Human Glypican 1 Antibody Summary
Asp24-Ser530
Accession # P35052
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Glypican 1 in MDA‑MB‑231 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Human Glypican 1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4519, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0107).
 View Larger
View Larger
Glypican 1 in MDA‑MB‑231 Human Cell Line. Glypican 1 was detected in immersion fixed MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line using Goat Anti-Human Glypican 1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4519) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI(blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasmic. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
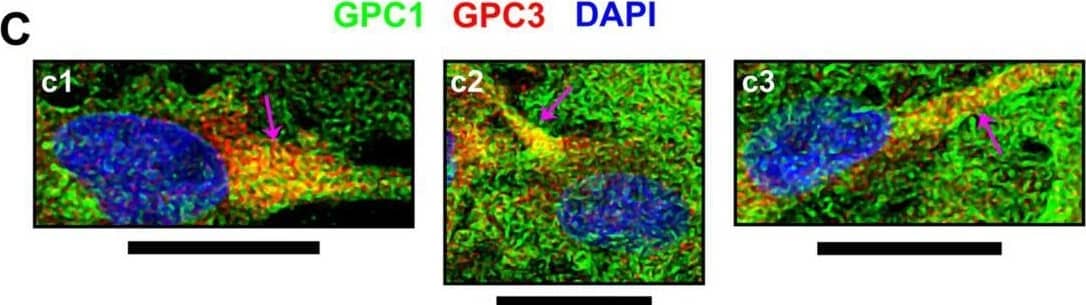
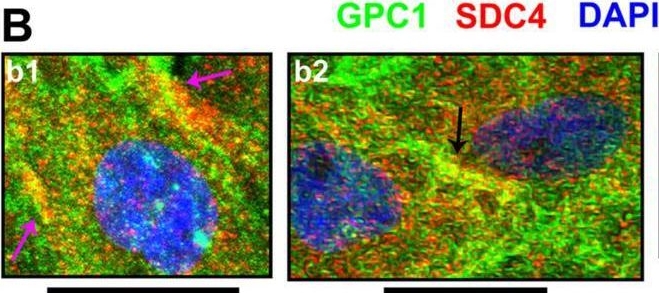
Detection of Glypican 1 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Cellular events indicating GPC1 and its association with SDC4 or GPC3.From immunofluorescence assays, through confocal microscopy, special events including (A) GPC1 and its co-localization with (B) SDC4 or (C) GPC3, both in red, were imaged. GPC1 is always represented in green, and DAPI staining for cells’ nuclei is in blue. Images were obtained from U-251 MG cells (b2, b3 and c1-c4) or C- (a1-a3 and b1) as there was evident GPC1 expression in these cell lines. Arrows have the following color code: detection in extracellular vesicles (white); extracellular vesicles’ interaction with the cellular membrane (cyan); co-localization in the cell membrane (magenta); co-localization in cell-cell junctions (black). The images were obtained with a Leica TCS SP8 CARS confocal microscope. All scale bars refer to 25 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32180897), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Glypican 1 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Cellular events indicating GPC1 and its association with SDC4 or GPC3.From immunofluorescence assays, through confocal microscopy, special events including (A) GPC1 and its co-localization with (B) SDC4 or (C) GPC3, both in red, were imaged. GPC1 is always represented in green, and DAPI staining for cells’ nuclei is in blue. Images were obtained from U-251 MG cells (b2, b3 and c1-c4) or C- (a1-a3 and b1) as there was evident GPC1 expression in these cell lines. Arrows have the following color code: detection in extracellular vesicles (white); extracellular vesicles’ interaction with the cellular membrane (cyan); co-localization in the cell membrane (magenta); co-localization in cell-cell junctions (black). The images were obtained with a Leica TCS SP8 CARS confocal microscope. All scale bars refer to 25 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32180897), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Glypican 1
The Glypicans (glypiated proteoglycans) are a small multigene family of GPI-linked proteoglycans that play a key role in growth factor signaling (1, 2, 3, 4). There are six known mammalian Glypicans. They all share a common-sized protein core of 60‑70 kDa, an N-terminus which likely forms a compact globular domain, 14 conserved cysteines that form multiple intrachain disulfide bonds, and a number of C-terminal N- and O-linked carbohydrate attachment sites. Based on exon organization and the location of O-linked glycosylation sites, at least two subfamilies of Glypicans are known, with one subfamily containing Glypicans 1, 2, 4 and 6, and another subfamily containing Glypicans 3 and 5 (3, 5). Human Glypican 1 (GPC-1) is synthesized as a 558 amino acid (aa) preproprecursor that contains a 23 aa signal sequence, a 507 aa mature segment, and a 28 aa C-terminal prosegment (6, 7). There are two potential N-linked and four potential O-linked sites for glycosylation or glycanation. There are potentially two heparan sulfate (HS) modifications on GPC-1 that could contribute to a native molecular weight of approximately 200 kDa (7, 8, 9). Mature human GPC-1 shares 91% aa identity with mature mouse GPC-1. There are two potential splice variants of human GPC-1. Both show an alternate start site at Met73, while one has an additional 65 aa substitution for the C-terminal 264 amino acids (10, 11). Cells known to express GPC-1 include neurons, smooth and skeletal muscle cells, keratinocytes, osteoblasts, Schwann cells, immature dendritic cells, and tumor, plus tumor-associated vascular endothelial cells (8, 9, 12‑15). The function of GPC-1 is complex and varied. As a proteoglycan, it appears to make use of its HS adduct to impact select growth factor activity (16). This is accomplished by having juxtramembrane HS attachment sites, and a flexible, GPI-linkage (17). Data suggests GPC-1 and sulfation enzymes may collaborate to regulate FGF signaling. HS modules that are rich in 2-O- and 6-O- sulfate upregulate FGF-2 activation of FGFR1c (18). Similarly, FGF-1 requires both 2-O- and 6-O-sulfation to bind to FGFR2c and 3c. By contract, FGF-1 requires no sulfation to bind to FGFR2b, and FGF-8b needs only 6-O-sulfation to activate FGFR3c. Thus, many FGF receptor isoform specific effects may be attributed to an interaction between Glypican family members and the cell sulfation system (19).
- Song, H.H. and J. Filmus (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1573:241.
- Fransson, L-A. et al. (2004) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61:1016.
- De Cat, B. and G. David (2001) Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:117.
- Lamoureux, F. et al. (2007) BioEssays 29:758.
- Veugelers, M. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:26968.
- GenBank Accession # P35052.
- David, G. et al. (1990) J. Cell Biol. 111:3165.
- Lories, V. et al. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267:1116.
- Lories, V. et al. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264:7009.
- GenBank Accession # EAW71184.
- GenBank Accession # EAW71183.
- Chernousov, M.A. et al. (2006) J. Neurosci. 26:508.
- Wegrowski, Y. et al. (2006) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 144:485.
- Qiao, D. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:16045.
- Kayed, H. et al. (2006) Int. J. Oncol. 29:1139.
- Selleck, S.B. (2006) SciSTKE, April 4:pe17.
- Qiao, D. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:16045.
- Su, G. et al. (2006) Am. J. Pathol. 168:2014.
- Allen, B.L. and A.C. Rapraeger (2003) J. Cell Biol. 163:637.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Glypican 1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
6
Citations: Showing 1 - 6
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Regulation of bone morphogenetic protein signalling and cranial osteogenesis by Gpc1 and Gpc3
Authors: Prem P. Dwivedi, Randall H. Grose, Jorge Filmus, Charles S.T. Hii, Cory J. Xian, Peter J. Anderson et al.
Bone
-
The Mycobacterium ulcerans toxin mycolactone causes destructive Sec61-dependent loss of the endothelial glycocalyx and vessel basement membrane to drive skin necrosis
Authors: Hsieh, LT;Hall, BS;Newcombe, J;Mendum, TA;Varela, SS;Umrania, Y;Deery, MJ;Shi, WQ;Diaz-Delgado, J;Salguero, FJ;Simmonds, RE;
eLife
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
The Glypican proteoglycans show intrinsic interactions with Wnt-3a in human prostate cancer cells that are not always associated with cascade activation
Authors: GFA de Moraes, E Listik, GZ Justo, CM Vicente, L Toma
BMC molecular and cell biology, 2021-05-04;22(1):26.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, IHC, Immunoprecipitation -
Cleavage of proteoglycans, plasma proteins and the platelet-derived growth factor receptor in the hemorrhagic process induced by snake venom metalloproteinases
Authors: AF Asega, MC Menezes, D Trevisan-S, D Cajado-Car, L Bertholim, AK Oliveira, A Zelanis, SMT Serrano
Sci Rep, 2020-07-31;10(1):12912.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Western Blot -
Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor Sunitinib and integrin antagonist peptide HM-3 show similar lipid raft dependent biphasic regulation of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis
Authors: J Hu, W Wang, C Liu, M Li, E Nice, H Xu
J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res., 2019-08-28;38(1):381.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: ICC, Western Blot -
Overexpression of glypican-1 implicates poor prognosis and their chemoresistance in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Authors: Hisashi Hara
Br J Cancer, 2016-06-16;115(1):66-75.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Protein, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Western Blot
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Glypican 1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Glypican 1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Glypican 1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image



