Mouse CCR6 Antibody Summary
Met1-Met367
Accession # O54689
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of CCR6 in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Mouse splenocytes were stained with (A) Rat Anti-Mouse CCR6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB590) or (B) Rat IgG2A control antibody (Catalog # MAB006) followed by Goat anti-Rat IgG APC-conjugated Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0113) and Rat Anti-Mouse B220/CD45R Fluorescein-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1217F). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
CCR6 in Mouse Thymus. CCR6 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse thymus using Mouse CCR6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB590) at 8 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS017) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to the plasma membrane of lymphocytes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
CCR6 in Mouse Spleen. CCR6 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse spleen using Rat Anti-Mouse CCR6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB590) at 0.3 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS017) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membranes in lymphocytes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Mouse CCR6 by Flow Cytometry Priming of pik3cg−/− CD4+ T cells is reduced during EAE.(A) Frequencies of CD4+ cells in draining LN that are CD69+ on day 9 post-immunisation for EAE as determined by flow cytometry. A representative histogram overlay gating on CD4+ cells is shown (filled = isotype control on WT, solid line = anti-CD69 on WT, dotted line = anti-CD69 on pik3cg−/−) (B) In vivo proliferation of CD4+ cells, measured by BrdU incorporation, is reduced in pik3cg−/− mice at day 9 post-immunization for EAE. (n = 6 mice per group). Representative dot plots gating on CD4+ cells are shown. (C) Expression of chemokine receptors by CD4+ T cells indicative of T cell activation was determined by flow cytometry. Representative histogram overlays showing expression of CCR7, CCR6 and CXCR3 are shown (filled = isotype control, solid line = WT, dotted line = pik3cg−/−). (D) Expression of CD62L, CD49d and PSGL-1 by CD4+ cells from spleen of day 9 immunised mice (n = 3 mice per group). All data shown are mean ± s.e.m. (*, p<0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045095), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
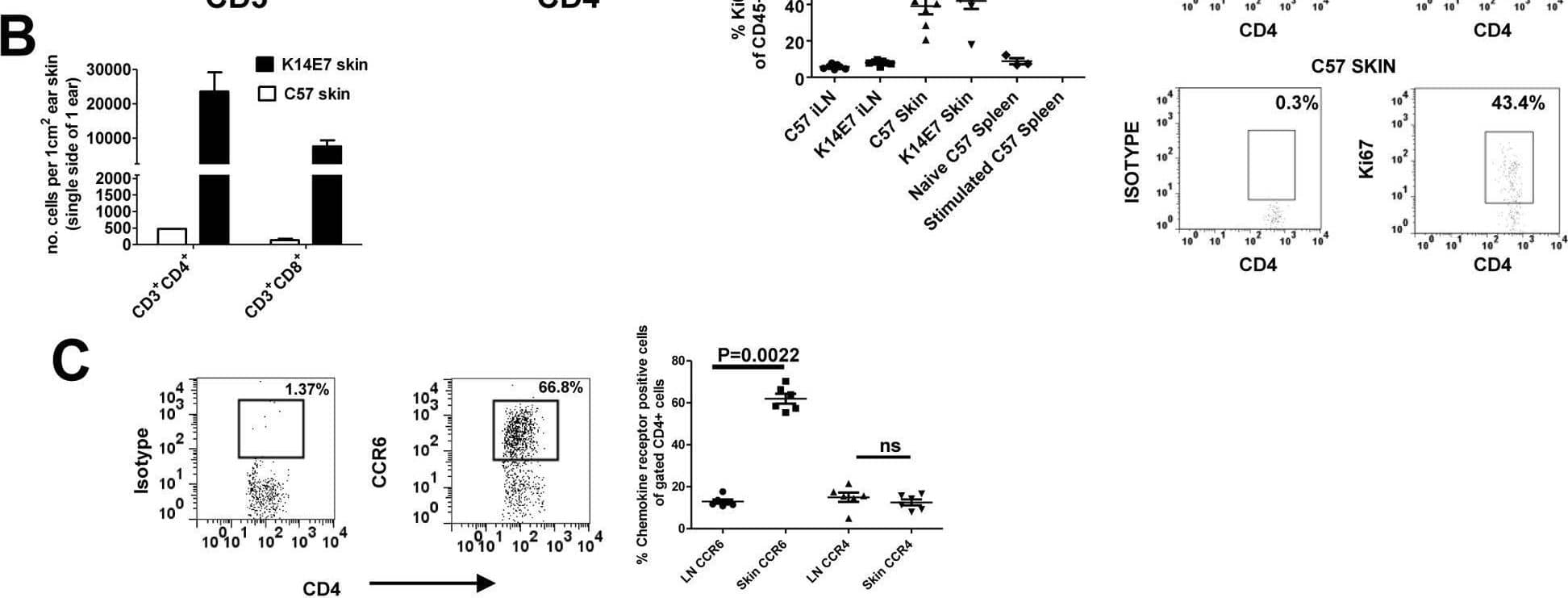
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry Endogenous T cells accumulate in K14E7 skin with an enrichment for CCR6-expressing CD4 T cells.(A) Ear skin tissue was taken from K14E7 mice in addition to control mice expressing the SIY epitope under the K14 promoter. CD4 and CD8 expression was measured on gated CD45+CD3+ cells. Data is representative of at least 4 mice/group (B) The numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in K14E7 skin or control C57 skin were enumerated per square centimetre of ear skin using flow count beads in flow cytometry. Data represents pooled mice from at least two independent experiments. (C) Gated CD3+ CD4+ T cells from the lymph node or skin of K14E7 mice were analysed for expression of the chemokine receptors, CCR6 and CCR4. The left hand panels show representative plots of isotype and CCR6 antibody staining for CD4+ T cells while the graph summarises chemokine receptor staining representative of 6 mice/group from 3 independent experiments. (D) Both K14E7 mice and C57 mice were analysed for the proliferative marker, Ki67, using intracellular staining of lymphocytes derived from the skin and inguinal lymph nodes (iLN). Naive C57 spleen cells (negative control) or C57 spleen cells treated for 3 days with PMA/Ionomycin (positive control) were also analysed. The K14E7 and C57 data represent 7 mice/group derived from 3 independent experiments while controls are spleen cells from a single mouse in 3 independent experiments. The lower right hand panels are representative plots showing isotype and Ki67 staining in K14E7 or C57 mouse skin. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23469070), licensed under a CC0-1.0 license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
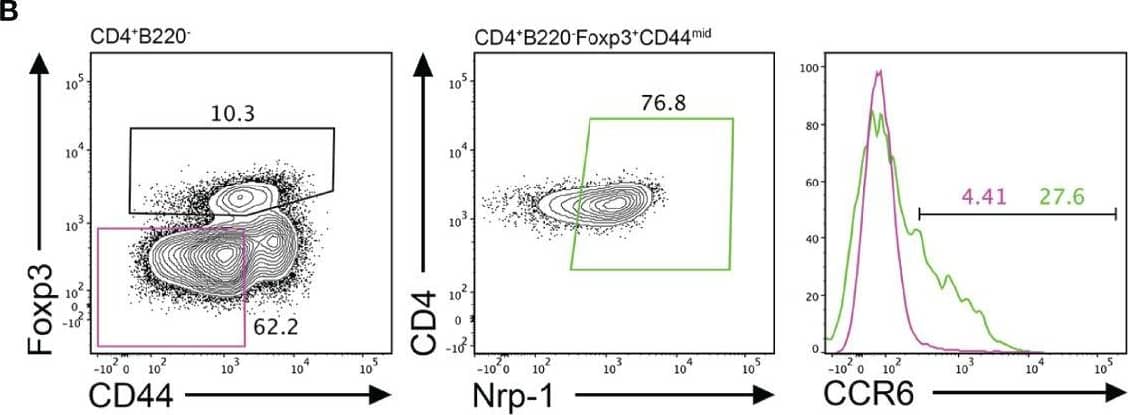
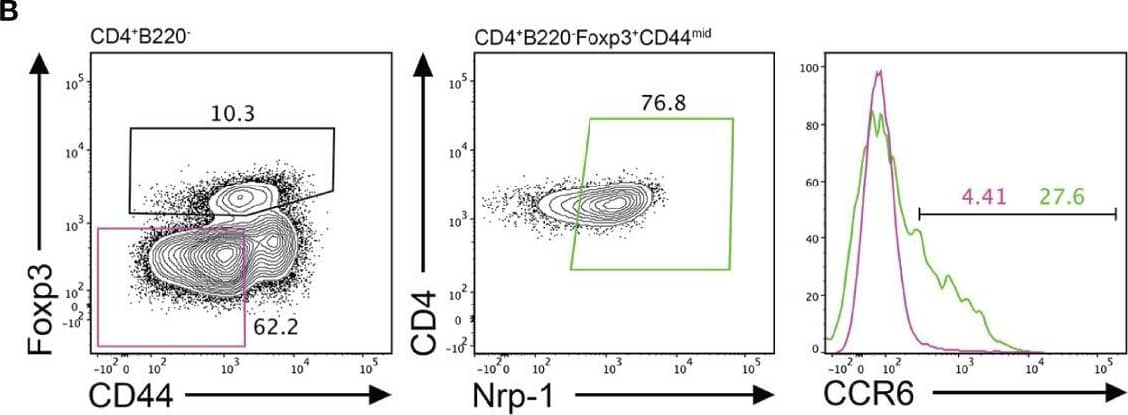
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry CCR6 expression is highest in TFR cells amongst follicular T cell populations. (A, B) Representative gating strategy for CCR6+ TFH cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3-), TFR cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3+), naïve CD4 T cells (CD4+B220-CD44loFoxp3-) and natural T-regulatory cells (nTreg: CD4+B220-CD44midFoxp3+Nrp-1+) 6 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Geometrical mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CCR6 and, (D) percentage of CCR6+ cells within populations from (A) and (B). (E) Representative gating strategy for TFH (Foxp3-) and TFR cells (Foxp3+) within CCR6+ follicular T cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiCCR6+). (F) Ratio of TFH : TFR cells within gating strategies from (A, E). (G) Frequency of CCR6+ TFH and TFR cells at indicated time points after i.p. NP-KLH/Alum immunization. (A–C, E, F) Data representative of two independent experiments, n=4 mice ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (G) n=4-5 mice per time-point ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. NS, Not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35812408), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
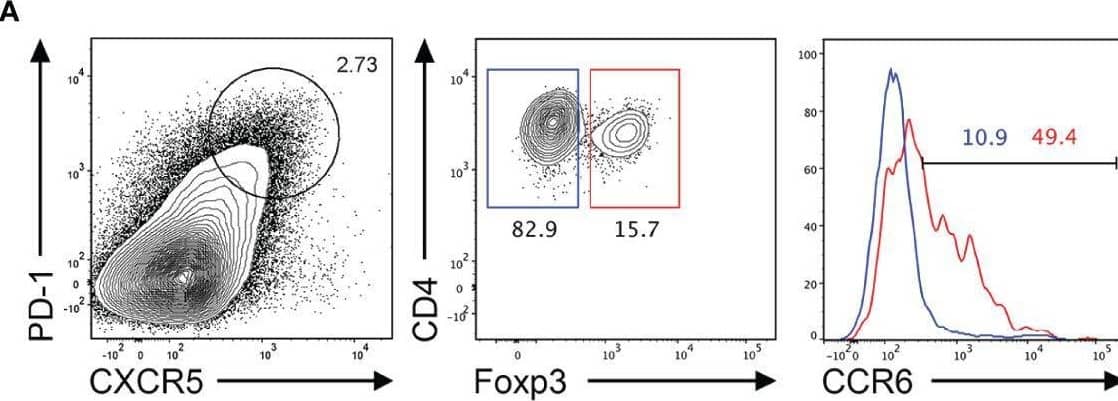
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry CCR6 expression is highest in TFR cells amongst follicular T cell populations. (A, B) Representative gating strategy for CCR6+ TFH cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3-), TFR cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3+), naïve CD4 T cells (CD4+B220-CD44loFoxp3-) and natural T-regulatory cells (nTreg: CD4+B220-CD44midFoxp3+Nrp-1+) 6 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Geometrical mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CCR6 and, (D) percentage of CCR6+ cells within populations from (A) and (B). (E) Representative gating strategy for TFH (Foxp3-) and TFR cells (Foxp3+) within CCR6+ follicular T cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiCCR6+). (F) Ratio of TFH : TFR cells within gating strategies from (A, E). (G) Frequency of CCR6+ TFH and TFR cells at indicated time points after i.p. NP-KLH/Alum immunization. (A–C, E, F) Data representative of two independent experiments, n=4 mice ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (G) n=4-5 mice per time-point ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. NS, Not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35812408), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
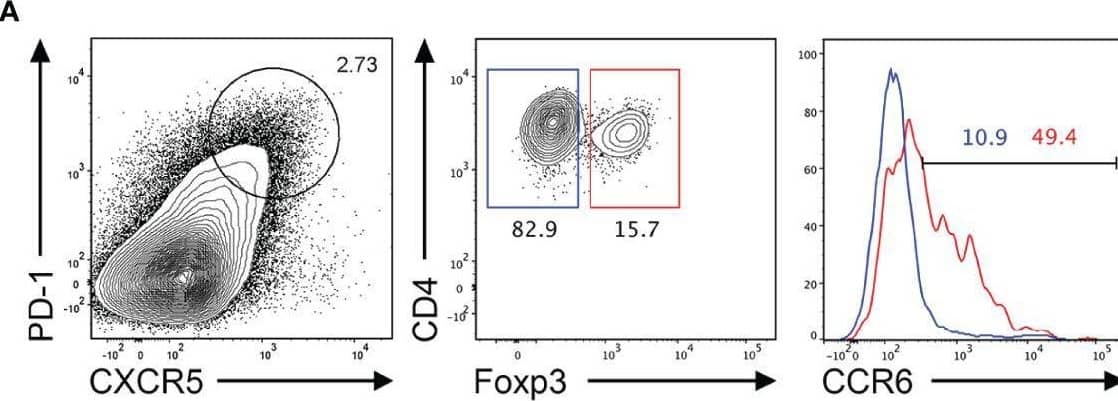 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry CCR6 expression is highest in TFR cells amongst follicular T cell populations. (A, B) Representative gating strategy for CCR6+ TFH cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3-), TFR cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3+), naïve CD4 T cells (CD4+B220-CD44loFoxp3-) and natural T-regulatory cells (nTreg: CD4+B220-CD44midFoxp3+Nrp-1+) 6 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Geometrical mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CCR6 and, (D) percentage of CCR6+ cells within populations from (A) and (B). (E) Representative gating strategy for TFH (Foxp3-) and TFR cells (Foxp3+) within CCR6+ follicular T cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiCCR6+). (F) Ratio of TFH : TFR cells within gating strategies from (A, E). (G) Frequency of CCR6+ TFH and TFR cells at indicated time points after i.p. NP-KLH/Alum immunization. (A–C, E, F) Data representative of two independent experiments, n=4 mice ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (G) n=4-5 mice per time-point ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. NS, Not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35812408), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
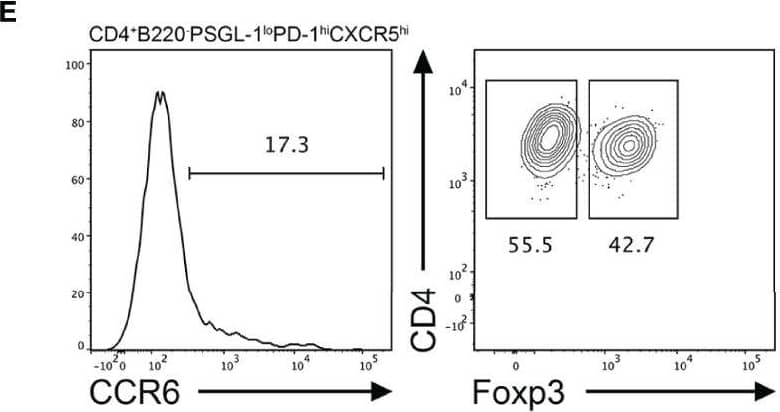 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry CCR6 expression is highest in TFR cells amongst follicular T cell populations. (A, B) Representative gating strategy for CCR6+ TFH cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3-), TFR cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3+), naïve CD4 T cells (CD4+B220-CD44loFoxp3-) and natural T-regulatory cells (nTreg: CD4+B220-CD44midFoxp3+Nrp-1+) 6 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Geometrical mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CCR6 and, (D) percentage of CCR6+ cells within populations from (A) and (B). (E) Representative gating strategy for TFH (Foxp3-) and TFR cells (Foxp3+) within CCR6+ follicular T cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiCCR6+). (F) Ratio of TFH : TFR cells within gating strategies from (A, E). (G) Frequency of CCR6+ TFH and TFR cells at indicated time points after i.p. NP-KLH/Alum immunization. (A–C, E, F) Data representative of two independent experiments, n=4 mice ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (G) n=4-5 mice per time-point ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. NS, Not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35812408), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
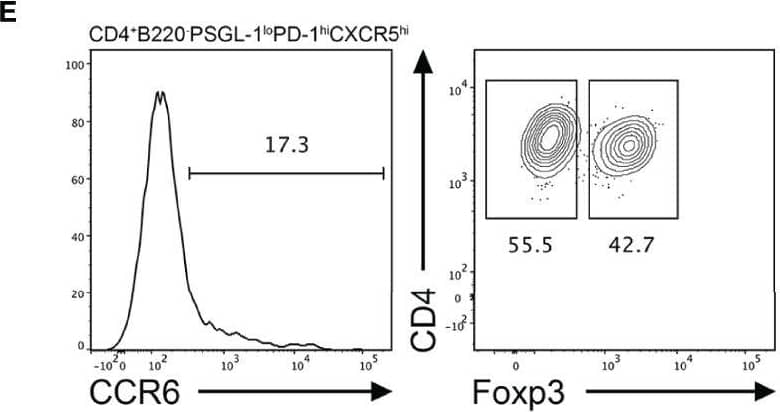 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry CCR6 expression is highest in TFR cells amongst follicular T cell populations. (A, B) Representative gating strategy for CCR6+ TFH cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3-), TFR cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3+), naïve CD4 T cells (CD4+B220-CD44loFoxp3-) and natural T-regulatory cells (nTreg: CD4+B220-CD44midFoxp3+Nrp-1+) 6 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Geometrical mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CCR6 and, (D) percentage of CCR6+ cells within populations from (A) and (B). (E) Representative gating strategy for TFH (Foxp3-) and TFR cells (Foxp3+) within CCR6+ follicular T cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiCCR6+). (F) Ratio of TFH : TFR cells within gating strategies from (A, E). (G) Frequency of CCR6+ TFH and TFR cells at indicated time points after i.p. NP-KLH/Alum immunization. (A–C, E, F) Data representative of two independent experiments, n=4 mice ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (G) n=4-5 mice per time-point ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. NS, Not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35812408), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of CCR6 by Flow Cytometry CCR6 expression is highest in TFR cells amongst follicular T cell populations. (A, B) Representative gating strategy for CCR6+ TFH cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3-), TFR cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiFoxp3+), naïve CD4 T cells (CD4+B220-CD44loFoxp3-) and natural T-regulatory cells (nTreg: CD4+B220-CD44midFoxp3+Nrp-1+) 6 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Geometrical mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CCR6 and, (D) percentage of CCR6+ cells within populations from (A) and (B). (E) Representative gating strategy for TFH (Foxp3-) and TFR cells (Foxp3+) within CCR6+ follicular T cells (CD4+B220-CXCR5hiPD-1hiCCR6+). (F) Ratio of TFH : TFR cells within gating strategies from (A, E). (G) Frequency of CCR6+ TFH and TFR cells at indicated time points after i.p. NP-KLH/Alum immunization. (A–C, E, F) Data representative of two independent experiments, n=4 mice ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, (G) n=4-5 mice per time-point ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. NS, Not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35812408), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CCR6
CCR6 is a seven transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptor that binds the chemokine MIP-3 alpha and mediates the chemoattraction of B and T lymphocytes.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Mouse CCR6 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
13
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Sciatic–Vagal Nerve Stimulation by Electroacupuncture Alleviates Inflammatory Arthritis in Lyme Disease-Susceptible C3H Mice
Authors: Lavoisier Akoolo, Vitomir Djokic, Sandra C. Rocha, Luis Ulloa, Nikhat Parveen
Frontiers in Immunology
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
IL-1? and IL-23 Promote Extrathymic Commitment of CD27(+)CD122(-) ?? T Cells to ??T17 Cells
Authors: A Muschaweck, F Petermann, T Korn
J. Immunol., 2017-08-30;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
IL-10+ Innate-like B Cells Are Part of the Skin Immune System and Require ?4?1 Integrin To Migrate between the Peritoneum and Inflamed Skin
Authors: SA Geherin, D Gómez, RA Glabman, G Ruthel, A Hamann, GF Debes
J. Immunol, 2016-02-05;196(6):2514-25.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
The chemokine receptor CCR6 facilitates the onset of mammary neoplasia in the MMTV-PyMT mouse model via recruitment of tumor-promoting macrophages.
Authors: Boyle S, Faulkner J, McColl S, Kochetkova M
Mol Cancer, 2015-06-06;14(0):115.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: ELISA Development (Capture) -
CCR6 is a prognostic marker for overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer, and its overexpression enhances metastasis in vivo.
Authors: Liu, Jinlin, Ke, Fang, Xu, Zhenyao, Liu, Zhaoyuan, Zhang, Lingyun, Yan, Sha, Wang, Zhe, Wang, Hong, Wang, Honglin
PLoS ONE, 2014-06-30;9(6):e101137.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: In Vivo
Applications: Neutralization -
SerpinB1 regulates homeostatic expansion of IL-17+ gammadelta and CD4+ Th17 cells.
Authors: Zhao P, Hou L, Farley K, Sundrud M, Remold-O'Donnell E
J Leukoc Biol, 2013-11-18;95(3):521-30.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
A role for the chemokine receptor CCR6 in mammalian sperm motility and chemotaxis
Authors: Pedro Caballero-Campo, Mariano G. Buffone, Fabian Benencia, José R. Conejo-García, Paolo F. Rinaudo, George L. Gerton
Journal of Cellular Physiology
-
Programmed downregulation of CCR6 is important for establishment of epidermal gammadeltaT cells by regulating their thymic egress and epidermal location.
Authors: Hu S, Xiong N
J Immunol, 2013-02-18;190(7):3267-75.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Colonic patch and colonic SILT development are independent and differentially regulated events.
Authors: Baptista A, Olivier B, Goverse G, Greuter M, Knippenberg M, Kusser K, Domingues R, Veiga-Fernandes H, Luster A, Lugering A, Randall T, Cupedo T, Mebius R
Mucosal Immunol, 2012-09-19;6(3):511-21.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
PI3K gamma drives priming and survival of autoreactive CD4(+) T cells during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Authors: Iain Comerford, Wendel Litchfield, Ervin Kara, Shaun R. McColl
PLoS ONE
-
CCR6 is required for epidermal trafficking of gammadelta-T cells in an IL-23-induced model of psoriasiform dermatitis.
Authors: Mabuchi T, Singh T, Takekoshi T, Jia G, Wu X, Kao M, Weiss I, Farber J, Hwang S
J Invest Dermatol, 2012-08-16;133(1):164-71.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-Fr -
Tumor-Associated Macrophages Recruit CCR6+ Regulatory T Cells and Promote the Development of Colorectal Cancer via Enhancing CCL20 Production in Mice
Authors: Jinlin Liu, Ning Zhang, Qun Li, Weiwei Zhang, Fang Ke, Qibin Leng et al.
PLoS ONE
-
Human beta-defensin 2 and 3 and their mouse orthologs induce chemotaxis through interaction with CCR2.
Authors: Rohrl J, Yang D, Oppenheim JJ, Hehlgans T
J. Immunol., 2010-05-17;184(12):6688-94.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Mouse CCR6 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Mouse CCR6 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:



