Human DPP6 Antibody Summary
Thr56-Asp803 (Glu458Val)
Accession # AAA35761
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of DPP6 in Human SHSY5Y Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. Human SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human DPP6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2360, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (MAB0041, open histogram), followed by APC-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (F0101B). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane Proteins protocol.
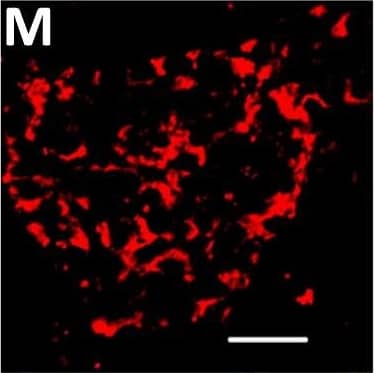 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
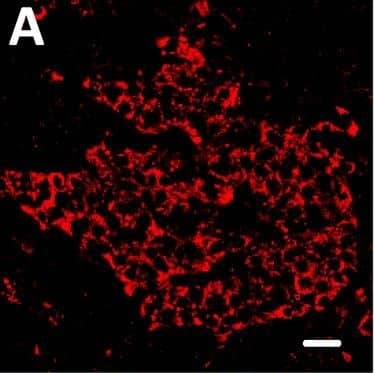 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
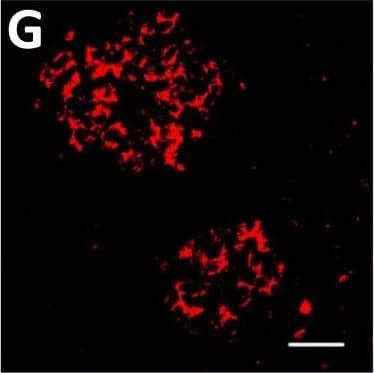 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
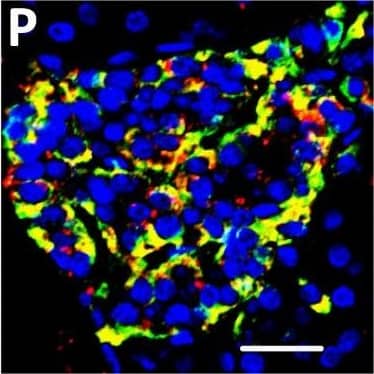
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
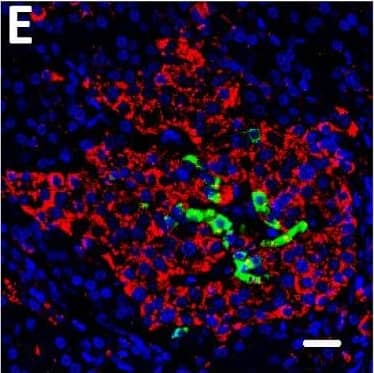
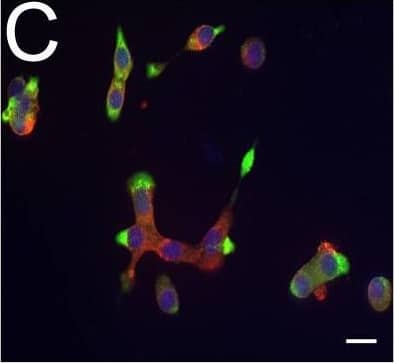
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Expression of DPP6 in human islets and EndoC-beta H1 cells and other tissues evaluated by qPCR and histology. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) of DPP6 mRNA expression (detecting a shared sequence among all DPP6 splice variants) in EndoC-beta H1 cells (n = 5) and human pancreatic islets (n = 4) that were exposed or not to cytokines (IL-1 beta + IFN-gamma ) for 48 h, as compared to pancreatic exocrine tissue (n = 6), two exocrine cell lines (Capan-2 (n = 3) and PANC (n = 3)), and 14 other non-pathological human tissues (n = 1). (B) Immunoblot of EndoC-beta H1 cells under control conditions or following a 48h exposure to cytokines (IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma ), with alpha-tubulin as a reference protein. A representative figure is shown at the top and densitometric analysis at the bottom (n = 5), this figure displays a cropped blot, the full-length version is included in supplementary figure 8; (C–F) Immunocytochemistry of EndoC-beta H1 cells. (C) An overlay with cells stained with an anti-DPP6 monoclonal antibody (mAb, red), co-stained for insulin (green) and Hoechst in blue. The separate channels are displayed in (D) insulin (green) and (E) DPP6 (red) (n = 3). The mostly surface localization of DPP6 (red) can be observed in (F) (n = 4), with blue signals indicating Hoechst staining. The negative staining control of EndoC-beta H1 cells (without the DPP6 antibody) is placed in the top right corner of panel F. White scale bar represents 1 µm. RT-qPCR and the western blot data are presented as means ± SEM. Paired and unpaired two-way ANOVA (indicated with * and $, respectively), and unpaired one-way ANOVA (indicated with #) with Šídák correction for multiple comparisons; *, $ and # p ≤ 0.05 as indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
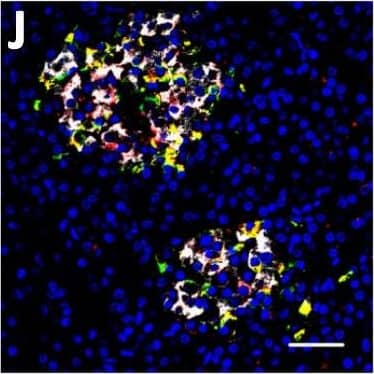
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
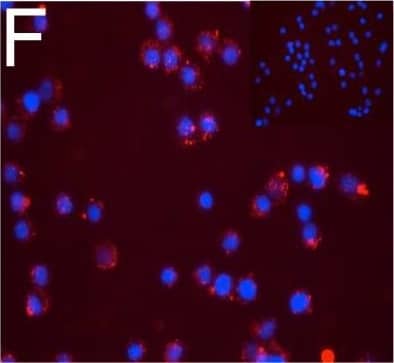
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Expression of DPP6 in human islets and EndoC-beta H1 cells and other tissues evaluated by qPCR and histology. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) of DPP6 mRNA expression (detecting a shared sequence among all DPP6 splice variants) in EndoC-beta H1 cells (n = 5) and human pancreatic islets (n = 4) that were exposed or not to cytokines (IL-1 beta + IFN-gamma ) for 48 h, as compared to pancreatic exocrine tissue (n = 6), two exocrine cell lines (Capan-2 (n = 3) and PANC (n = 3)), and 14 other non-pathological human tissues (n = 1). (B) Immunoblot of EndoC-beta H1 cells under control conditions or following a 48h exposure to cytokines (IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma ), with alpha-tubulin as a reference protein. A representative figure is shown at the top and densitometric analysis at the bottom (n = 5), this figure displays a cropped blot, the full-length version is included in supplementary figure 8; (C–F) Immunocytochemistry of EndoC-beta H1 cells. (C) An overlay with cells stained with an anti-DPP6 monoclonal antibody (mAb, red), co-stained for insulin (green) and Hoechst in blue. The separate channels are displayed in (D) insulin (green) and (E) DPP6 (red) (n = 3). The mostly surface localization of DPP6 (red) can be observed in (F) (n = 4), with blue signals indicating Hoechst staining. The negative staining control of EndoC-beta H1 cells (without the DPP6 antibody) is placed in the top right corner of panel F. White scale bar represents 1 µm. RT-qPCR and the western blot data are presented as means ± SEM. Paired and unpaired two-way ANOVA (indicated with * and $, respectively), and unpaired one-way ANOVA (indicated with #) with Šídák correction for multiple comparisons; *, $ and # p ≤ 0.05 as indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
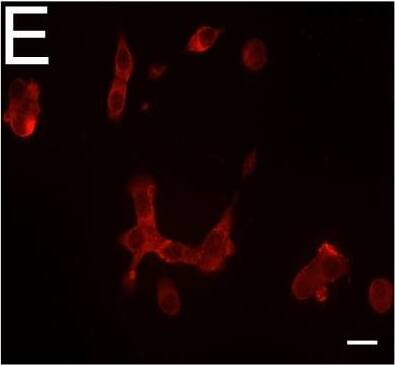
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Expression of DPP6 in human islets and EndoC-beta H1 cells and other tissues evaluated by qPCR and histology. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) of DPP6 mRNA expression (detecting a shared sequence among all DPP6 splice variants) in EndoC-beta H1 cells (n = 5) and human pancreatic islets (n = 4) that were exposed or not to cytokines (IL-1 beta + IFN-gamma ) for 48 h, as compared to pancreatic exocrine tissue (n = 6), two exocrine cell lines (Capan-2 (n = 3) and PANC (n = 3)), and 14 other non-pathological human tissues (n = 1). (B) Immunoblot of EndoC-beta H1 cells under control conditions or following a 48h exposure to cytokines (IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma ), with alpha-tubulin as a reference protein. A representative figure is shown at the top and densitometric analysis at the bottom (n = 5), this figure displays a cropped blot, the full-length version is included in supplementary figure 8; (C–F) Immunocytochemistry of EndoC-beta H1 cells. (C) An overlay with cells stained with an anti-DPP6 monoclonal antibody (mAb, red), co-stained for insulin (green) and Hoechst in blue. The separate channels are displayed in (D) insulin (green) and (E) DPP6 (red) (n = 3). The mostly surface localization of DPP6 (red) can be observed in (F) (n = 4), with blue signals indicating Hoechst staining. The negative staining control of EndoC-beta H1 cells (without the DPP6 antibody) is placed in the top right corner of panel F. White scale bar represents 1 µm. RT-qPCR and the western blot data are presented as means ± SEM. Paired and unpaired two-way ANOVA (indicated with * and $, respectively), and unpaired one-way ANOVA (indicated with #) with Šídák correction for multiple comparisons; *, $ and # p ≤ 0.05 as indicated by bars. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
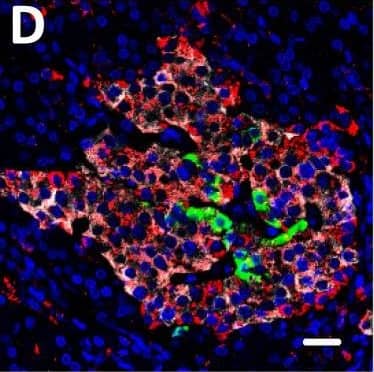
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
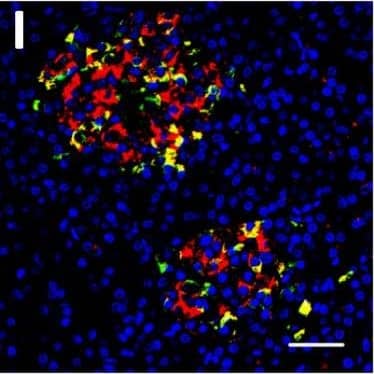
Detection of Human DPP6 by Immunohistochemistry Localization of DPP6 expression in human pancreas. (A–E) A representative human pancreas stained for DPP6 (A, red), insulin (B, white), somatostatin (C, green); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and somatostatin (green) (D); overlay of DPP6 (red) and somatostatin (green) (E); the data indicate co-staining of insulin and DPP6, but not somatostatin and DPP6; (F–J) A representative human pancreas stained for glucagon (F, green), DPP6 (G, red), insulin (H, white); DPP6 (red) and glucagon (green) overlay (I); overlay of DPP6 (red), insulin (white) and glucagon (green) (J), the data indicate co-staining of both insulin and glucagon with DPP6; (K) Morphometric quantification of DPP6 area in pancreata from T1D patients as compared to control, non-diabetic individuals (n = 3). (L–P) A representative human pancreas from a subject with long-term type 1 diabetes (16 years of disease) stained for glucagon (L, green), DPP6 (M, red), insulin (N, white); Hoechst (O, blue); (P) overlay of DPP6 (green), glucagon (red), insulin (white) and Hoechst (blue), indicating that in the absence of insulin positive cells, the remaining glucagon positive cells co-stain for DPP6. In total, 3 pancreata from normoglycemic individuals and 3 from type 1 diabetes subjects were analysed. White scale bar represents 20 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29123178), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: DPP6
DPP6, also known as DPPX and DPPIV/CD26 related protein, is a critical component of neuronal A-type K+ channels but lacks protease activity.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human DPP6 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
2
Citations: Showing 1 - 2
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
A nanobody-based nuclear imaging tracer targeting dipeptidyl peptidase 6 to determine the mass of human beta cell grafts in mice
Authors: Stéphane Demine, Rita Garcia Ribeiro, Julien Thevenet, Lorella Marselli, Piero Marchetti, François Pattou et al.
Diabetologia
-
A nanobody-based tracer targeting DPP6 for non-invasive imaging of human pancreatic endocrine cells
Authors: A Balhuizen, S Massa, I Mathijs, JV Turatsinze, J De Vos, S Demine, C Xavier, O Villate, I Millard, D Egrise, C Capito, R Scharfmann, P In't Veld, P Marchetti, S Muylderman, S Goldman, T Lahoutte, L Bouwens, DL Eizirik, N Devoogdt
Sci Rep, 2017-11-09;7(1):15130.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells, Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC, IHC-P
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human DPP6 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human DPP6 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human DPP6 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
