± SD. NS, not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38502885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
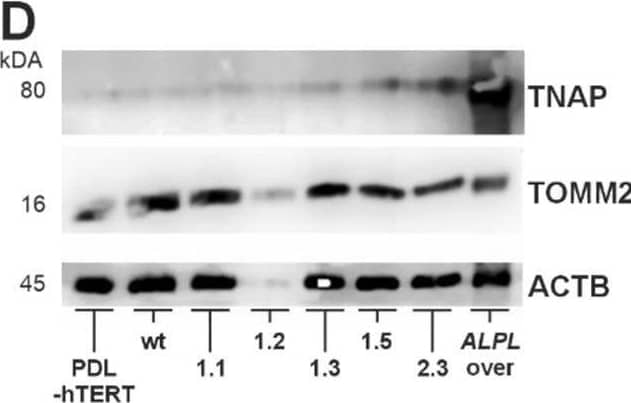
Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL by Western Blot Analyses of TNAP expression and activity by immunofluorescence staining, Western blot, and enzyme activity assay. Cell analyses were performed in five different ALPLtg PDL-hTERT cell lines, the wt line and control PDL-hTERT that did not undergo genome editing. (A) TNAP expression (green) was detected by immunofluorescence after nuclear counterstaining with DAPI (blue). Representative images are shown. Scale bars = 50 µm. (B) Quantification of TNAP signals in IF images were done by corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) for ten random cells per image, and five images per cell line (n = 50). (C) Specific TNAP activity was measured by a CSPD assay confirming the spontaneous activity of the expressed protein. N = 4 per condition. (D–F) TNAP expression level and the expression of the mitochondrial protein TOMM20 in total cell lysates were determined semi-quantitatively by Western blot analysis in relation to the housekeeping protein beta -actin/ACTB. A lysate of a TNAP overexpressing cell line (ALPL over) was used as positive control. A representative immunoblot is shown in (C). White pixels indicate signal oversaturation. Quantification results in E and F are presented as mean ± SEM, N = 3 per condition. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40530336), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL
Four distinct genes encode alkaline phosphatases (APs) in humans (1). The ALPL gene encodes the liver/bone/kidney isozyme, also known as the tissue-nonspecific AP (TNAP). In comparison, ALPI, ALPP and ALPPL2 encode intestinal, placental and placental-like or germ cell APs, respectively. The serum levels of human APs are useful tumor markers (2). There are many mutations in the ALPL gene, leading to different forms of hypophosphatasia, characterized by poorly mineralized cartilage and bones (3). The native ALPL is a glycosylated homodimer attached to the membrane through a GPI-anchor. The C-terminal pro peptide (residues 503‑524) is not present in the mature form.
- Le Du, M-H. and J.L. Millan (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:49808.
- Millan, J.L. and W.H. Fishman (1995) Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 32:1.
- Di Mauro, S. et al. (2002) J. Bone Miner. Res. 17:1383.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
5
Citations: Showing 1 - 5
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
The Natural Product Andrographolide Ameliorates Calcific Aortic Valve Disease by Regulating the Proliferation of Valve Interstitial Cells via the MAPK-ERK Pathway
Authors: Yuming Huang, Ming Liu, Chungeng Liu, Nianguo Dong, Liang Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology
-
Unprecedented nor-seco-diterpene lactones inhibited osteogenic differentiation of valve interstitial cells
Authors: Wei, J;Jin, X;Fan, P;Li, X;Chen, X;Zhai, W;Zhang, Y;Hu, Z;Wu, Z;
Bioorganic chemistry
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Tissue Homogenates
-
ALPL-1 is a target for chimeric antigen receptor therapy in osteosarcoma
Authors: Mensali, N;Köksal, H;Joaquina, S;Wernhoff, P;Casey, NP;Romecin, P;Panisello, C;Rodriguez, R;Vimeux, L;Juzeniene, A;Myhre, MR;Fåne, A;Ramírez, CC;Maggadottir, SM;Duru, AD;Georgoudaki, AM;Grad, I;Maturana, AD;Gaudernack, G;Kvalheim, G;Carcaboso, AM;de Alava, E;Donnadieu, E;Bruland, ØS;Menendez, P;Inderberg, EM;Wälchli, S;
Nature communications
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Skeletal dysplasia-causing TRPV4 mutations suppress the hypertrophic differentiation of human iPSC-derived chondrocytes
Authors: AR Dicks, GI Maksaev, Z Harissa, A Savadipour, R Tang, N Steward, W Liedtke, CG Nichols, CL Wu, F Guilak
Elife, 2023-02-22;12(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Mitochondrial TNAP controls thermogenesis by hydrolysis of phosphocreatine
Authors: Y Sun, JF Rahbani, MP Jedrychows, CL Riley, S Vidoni, D Bogoslavsk, B Hu, PA Dumesic, X Zeng, AB Wang, NH Knudsen, CR Kim, A Marasciull, JL Millán, ET Chouchani, L Kazak, BM Spiegelman
Nature, 2021-05-12;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Alkaline Phosphatase/ALPL Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
