Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
R&D Systems | Catalog # AF1447


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Val235-Gly345
Accession # Q8CI19
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
PDGF‑C in Mouse Kidney.
PDGF‑C was detected in perfusion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of mouse kidney using Goat Anti-Mouse PDGF‑C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1447) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm and plasma membrane in convoluted tubules. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.
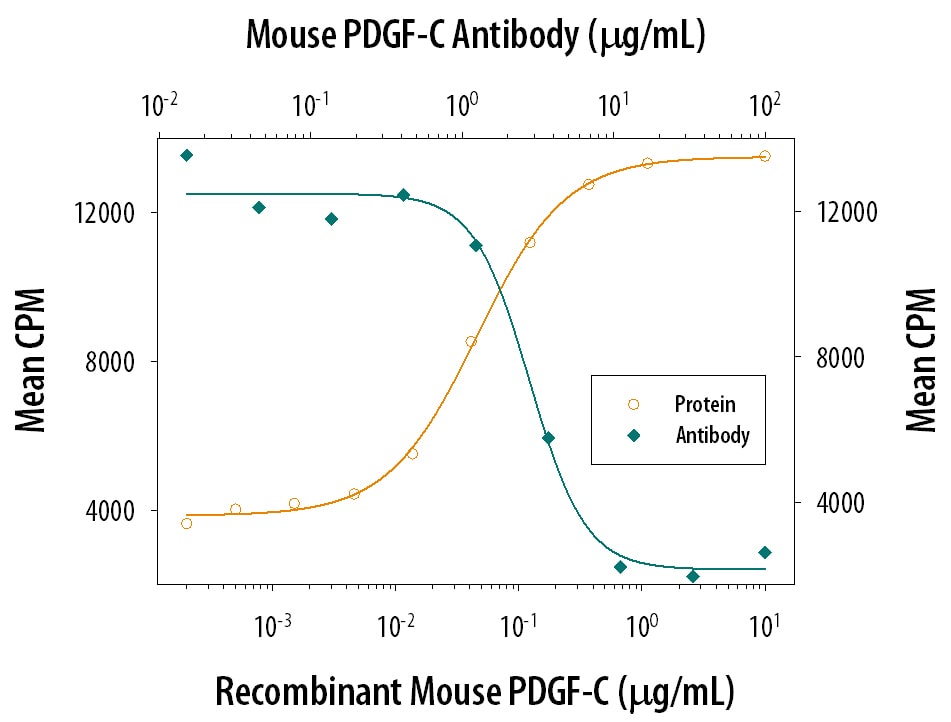
Cell Proliferation Induced by PDGF‑CC and Neutralization by Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody.
Recombinant Mouse PDGF‑CC stimulates proliferation in the NR6R‑3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by 0.8 µg/mL Recombinant Mouse PDGF‑CC is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Mouse PDGF-C Antigen Affinity-purified Poly-clonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1447). The ND50 is typically 4‑16 µg/mL.Detection of Mouse PDGF-C by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
FREM1 regulates activation of AKT and MAPK upon PDGFC stimulation. (A) Representative western blotting of phosphorylation of AKT and MAPK ERK1/2 in MEFs from WT and bat mouse embryos stimulated with PDGFCC for the indicated time periods. (B) Relative quantification of AKT phosphorylation levels. WT cells 10 minutes after stimulation were assigned a value of 1 and all other samples are standardised against this value. Graph represents average of up to nine WT and 16 bat samples, performed across four independent experiments from at least three different cell lines for each genotype. Black bars: WT; white bars, bat mutant. (C) FREM1 mutation in bat mutants reduces phosphorylation of PDGFR alpha in response to the addition of exogenous PDGFCC. IP, immunoprecipitation antibody; WB, western blotting antibody. (D) E13.5 WT embryo head skin sections stained for PDGFC (green), PDGFR alpha (red) and nuclear dye DAPI (blue). Error bars represent standard error of the mean (s.e.m.); *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24046351), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse PDGF-C by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
FREM1 regulates activation of AKT and MAPK upon PDGFC stimulation. (A) Representative western blotting of phosphorylation of AKT and MAPK ERK1/2 in MEFs from WT and bat mouse embryos stimulated with PDGFCC for the indicated time periods. (B) Relative quantification of AKT phosphorylation levels. WT cells 10 minutes after stimulation were assigned a value of 1 and all other samples are standardised against this value. Graph represents average of up to nine WT and 16 bat samples, performed across four independent experiments from at least three different cell lines for each genotype. Black bars: WT; white bars, bat mutant. (C) FREM1 mutation in bat mutants reduces phosphorylation of PDGFR alpha in response to the addition of exogenous PDGFCC. IP, immunoprecipitation antibody; WB, western blotting antibody. (D) E13.5 WT embryo head skin sections stained for PDGFC (green), PDGFR alpha (red) and nuclear dye DAPI (blue). Error bars represent standard error of the mean (s.e.m.); *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24046351), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Perfusion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of mouse kidney
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse PDGF-C
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Reconstitute at 0.2 mg/mL in sterile PBS. For liquid material, refer to CoA for concentration.
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Calculators
Background: PDGF-C
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional PDGF-C Products
Product Documents for Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
Certificate of Analysis
To download a Certificate of Analysis, please enter a lot or batch number in the search box below.
Note: Certificate of Analysis not available for kit components.
Product Specific Notices for Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
For research use only
Related Research Areas
Citations for Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
Customer Reviews for Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Mouse PDGF‑C Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card!
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10CAN/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Submit a review
Protocols
Find general support by application which include: protocols, troubleshooting, illustrated assays, videos and webinars.
- Antigen Retrieval Protocol (PIER)
- Antigen Retrieval for Frozen Sections Protocol
- Appropriate Fixation of IHC/ICC Samples
- Cellular Response to Hypoxia Protocols
- Chromogenic IHC Staining of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Protocol
- Chromogenic Immunohistochemistry Staining of Frozen Tissue
- ClariTSA™ Fluorophore Kits
- Detection & Visualization of Antibody Binding
- Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Protocol
- Graphic Protocol for Heat-induced Epitope Retrieval
- Graphic Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections
- Graphic Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections
- Graphic Protocol for the Preparation of Gelatin-coated Slides for Histological Tissue Sections
- IHC Sample Preparation (Frozen sections vs Paraffin)
- Immunofluorescent IHC Staining of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Protocol
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Protocols
- Immunohistochemistry Frozen Troubleshooting
- Immunohistochemistry Paraffin Troubleshooting
- Preparing Samples for IHC/ICC Experiments
- Preventing Non-Specific Staining (Non-Specific Binding)
- Primary Antibody Selection & Optimization
- Protocol for Heat-Induced Epitope Retrieval (HIER)
- Protocol for Making a 4% Formaldehyde Solution in PBS
- Protocol for VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Detection Reagent
- Protocol for the Preparation & Fixation of Cells on Coverslips
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections - Graphic
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation and Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections - Graphic
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation and Fluorescent IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections
- Protocol for the Preparation of Gelatin-coated Slides for Histological Tissue Sections
- R&D Systems Quality Control Western Blot Protocol
- TUNEL and Active Caspase-3 Detection by IHC/ICC Protocol
- The Importance of IHC/ICC Controls
- Troubleshooting Guide: Immunohistochemistry
- Troubleshooting Guide: Western Blot Figures
- Western Blot Conditions
- Western Blot Protocol
- Western Blot Protocol for Cell Lysates
- Western Blot Troubleshooting
- Western Blot Troubleshooting Guide
- View all Protocols, Troubleshooting, Illustrated assays and Webinars