Human FGFR4 Antibody Summary
Leu22-Asp369 (predicted)
Accession # P22455
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human FGF R4 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line and Huh-7 human hepatoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.2 µg/mL of Rat Anti-Human FGF R4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6852) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF005). A specific band was detected for FGF R4 at approximately 110 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
View Larger
FGF R4 in Human Pancreas. FGF R4 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human pancreas using Rat Anti-Human FGF R4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6852) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; CTS017) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
 View Larger
View Larger
FGF R4 in MCF‑7 Human Cell Line. FGF R4 was detected in immersion fixed MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line using Rat Anti-Human FGF R4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6852) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL013) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of FGFR4 in HepG2 cells by Flow Cytometry. HepG2 cells were stained with Rat Anti-Human FGFR4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6852, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB006, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0105B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
 View Larger
View Larger
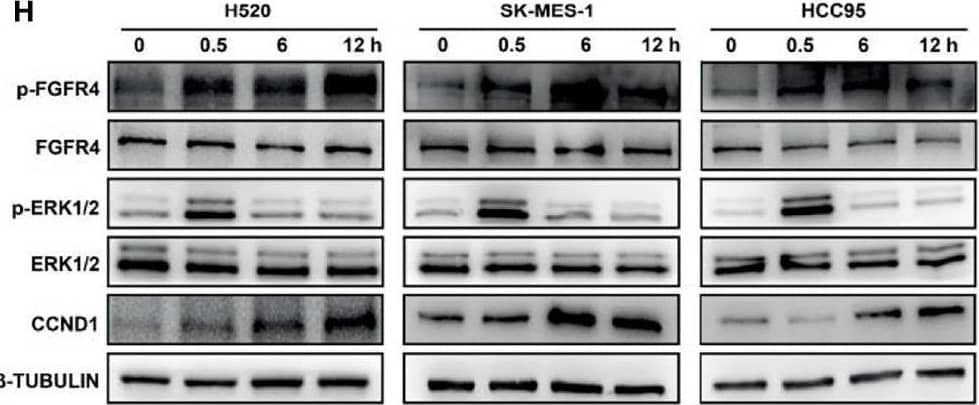
Detection of FGFR4 by Western Blot FGF19 enhances CCND1 expression by FGF19-FGFR4-ERK1/2 axis in LUSC cells. (A) Recombinant human FGF19 (rhFGF19) (25 ng/ml) promoted expression of CCND1 in SK-MES-1 and H520 cells (serum starved for 12 h before treatment) in a time-dependent manner. (B) CCND1 mRNA expression levels in LUSC cell lines after treatment with rhFGF2 for 12 h. (C) Expression of CCND1 in FGF19 overexpression LUSC cell line. (D) Expression of CCND1 in FGF19 knockdown LUSC cell line. (E) A panel of inhibitors against a number of signaling pathways was used to dissect the leading factors of regulated by FGF19. (F) Western blot and (G) qPCR analysis of CCND1 expression in H520 and HCC95 LUSC cells after treatment of FGF19, FGF19 and SCH772984, FGF19 & BLU9931, or DMSO as control. (H) Effects of the FGF19/FGFR4 pathway on protein levels of CCND1, p-FGFR4, and p-ERK1/2 by western blot analysis. H520, SK-MES-1 and HCC95 cells were treated with FGF19 (25 ng/ml, 0/0.5/6/12 h) to activate the FGF19/FGFR4 signaling pathway. Data were shown as mean ± SD bars and compared by unpaired t-test. **p <0.01; ****p <0.0001; ns, not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35463335), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
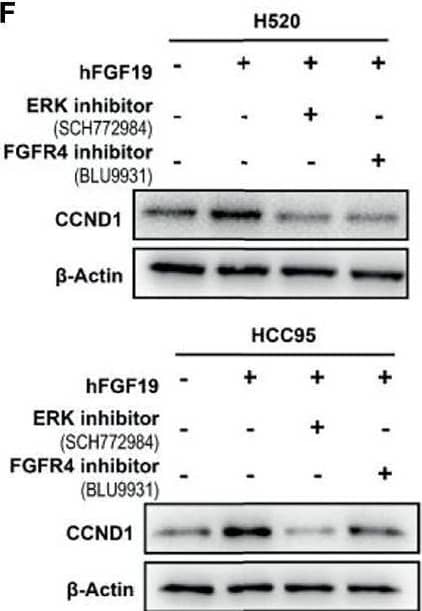
Detection of FGFR4 by Western Blot FGF19 enhances CCND1 expression by FGF19-FGFR4-ERK1/2 axis in LUSC cells. (A) Recombinant human FGF19 (rhFGF19) (25 ng/ml) promoted expression of CCND1 in SK-MES-1 and H520 cells (serum starved for 12 h before treatment) in a time-dependent manner. (B) CCND1 mRNA expression levels in LUSC cell lines after treatment with rhFGF2 for 12 h. (C) Expression of CCND1 in FGF19 overexpression LUSC cell line. (D) Expression of CCND1 in FGF19 knockdown LUSC cell line. (E) A panel of inhibitors against a number of signaling pathways was used to dissect the leading factors of regulated by FGF19. (F) Western blot and (G) qPCR analysis of CCND1 expression in H520 and HCC95 LUSC cells after treatment of FGF19, FGF19 and SCH772984, FGF19 & BLU9931, or DMSO as control. (H) Effects of the FGF19/FGFR4 pathway on protein levels of CCND1, p-FGFR4, and p-ERK1/2 by western blot analysis. H520, SK-MES-1 and HCC95 cells were treated with FGF19 (25 ng/ml, 0/0.5/6/12 h) to activate the FGF19/FGFR4 signaling pathway. Data were shown as mean ± SD bars and compared by unpaired t-test. **p <0.01; ****p <0.0001; ns, not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35463335), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
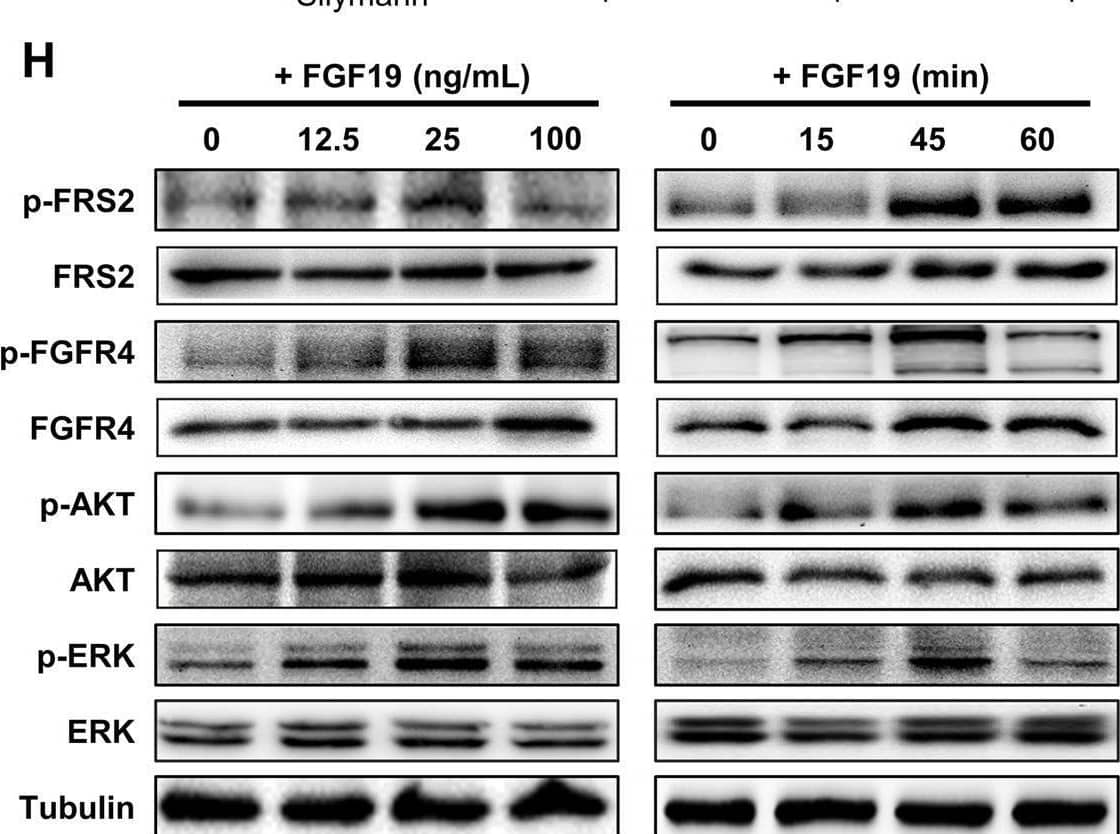
Detection of FGFR4 by Western Blot CDCA and ER stress induce FGF19 upregulation and hFGF19 activates ERK/AKT signaling to promote LSQ cell proliferation. A FGF19 (a) and FGFR4 (b) mRNA expression levels in LSQ cell lines and Beas-2b. b Protein expression levels of FGF19 and FGFR4 in LSQ cell lines and bronchial epithelial cell line Beas-2b. c The effects of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) treatment on FGF19 protein levels in Beas-2b cells in a dose-dependent (ranging from 0 to 100 µM, upper panel) and time-dependent (within 48 h, lower panel) manner. d The effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment (50 µM) on the apoptosis of Beas-2b cells with quantifications of the results on the right panel. e mRNA expression of FGF19 (left panel) and GRP78 (right panel) of LSQ cell lines H520 and SK-MES-1 treated with thapsigargin (TG) or tunicamycin (TM) for 24 h. f FGF19 protein expression of H520 and SK-MES-1 treated with TG or TM for 24 h, in the presence or absence of ER stress suppressor silymarin. g Cell proliferation of SK-MES-1 cells treated with conditioned medium from H520 cells overexpressing FGF19 was determined by CCK-8 assays. h The effects of hFGF19 on the activation of ERK/AKT signaling in SK-MES-1 cells in a dose-dependent (left panel) or time-dependent (right panel) manner. i Enrichment plots of mTOR expression signatures according to FGF19 expression levels in an LSQ cohort. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32111983), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
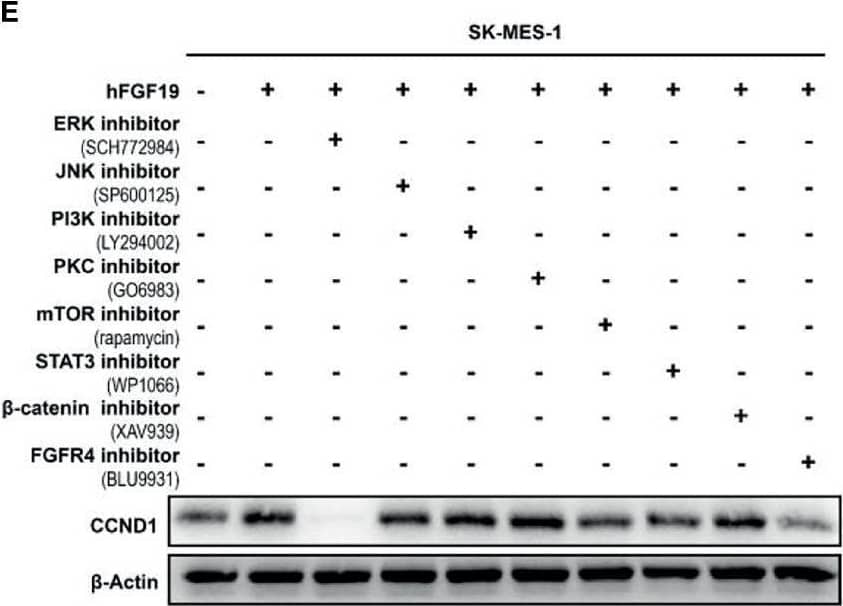
Detection of FGFR4 by Western Blot FGF19 enhances CCND1 expression by FGF19-FGFR4-ERK1/2 axis in LUSC cells. (A) Recombinant human FGF19 (rhFGF19) (25 ng/ml) promoted expression of CCND1 in SK-MES-1 and H520 cells (serum starved for 12 h before treatment) in a time-dependent manner. (B) CCND1 mRNA expression levels in LUSC cell lines after treatment with rhFGF2 for 12 h. (C) Expression of CCND1 in FGF19 overexpression LUSC cell line. (D) Expression of CCND1 in FGF19 knockdown LUSC cell line. (E) A panel of inhibitors against a number of signaling pathways was used to dissect the leading factors of regulated by FGF19. (F) Western blot and (G) qPCR analysis of CCND1 expression in H520 and HCC95 LUSC cells after treatment of FGF19, FGF19 and SCH772984, FGF19 & BLU9931, or DMSO as control. (H) Effects of the FGF19/FGFR4 pathway on protein levels of CCND1, p-FGFR4, and p-ERK1/2 by western blot analysis. H520, SK-MES-1 and HCC95 cells were treated with FGF19 (25 ng/ml, 0/0.5/6/12 h) to activate the FGF19/FGFR4 signaling pathway. Data were shown as mean ± SD bars and compared by unpaired t-test. **p <0.01; ****p <0.0001; ns, not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35463335), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
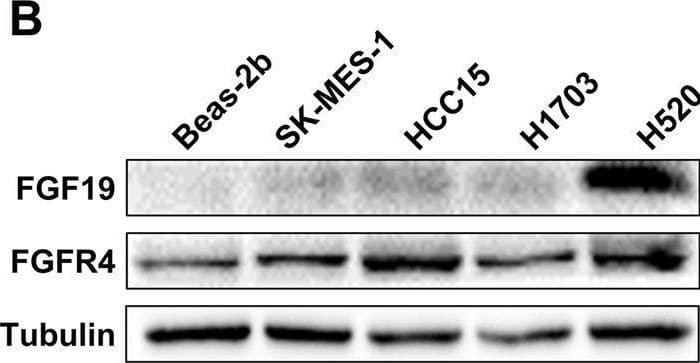
Detection of FGFR4 by Western Blot CDCA and ER stress induce FGF19 upregulation and hFGF19 activates ERK/AKT signaling to promote LSQ cell proliferation. A FGF19 (a) and FGFR4 (b) mRNA expression levels in LSQ cell lines and Beas-2b. b Protein expression levels of FGF19 and FGFR4 in LSQ cell lines and bronchial epithelial cell line Beas-2b. c The effects of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) treatment on FGF19 protein levels in Beas-2b cells in a dose-dependent (ranging from 0 to 100 µM, upper panel) and time-dependent (within 48 h, lower panel) manner. d The effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment (50 µM) on the apoptosis of Beas-2b cells with quantifications of the results on the right panel. e mRNA expression of FGF19 (left panel) and GRP78 (right panel) of LSQ cell lines H520 and SK-MES-1 treated with thapsigargin (TG) or tunicamycin (TM) for 24 h. f FGF19 protein expression of H520 and SK-MES-1 treated with TG or TM for 24 h, in the presence or absence of ER stress suppressor silymarin. g Cell proliferation of SK-MES-1 cells treated with conditioned medium from H520 cells overexpressing FGF19 was determined by CCK-8 assays. h The effects of hFGF19 on the activation of ERK/AKT signaling in SK-MES-1 cells in a dose-dependent (left panel) or time-dependent (right panel) manner. i Enrichment plots of mTOR expression signatures according to FGF19 expression levels in an LSQ cohort. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32111983), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: FGFR4
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) comprise a family of at least eighteen structurally related proteins that are involved in a multitude of physiological and pathological cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, angiogenesis, wound healing and tumorgenesis. The biological activities of the FGFs are mediated by a family of type I transmembrane tyrosine kinases which undergo dimerization and autophosphorylation after ligand binding. Four distinct genes encoding closely related FGF receptors, FGF R1‑4, are known. All four genes for FGF Rs encode proteins with an N-terminal signal peptide, three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, an acid-box region containing a run of acidic residues between the IgI and IgII domains, a transmembrane domain and the split tyrosine-kinase domain. Multiple forms of FGF R1‑3 are generated by alternative splicing of the mRNAs. A frequent splicing event involving FGF R1 and 2 results in receptors containing all three Ig domains, referred to as the alpha isoform, or only IgII and IgIII, referred to as the beta isoform. Only the alpha isoform has been identified for FGF R3 and FGF R4. Additional splicing events for FGF R1‑3, involving the C-terminal half of the IgIII domain encoded by two mutually exclusive alternative exons, generate FGF receptors with alternative IgIII domains (IIIb and IIIc). A IIIa isoform which is a secreted FGF binding protein containing only the N-terminal half of the IgIII domain plus some intron sequences has also been reported for FGF R1. Mutations in FGF R1‑3 have been found in patients with birth defects involving craniosynostosis. The complex patterns of expression of these receptors as well as the specificity of their interactions with the various FGF ligand family members are under investigation.
- Galzie, Z. et al. (1997) Biochem. Cell Biol. 75:669.
- Burke, D. et al. (1998) Trends Biochem. Sci. 23:59.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human FGFR4 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
2
Citations: Showing 1 - 2
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
FGF19 Is Coamplified With CCND1 to Promote Proliferation in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Combined Inhibition Shows Improved Efficacy
Authors: Yanshuang Zhang, Tingyu Wu, Fan Li, Yirui Cheng, Qing Han, Xin Lu et al.
Frontiers in Oncology
-
ONECUT2 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by transcriptionally upregulating FGF2 and ACLY
Authors: D Liu, T Zhang, X Chen, B Zhang, Y Wang, M Xie, X Ji, M Sun, W Huang, L Xia
Cell Death & Disease, 2021-11-27;12(12):1113.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: IHC
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human FGFR4 Antibody
Average Rating: 5 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human FGFR4 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:





