Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B Antibody Summary
Ala54-Glu182
Accession # Q6FH58
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF631) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF019). A specific band was detected for TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B at approximately 45 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 8.
 View Larger
View Larger
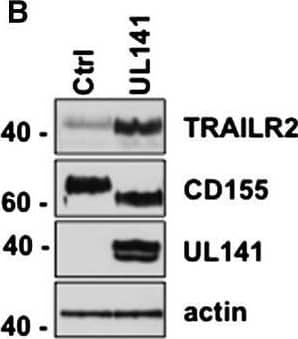
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot UL141 Blockade of Both TRAIL DR and CD155 Contributes to NK Cell Inhibition(A) RAd control or UL141 transduced A549 cells were analyzed for expression of TRAIL-R2, CD155 and CD112 at the time of NK cell addition by flow cytometry.(B) Western blot of RAd-transduced A549 cells.(C) Expression of TRAIL by IFN alpha activated (blue) or unactivated (red) human NK cells assessed by flow cytometry.(D) IFN alpha -activated NK cells were purified from human peripheral blood and added to A549 lung epithelial cells transduced with either control adenovirus vector (Rad-Cntrl) or Rad-UL141 (effector to target [E:T] ratio of 2). Blocking alpha DNAM-1 antibody or blocking soluble TRAIL-R2 (10 μg/ml) was added to cultures where indicated (+), and control mIgG or sCD30 was added as a control to the other cultures. Apoptosis of A549 cells was assessed 4 hr later. Shown are two representative experiments of more than six performed.(E) Summary of NK killing data from eight separate experiments and four different donors. †Data are mean ± SEM from n = 1 to 3 wells. ∗Bonferroni post test shows significance at p < 0.05.See also Figure S5. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23498957), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
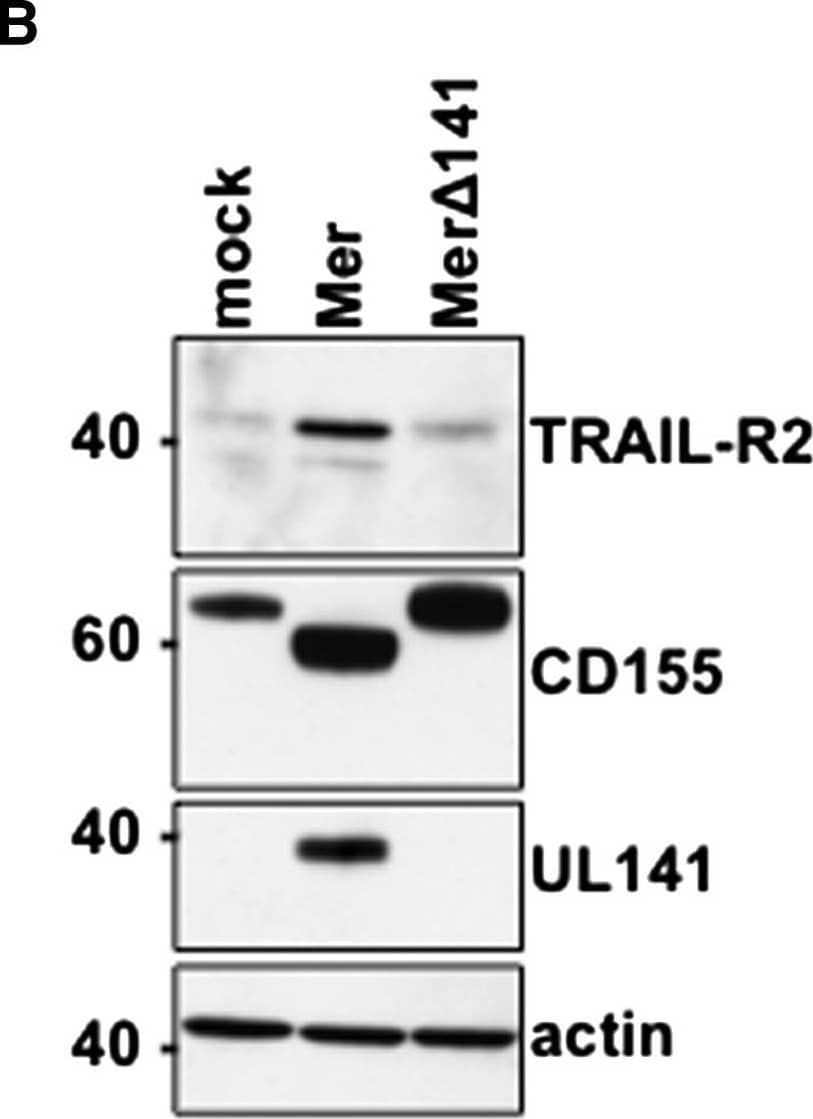
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot TRAIL-R2 Expression in HCMV-Infected Cells Human foreskin fibroblasts (HFFs) were infected (72 hr, MOI = 20) with HCMV Merlin (Mer) or Merlin delta UL141 (Mer delta 141) and analyzed for TRAIL-R2 expression by (A) flow cytometry and (B) Western blot. IgG(–), isotype control antibody staining. Results are representative of six to ten performed experiments. See also Figure S2. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23498957), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
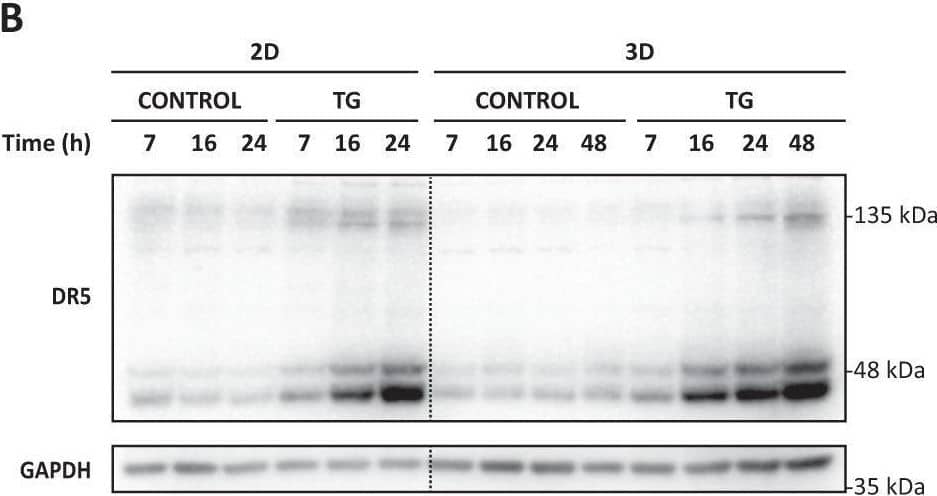
Detection of TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot PERK pathway activation upon ER stress in bidimensional cultures and multicellular tumor spheroids.HCT116 cells, in conventional 2D cultures or spheroids (3D) (10-days), were treated with TG (100 nM) for the indicated times. Activation of the PERK signaling pathway (A) and TRAIL-R2/DR5 protein levels (B) were assessed in whole-cell extracts by western blotting. alpha -tubulin or GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35115486), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
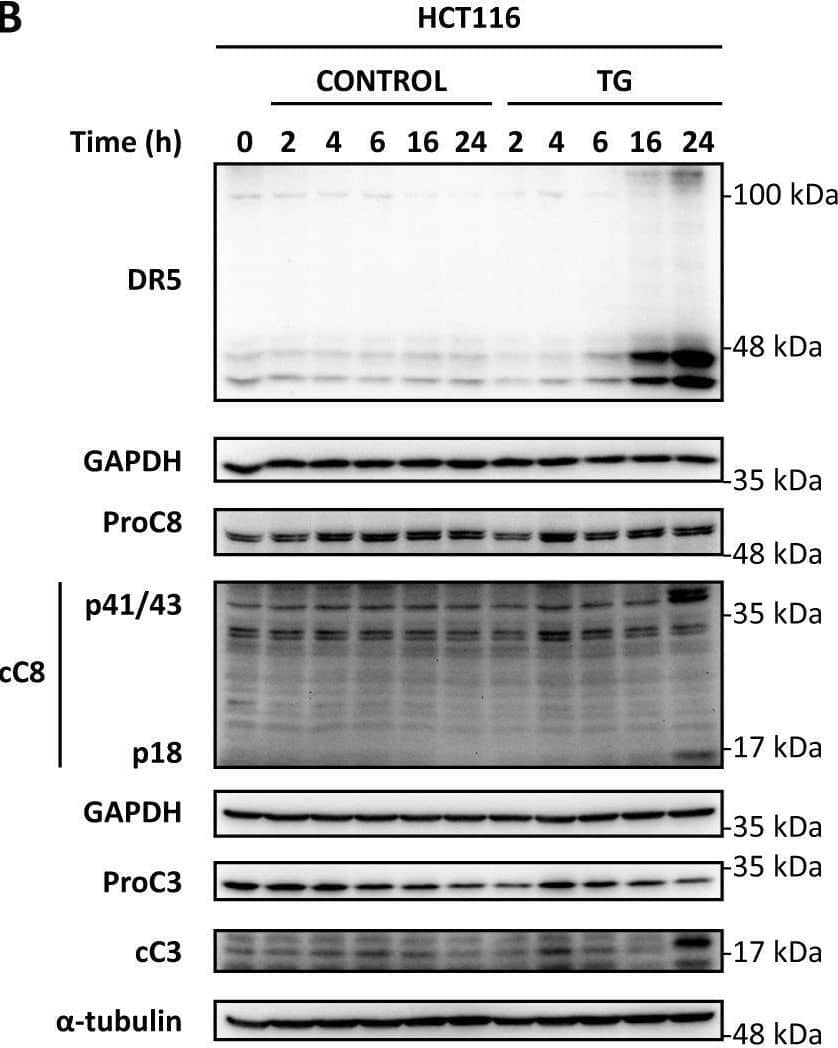
Detection of TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot cFLIP levels and caspase-8 activation upon ER stress in tumor cells.HCT116 cells were treated with TG (100 nM) for the indicated times. cFLIP and CHOP levels (A) as well as TRAIL-R2/DR5 upregulation, caspase-8 and caspase-3 processing (B) were determined in whole-cell extracts by western blotting. Levels of both cFLIP isoforms were quantified with Image LabTM 6.0 software using GAPDH as protein-loading control and graphed relative to time 0 levels. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. In A, two different exposures of the western blot are shown to follow the levels of the short isoform of cFLIP. C HCT116 cells were treated with TG (100 nM) for the indicated times and mRNA relative levels of cFLIPL (upper panel) and cFLIPS (lower panel) were examined by RT-qPCR as described in materials and methods and referred to time 0 h levels (ns = not statistically significant. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35115486), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
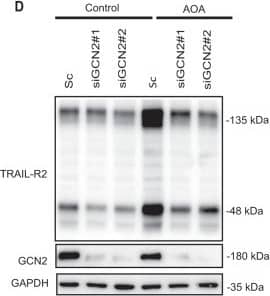
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot GCN2-dependent activation of the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis in tumor cells treated with AOA.A Apoptosis in HCT116 cells cultured for 48 h in complete medium with or without AOA in the presence or absence of non-essential amino acids (NEAA). B, C HCT116 cells were transfected either with a scrambled oligonucleotide (Sc) or with two different siRNAs targeting GCN2 (siGCN2#1 or #2). 48 hours after transfection, cells were either incubated for 16 h in the presence of absence of AOA to assess phosphorylated eIF2 alpha, eIF2 alpha and CHOP levels by Western blotting (B), or during 24 h to measure apoptosis (C). D HCT116 cells were transfected and treated as described in B. TRAIL-R2 and GCN2 levels were assessed by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as protein-loading control. E HCT116 cells stably expressing scrambled, caspase-8, or TRAIL-R2 targeting shRNA, were cultured in the presence or absence of AOA, and apoptosis was measured at 24 or 48 h. Caspase 8 and TRAIL-R2 knockdown were determined by Western blotting. In A, C and E, data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
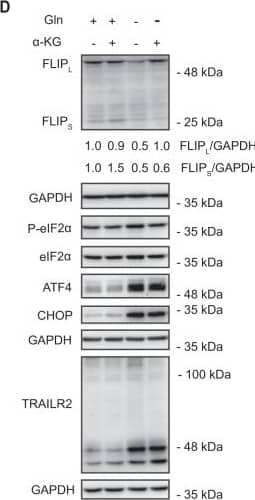
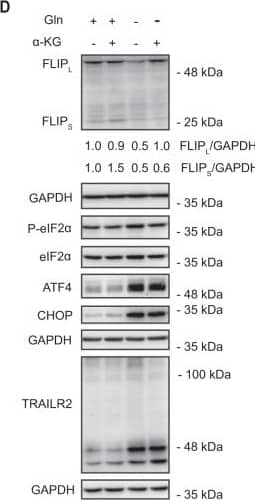
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot Role of FLIP in cell death induced by glutamine deprivation.A HCT116 (left panel) or MDA-MB468 (right panel) cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times. Tubulin and GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Following these treatments, FLIPL and FLIPS levels were assessed by Western blotting. B Apoptosis was assessed in pBabe or FLIPL overexpressing HCT116 cells cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 48 h (left panel). Procaspase-8 levels, caspase-8 activation (cC8) and FLIPL overexpression were determined by Western-blotting after 30 h of glutamine starvation (right panel). C Apoptosis was assessed in pBabe or FLIPL-overexpressing MDA-MB468 cells cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 48 h. FLIPL overexpression was detected by Western blotting. In B and C data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. D HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 16 h, with or without dimethyl alpha -ketoglutarate (5 mM). FLIP levels, ISR activation and TRAIL-R2 upregulation were assessed by Western blotting. In E apoptosis was assessed in HCT116 cells cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 48 hours, with or without dimethyl alpha -ketoglutarate. Data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
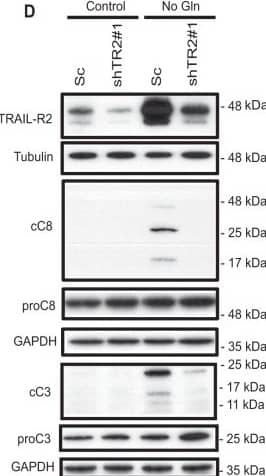
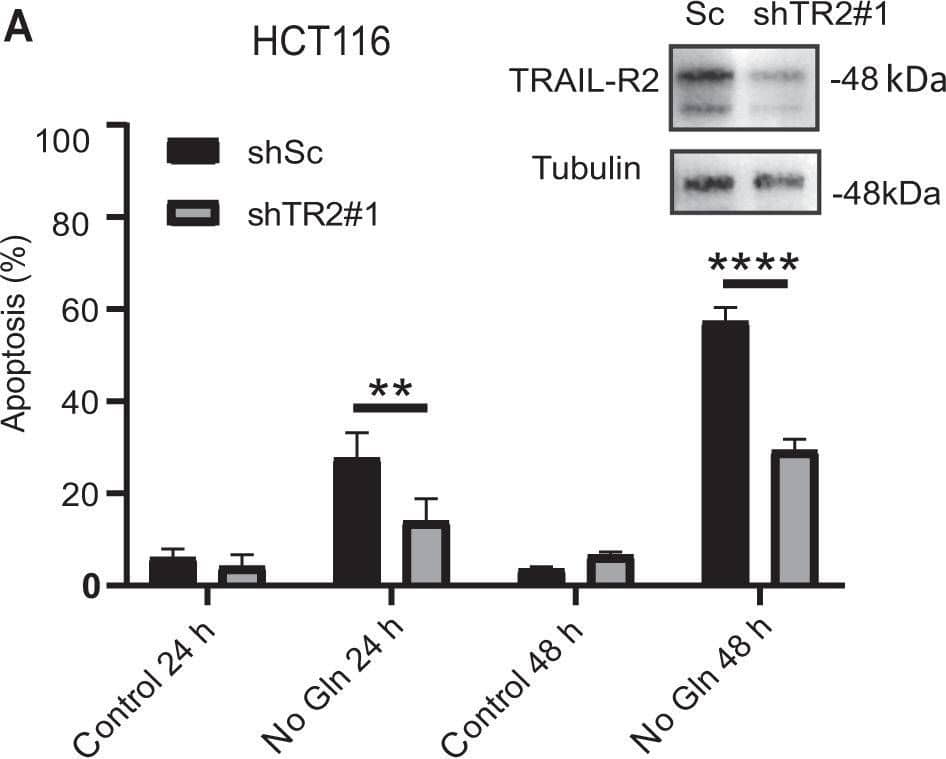
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot Role of TRAIL-R2 in apoptosis induced by glutamine deprivation in tumor cells.A (HCT116) or B (MDA-MB468) cells stably expressing a scrambled (shSc) or a TRAIL-R2 targeting shRNA (shTRAIL-R2#1) were cultured with or without glutamine and apoptosis was assessed at the indicated times (HCT116) or 48 h (MDA-MB468). TRAIL-R2 knockdown was determined by Western blotting. Tubulin and GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. C Procaspase-8 levels and caspase-8 activation (cC8) in HCT116 cells incubated in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times. D Scrambled (Sc) or shTRAIL-R2#1 HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 24 h. Following this incubation, TRAIL-R2 levels, caspase-8 and caspase-3 activation, as well as procaspase-8 or procaspase-3 levels were assessed by Western blotting. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
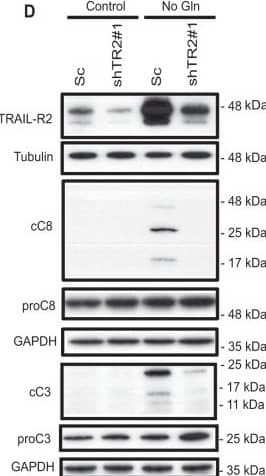
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot Role of TRAIL-R2 in apoptosis induced by glutamine deprivation in tumor cells.A (HCT116) or B (MDA-MB468) cells stably expressing a scrambled (shSc) or a TRAIL-R2 targeting shRNA (shTRAIL-R2#1) were cultured with or without glutamine and apoptosis was assessed at the indicated times (HCT116) or 48 h (MDA-MB468). TRAIL-R2 knockdown was determined by Western blotting. Tubulin and GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. C Procaspase-8 levels and caspase-8 activation (cC8) in HCT116 cells incubated in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times. D Scrambled (Sc) or shTRAIL-R2#1 HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 24 h. Following this incubation, TRAIL-R2 levels, caspase-8 and caspase-3 activation, as well as procaspase-8 or procaspase-3 levels were assessed by Western blotting. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot Role of TRAIL-R2 in apoptosis induced by glutamine deprivation in tumor cells.A (HCT116) or B (MDA-MB468) cells stably expressing a scrambled (shSc) or a TRAIL-R2 targeting shRNA (shTRAIL-R2#1) were cultured with or without glutamine and apoptosis was assessed at the indicated times (HCT116) or 48 h (MDA-MB468). TRAIL-R2 knockdown was determined by Western blotting. Tubulin and GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. C Procaspase-8 levels and caspase-8 activation (cC8) in HCT116 cells incubated in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times. D Scrambled (Sc) or shTRAIL-R2#1 HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 24 h. Following this incubation, TRAIL-R2 levels, caspase-8 and caspase-3 activation, as well as procaspase-8 or procaspase-3 levels were assessed by Western blotting. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
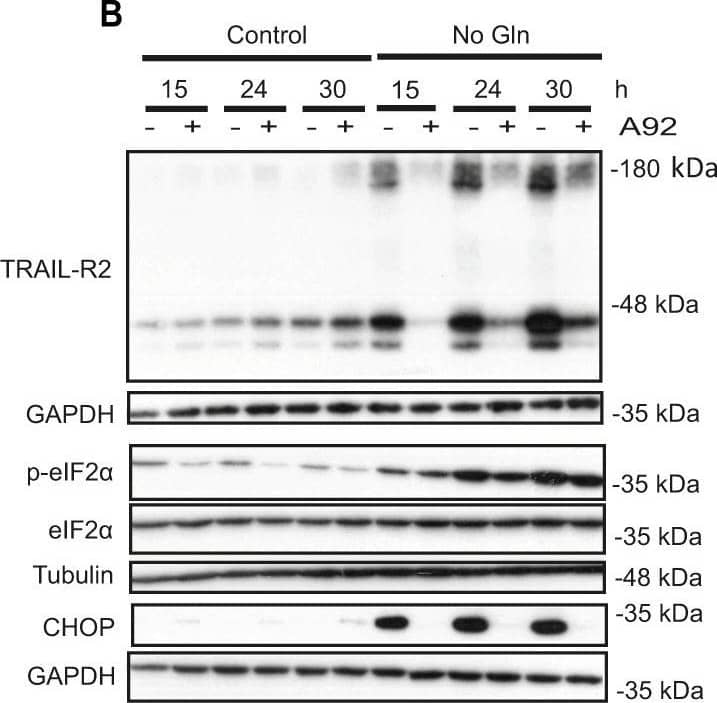
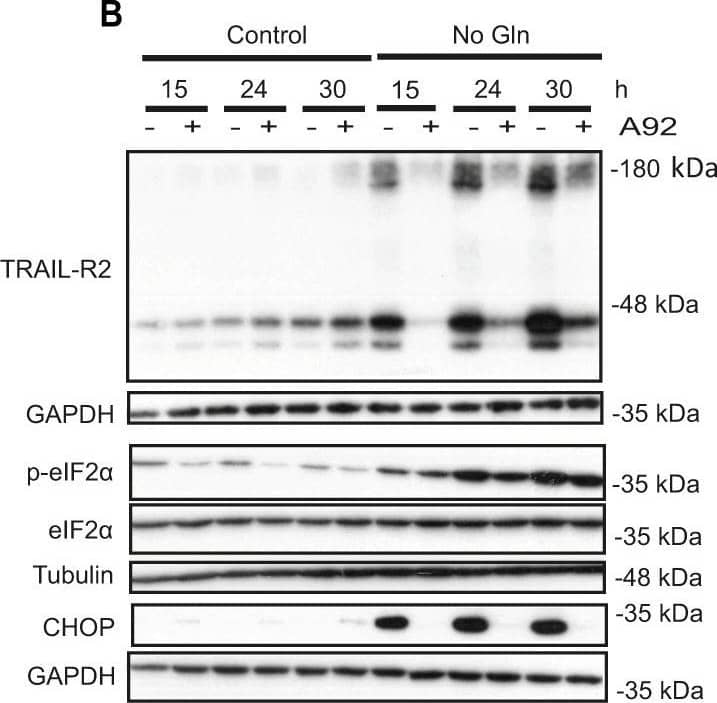
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot GCN2-dependent TRAIL-R2 upregulation upon glutamine deprivation in tumor cells.A HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times and TRAIL-R2 mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR (left panel). TRAIL-R2 and TRAIL-R1 protein levels were assessed by Western blotting (middle panel). GAPDH was used as protein-loading control. Cell surface TRAIL-R2 levels (right panel) were also analyzed in HCT116 and MDA-MB468 cell lines after 24 h of glutamine deprivation in the presence of 20 µM Q-VD-OPh, as described in Materials and Methods (MFI: geometric mean fluorescent intensity). B HCT116 cells were incubated for the indicated times in medium with or without glutamine, in the presence or absence of 1 µM A92. Western blotting was performed to determine TRAIL-R2, p-eIF2 alpha, eIF2 alpha and CHOP levels. C HCT116 cells stably expressing either a scrambled (Sc) or a GCN2 targeting sequence (shGCN2), were incubated for 17 h in the presence or absence of glutamine. Following this incubation, TRAIL-R2 mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR (left panel) and GCN2, CHOP and TRAIL-R2 protein levels were assessed by Western blotting (right panel). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot GCN2-dependent TRAIL-R2 upregulation upon glutamine deprivation in tumor cells.A HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times and TRAIL-R2 mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR (left panel). TRAIL-R2 and TRAIL-R1 protein levels were assessed by Western blotting (middle panel). GAPDH was used as protein-loading control. Cell surface TRAIL-R2 levels (right panel) were also analyzed in HCT116 and MDA-MB468 cell lines after 24 h of glutamine deprivation in the presence of 20 µM Q-VD-OPh, as described in Materials and Methods (MFI: geometric mean fluorescent intensity). B HCT116 cells were incubated for the indicated times in medium with or without glutamine, in the presence or absence of 1 µM A92. Western blotting was performed to determine TRAIL-R2, p-eIF2 alpha, eIF2 alpha and CHOP levels. C HCT116 cells stably expressing either a scrambled (Sc) or a GCN2 targeting sequence (shGCN2), were incubated for 17 h in the presence or absence of glutamine. Following this incubation, TRAIL-R2 mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR (left panel) and GCN2, CHOP and TRAIL-R2 protein levels were assessed by Western blotting (right panel). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot Role of FLIP in cell death induced by glutamine deprivation.A HCT116 (left panel) or MDA-MB468 (right panel) cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times. Tubulin and GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Following these treatments, FLIPL and FLIPS levels were assessed by Western blotting. B Apoptosis was assessed in pBabe or FLIPL overexpressing HCT116 cells cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 48 h (left panel). Procaspase-8 levels, caspase-8 activation (cC8) and FLIPL overexpression were determined by Western-blotting after 30 h of glutamine starvation (right panel). C Apoptosis was assessed in pBabe or FLIPL-overexpressing MDA-MB468 cells cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 48 h. FLIPL overexpression was detected by Western blotting. In B and C data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. D HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 16 h, with or without dimethyl alpha -ketoglutarate (5 mM). FLIP levels, ISR activation and TRAIL-R2 upregulation were assessed by Western blotting. In E apoptosis was assessed in HCT116 cells cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 48 hours, with or without dimethyl alpha -ketoglutarate. Data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
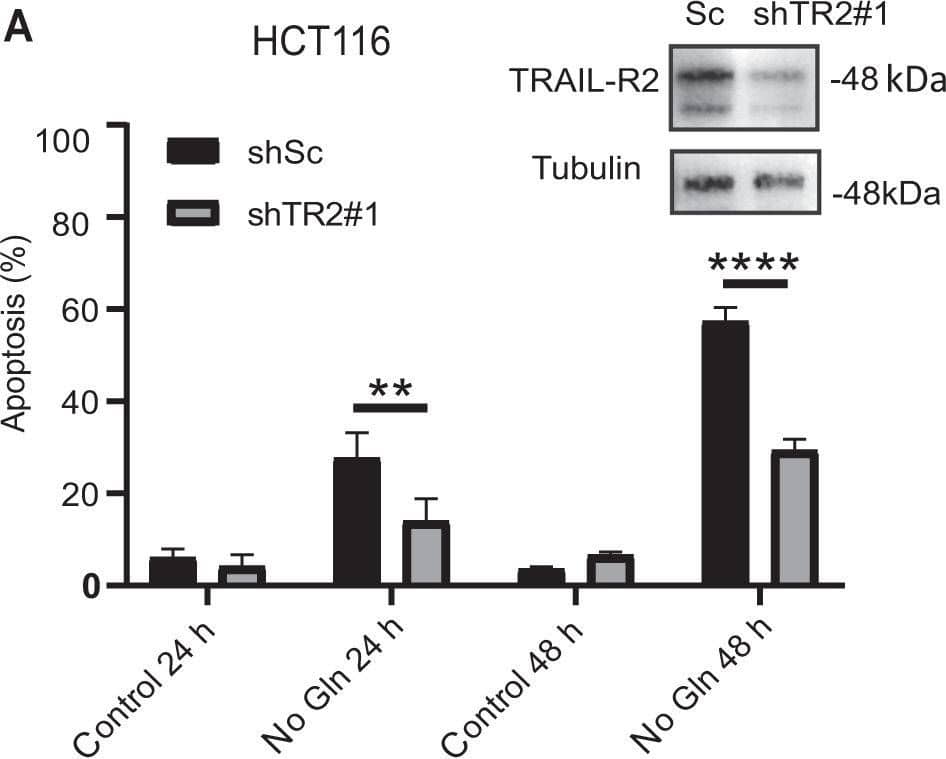 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot Role of TRAIL-R2 in apoptosis induced by glutamine deprivation in tumor cells.A (HCT116) or B (MDA-MB468) cells stably expressing a scrambled (shSc) or a TRAIL-R2 targeting shRNA (shTRAIL-R2#1) were cultured with or without glutamine and apoptosis was assessed at the indicated times (HCT116) or 48 h (MDA-MB468). TRAIL-R2 knockdown was determined by Western blotting. Tubulin and GAPDH were used as protein-loading controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. C Procaspase-8 levels and caspase-8 activation (cC8) in HCT116 cells incubated in the presence or absence of glutamine for the indicated times. D Scrambled (Sc) or shTRAIL-R2#1 HCT116 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of glutamine for 24 h. Following this incubation, TRAIL-R2 levels, caspase-8 and caspase-3 activation, as well as procaspase-8 or procaspase-3 levels were assessed by Western blotting. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
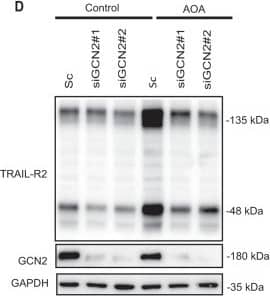 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B by Western Blot GCN2-dependent activation of the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis in tumor cells treated with AOA.A Apoptosis in HCT116 cells cultured for 48 h in complete medium with or without AOA in the presence or absence of non-essential amino acids (NEAA). B, C HCT116 cells were transfected either with a scrambled oligonucleotide (Sc) or with two different siRNAs targeting GCN2 (siGCN2#1 or #2). 48 hours after transfection, cells were either incubated for 16 h in the presence of absence of AOA to assess phosphorylated eIF2 alpha, eIF2 alpha and CHOP levels by Western blotting (B), or during 24 h to measure apoptosis (C). D HCT116 cells were transfected and treated as described in B. TRAIL-R2 and GCN2 levels were assessed by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as protein-loading control. E HCT116 cells stably expressing scrambled, caspase-8, or TRAIL-R2 targeting shRNA, were cultured in the presence or absence of AOA, and apoptosis was measured at 24 or 48 h. Caspase 8 and TRAIL-R2 knockdown were determined by Western blotting. In A, C and E, data are presented as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA test. Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36302756), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B
Human TRAIL R2, also called DR5 and TRICK 2 is a type 1, TNF R family, membrane protein which is a receptor for TRAIL (APO2 ligand). In the new TNF superfamily nomenclature, TRAIL R2 is referred to as TNFRSF10B. TRAIL R2 cDNA encodes a 440 amino acid residue precursor protein containing extracellular cysteine-rich domains, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic death domain. Among TNF receptor family proteins, TRAIL R2 is most closely related to TRAIL R1/DR4, sharing 55% amino acid sequence identity. Binding of trimeric TRAIL to TRAIL R2 induces apoptosis. The induction of apoptosis likely requires oligomerization of the receptor. The human TRAIL R2/Fc chimera neutralizes the ability of TRAIL to induce apoptosis. Besides TRAIL R2, an additional TRAIL R1/DR4, which tranduces apoptosis signaling, and two TRAIL decoy receptors, which antagonize TRAIL-induced apoptosis, have been reported.
- Chaudhary, P.M. et al. (1997) Immunity 7:821.
- Walczak, H. et al. (1997) EMBO J. 16:5386.
- Golstein, P. (1997) Curr. Biol. 7:R750.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
32
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Soluble Fas ligand drives autoantibody-induced arthritis by binding to DR5/TRAIL-R2
Authors: Dongjin Jeong, Hye Sung Kim, Hye Young Kim, Min Jueng Kang, Hyeryeon Jung, Yumi Oh et al.
eLife
-
Off-Target Lapatinib Activity Sensitizes Colon Cancer Cells Through TRAIL Death Receptor Up-Regulation
Authors: Nathan G. Dolloff, Patrick A. Mayes, Lori S. Hart, David T. Dicker, Robin Humphreys, Wafik S. El-Deiry
Science Translational Medicine
-
Limiting glutamine utilization activates a GCN2/TRAIL-R2/Caspase-8 apoptotic pathway in glutamine-addicted tumor cells
Authors: R Yerbes, R Mora-Molin, FJ Fernández-, L Hiraldo, A López-Riva, C Palacios
Cell Death & Disease, 2022-10-27;13(10):906.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
cFLIP downregulation is an early event required for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in tumor cells
Authors: R Mora-Molin, D Stöhr, M Rehm, A López-Riva
Cell Death & Disease, 2022-02-03;13(2):111.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Western Blot -
Cytotoxic Efficacy and Resistance Mechanism of a TRAIL and VEGFA-Peptide Fusion Protein in Colorectal Cancer Models
Authors: M Kopczynski, M Statkiewic, M Cybulska, U Kuklinska, K Unrug-Biel, Z Sandowska-, A Grochowska, M Gajewska, M Kulecka, J Ostrowski, M Mikula
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021-03-19;22(6):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Death agonist antibody against TRAILR2/DR5/TNFRSF10B enhances birinapant anti-tumor activity in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
Authors: Y An, J Jeon, L Sun, A Derakhshan, J Chen, S Carlson, H Cheng, C Silvin, X Yang, C Van Waes, Z Chen
Scientific Reports, 2021-03-18;11(1):6392.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Dual role of DR5 in death and survival signaling leads to TRAIL resistance in cancer cells
Authors: Y Shlyakhtin, V Pavet, H Gronemeyer
Cell Death Dis, 2017-08-31;8(8):e3025.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Immunoprecipitation -
Anticancer efficacy of the hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide is enhanced in combination with proapoptotic receptor agonists against osteosarcoma
Authors: V Liapis, A Zysk, M DeNichilo, I Zinonos, S Hay, V Panagopoul, A Shoubridge, C Difelice, V Ponomarev, W Ingman, GJ Atkins, DM Findlay, ACW Zannettino, A Evdokiou
Cancer Med, 2017-08-10;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Potential application of temozolomide in mesenchymal stem cell-based TRAIL gene therapy against malignant glioma.
Authors: Kim, Seong Mu, Woo, Ji Sun, Jeong, Chang Hy, Ryu, Chung He, Jang, Jae-Deog, Jeun, Sin-Soo
Stem Cells Transl Med, 2014-01-16;3(2):172-82.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Down-regulation of FoxO-dependent c-FLIP expression mediates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in activated hepatic stellate cells.
Authors: Park SJ, Sohn HY, Yoon J, Park SI
Cell. Signal., 2009-05-24;21(10):1495-503.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Sensitization of imatinib-resistant CML cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis is mediated through down-regulation of Bcr-Abl as well as c-FLIP.
Authors: Park SJ, Kim MJ, Kim HB, Kang CD, Kim SH
Biochem. J., 2009-04-28;420(1):73-81.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Neutralization -
Trichostatin A sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by down-regulation of c-FLIPL via inhibition of EGFR pathway.
Authors: Park SJ, Kim MJ, Kim HB, Sohn HY, Bae JH, Kang CD, Kim SH
Biochem. Pharmacol., 2009-01-24;77(8):1328-36.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Downmodulation of dimethyl transferase activity enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells.
Authors: Festuccia C, Gravina GL, D'Alessandro AM, Millimaggi D, Di Rocco C, Dolo V, Ricevuto E, Vicentini C, Bologna M
Int. J. Oncol., 2008-08-01;33(2):381-8.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
TRAIL recombinant adenovirus triggers robust apoptosis in multidrug-resistant HL-60/Vinc cells preferentially through death receptor DR5.
Authors: Wu CH, Kao CH, Safa AR
Hum. Gene Ther., 2008-07-01;19(7):731-43.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Arsenic trioxide sensitizes human glioma cells, but not normal astrocytes, to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein-dependent DR5 up-regulation.
Authors: Kim EH, Yoon MJ, Kim SU, Kwon TK, Sohn S, Choi KS
Cancer Res., 2008-01-01;68(1):266-75.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Differential response of p53 and p21 on HDAC inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
Authors: Zopf S, Neureiter D, Bouralexis S, Abt T, Glaser KB, Okamoto K, Ganslmayer M, Hahn EG, Herold C, Ocker M
Int. J. Oncol., 2007-12-01;31(6):1391-402.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Cells
Applications: Functional Assay, Western Blot -
P-glycoprotein enhances TRAIL-triggered apoptosis in multidrug resistant cancer cells by interacting with the death receptor DR5.
Authors: Park SJ, Wu CH, Choi MR, Najafi F, Emami A, Safa AR
Biochem. Pharmacol., 2006-05-04;72(3):293-307.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Acquired resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells is conferred by increased turnover of mature caspase-3.
Authors: Lane D, Cote M, Grondin R, Couture MC, Piche A
Mol. Cancer Ther., 2006-03-01;5(3):509-21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Western Blot -
Death receptors, Fas and TRAIL receptors, are involved in human osteoclast apoptosis.
Authors: Roux S, Lambert-Comeau P, Saint-Pierre C, Lepine M, Sawan B, Parent JL
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2005-07-22;333(1):42-50.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation through mitogen-activated protein kinases and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt.
Authors: Morel J, Audo R, Hahne M, Combe B
J. Biol. Chem., 2005-01-31;280(16):15709-18.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Absence of caspase 8 and high expression of PED protect primitive neural cells from cell death.
Authors: Ricci-Vitiani L, Pedini F, Mollinari C, Condorelli G, Bonci D, Bez A, Colombo A, Parati E, Peschle C, De Maria R
J. Exp. Med., 2004-11-15;200(10):1257-66.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Synergistic induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells by cotreatment with butyrate and TNF-alpha, TRAIL, or anti-Fas agonist antibody involves enhancement of death receptors' signaling and requires P21(waf1).
Authors: Chopin V, Slomianny C, Hondermarck H, Le Bourhis X
Exp. Cell Res., 2004-08-15;298(2):560-73.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) decoy receptor TRAIL-R3 is up-regulated by p53 in breast tumor cells through a mechanism involving an intronic p53-binding site.
Authors: Ruiz de Almodovar C, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Rodriguez A, Ortiz-Ferron G, Redondo JM, Lopez-Rivas A
J. Biol. Chem., 2003-11-17;279(6):4093-101.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TNF-alpha promote the NF-kappaB-dependent maturation of normal and leukemic myeloid cells.
Authors: Secchiero P, Milani D, Gonelli A, Melloni E, Campioni D, Gibellini D, Capitani S, Zauli G
J. Leukoc. Biol., 2003-08-01;74(2):223-32.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Regulation of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines.
Authors: Mouzakiti A, Packham G
Br. J. Haematol., 2003-07-01;122(1):61-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
An antibody against DR4 (TRAIL-R1) in combination with doxorubicin selectively kills malignant but not normal prostate cells.
Authors: Voelkel-Johnson C
Cancer Biol. Ther., 2003-05-01;2(3):283-90.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization -
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) sequentially upregulates nitric oxide and prostanoid production in primary human endothelial cells.
Authors: Zauli G, Pandolfi A, Gonelli A, Di Pietro R, Guarnieri S, Ciabattoni G, Rana R, Vitale M, Secchiero P
Circ. Res., 2003-03-20;92(7):732-40.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Interferon-alpha sensitizes human hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DR5 upregulation and NF-kappa B inactivation.
Authors: Shigeno M, Nakao K, Ichikawa T, Suzuki K, Kawakami A, Abiru S, Miyazoe S, Nakagawa Y, Ishikawa H, Hamasaki K, Nakata K, Ishii N, Eguchi K
Oncogene, 2003-03-20;22(11):1653-62.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Activation of NF-kappaB and upregulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins via the IGF-1/Akt signaling in human multiple myeloma cells: therapeutic implications.
Authors: Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Schlossman R, Akiyama M, Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Treon SP, Munshi NC, Richardson PG, Anderson KC
Oncogene, 2002-08-22;21(37):5673-83.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Inflammatory cytokine regulation of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in thyroid epithelial cells.
Authors: Bretz JD, Mezosi E, Giordano TJ, Gauger PG, Thompson NW, Baker JR
Cell Death Differ., 2002-03-01;9(3):274-86.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry, Functional Assay, Western Blot -
Plasminogen activator urokinase expression reveals TRAIL responsiveness and supports fractional survival of cancer cells
Authors: V Pavet, Y Shlyakhtina, T He, D G Ceschin, P Kohonen, M Perälä et al.
Cell Death & Disease
-
Combination treatment with VPA and MSCs‑TRAIL could increase anti‑tumor effects against intracranial glioma
Authors: Soon A. Park, Hye Rim Han, Stephen Ahn, Chung Heon Ryu, Sin‑Soo Jeun
Oncology Reports
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human TRAIL R2/TNFRSF10B Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image


