Human Glut1 Antibody Summary
Met1-Val492
Accession # AAA52571
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Glut1 in HepG2 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human Glut1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1418, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB0041, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0101B).
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Glut1 in Jurkat Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line either (A) untreated or (B) cultured in nutrient-depleted media was stained with Mouse Anti-Human Glut1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1418, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB0041, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B).
 View Larger
View Larger
Glut1 in HepG2 Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line. Glut1 was detected in immersion fixed HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line using Mouse Anti-Human Glut1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1418) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI(blue). Specific staining was localized to the plasma membrane. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
View Larger
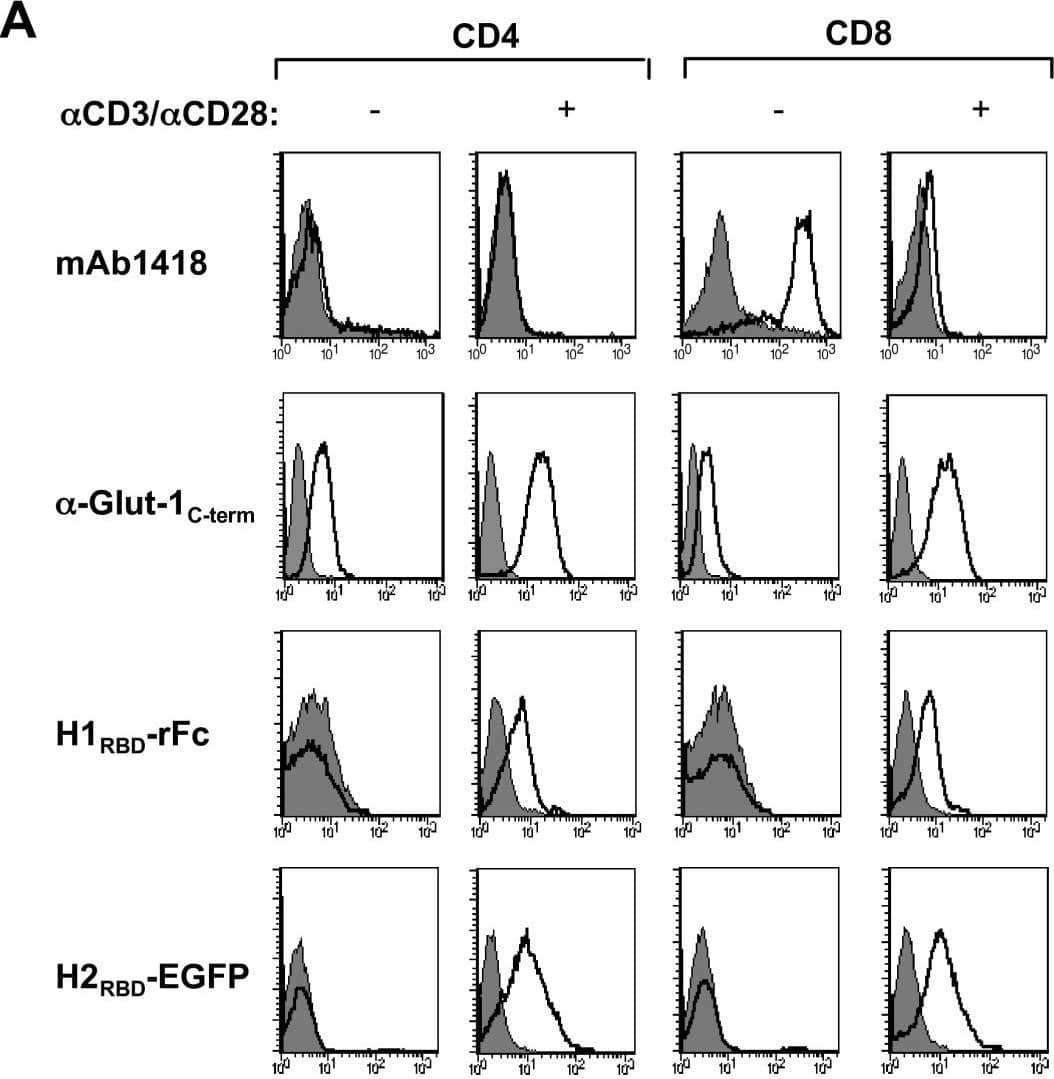
Detection of Human Glut1 by Flow Cytometry TCR stimulation results in Glut-1 expression and concomitant glucose uptake in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes: Induction of H1RBD and H2RBD binding. CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes were isolated by negative selection and stimulated via the TCR using alpha CD3/ alpha CD28 mAbs. (A) Non-activated and TCR-activated T cells were used for binding assays with mAb1418 followed by incubation with a FITC-conjugated alpha mouse IgG. Intracellular Glut-1 levels were monitored in permeabilized cells using the C-term Glut-1 polyclonal antibody followed by incubation with a FITC-conjugated sheep alpha rabbit IgG antibody. Filled histograms depict binding in the presence of the secondary FITC-conjugated antibody alone. Expression of the HTLV-1 Env receptor was detected by a 30 min incubation of the non-activated and TCR-activated cells with rabbit rFc-tagged H1RBD fusion protein at 37°C and binding was revealed by a 20 min incubation at 4°C with a FITC-conjugated sheep alpha rabbit IgG antibody. Binding to the H2RBD domain fused directly to EGFP (H2RBD-EGFP) was detected following a 30 min incubation at 37°C. (B) Glucose uptake was assayed by incubating non-activated and TCR-activated CD4 and CD8 T cells (1 × 106) with 2-deoxy-D [1-3H]glucose (2 μCi) for 45 min at 37°C. Uptake for each cell population is expressed as mean counts per minute (CPM) for triplicate samples, error bars indicate SD. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17504522), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
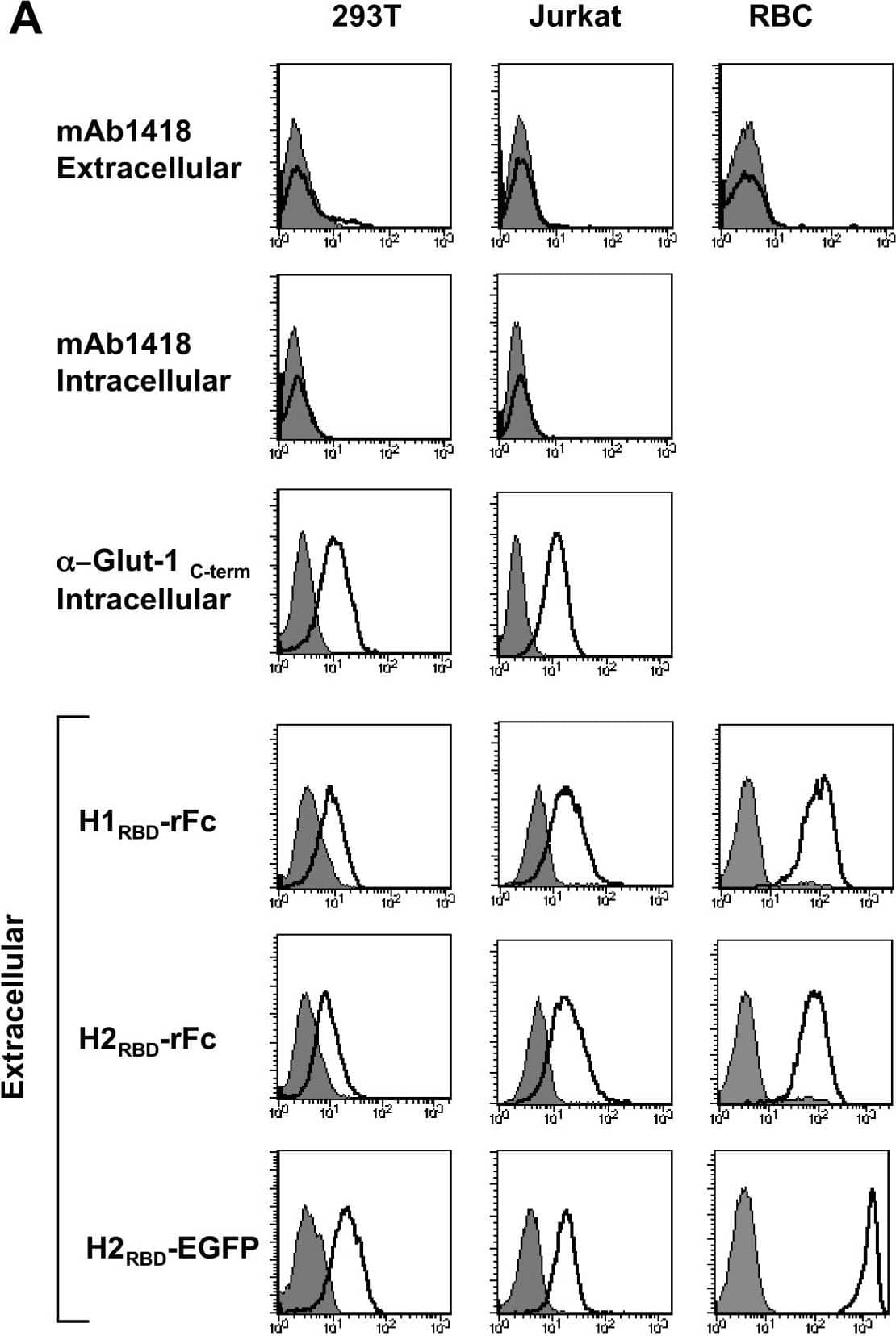
Detection of Human Glut1 by Flow Cytometry Endogenous Glut-1 expression in diverse cell types is not reflected by mAb1418 reactivity but correlates with binding of the HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 Env RBDs. (A) 293T, Jurkat and primary human erythrocytes were stained with mAb1418 and control binding with the secondary FITC-conjugated antibody is shown in all histograms (filled). Intracellular Glut-1 levels in permeabilized 293T and Jurkat cells were monitored with mAb1418 as well as the C-term polyclonal Glut-1 antibody. Expression of the HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 receptor was monitored by incubation of cells for 30 min at 37°C with the rFc-tagged H1RBD and H2RBD fusion proteins as well as the H2RBD-EGFP fusion protein. Binding is shown in solid line histograms whereas control immunofluorescence is shown in filled histograms. (B) Total Glut-1 protein levels in cell extracts from 293T, Jurkat and human erythrocytes were monitored by immunoblotting with an anti-C-term Glut-1 antibody. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17504522), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
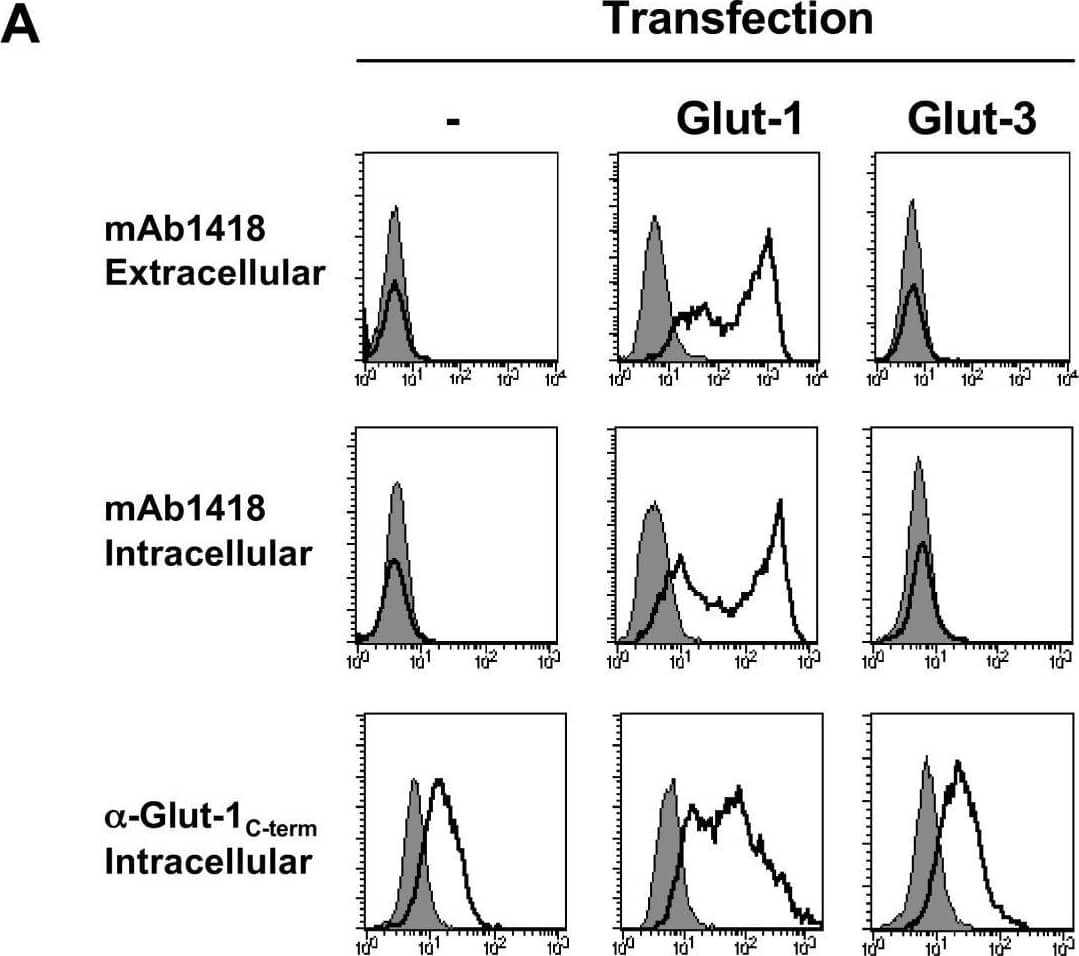
Detection of Human Glut1 by Flow Cytometry Antibody and HRBD binding following transfection of the Glut-1 and Glut-3 glucose transporters. (A) 293T cells were transfected with Glut-1 or Glut-3 expression vectors and assayed for binding to the mAb1418 and C-term anti-Glut-1 polyclonal Ab. The former stainings were performed on whole cells as well as permeabilized cells to determine cell surface and total binding, respectively. All stainings using the anti-Glut-1 pAb were performed on permeabilized cells as the recognized epitope is intracellular. Staining was performed at 4°C. Specific binding and background fluorescence due to the secondary conjugated Ab are indicated in solid line and filled histograms, respectively. (B) Control and transfected 293T cells were incubated with rFc-tagged H1RBD and H2RBD fusion proteins for 30 min at 37°C followed by incubation with a FITC-conjugated alpha rabbit-Fc antibody at 4°C. Direct binding to H2RBD was demonstrated by incubation of cells with an EGFP-tagged envelope (H2RBD-EGFP). Binding is shown in solid line histograms whereas control immunofluorescence is shown in filled histograms. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17504522), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
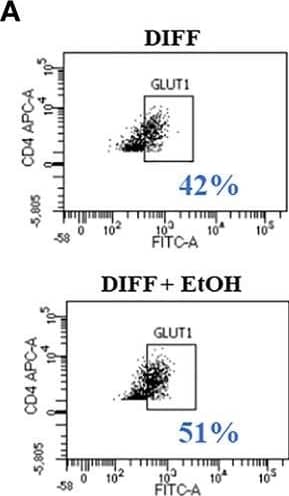 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Glut1 by Flow Cytometry Effect of ethanol on CD4+ T cell glucose metabolism. (A) Representative FACS plots of GLUT1 expression in DIFF and DIFF + EtOH CD4+ T cells. (B) Ethanol increased CD4+ T cell GLUT1 expression. (C) Representative FACS histograms of 2-NBDG uptake in DIFF and DIFF + EtOH CD4+ T cells. (D) Ethanol increased glucose uptake within differentiated CD4+ T cells. (E) All experimental groups were analyzed using the Glycolytic Stress test. Ethanol increased glycolysis (F) and glycolytic capacity (G) within differentiated groups. MFI = mean fluorescent intensity, 2-NBDG = 2-Deoxy-2-[(7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl)amino]-D-glucose, ECAR = extracellular acidification rate, Naïve = undifferentiated and no ethanol treatment, EtOH = undifferentiated and ethanol-treated, DIFF = differentiated and no ethanol treatment, and DIFF + EtOH = differentiated and ethanol-treated. Data represents average values using CD4+ T cells from 6 donors expressed as mean ± SEM. Significant differences (p<0.05) were determined by repeated measures 2-way ANOVA. *p ≤ 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35634279), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
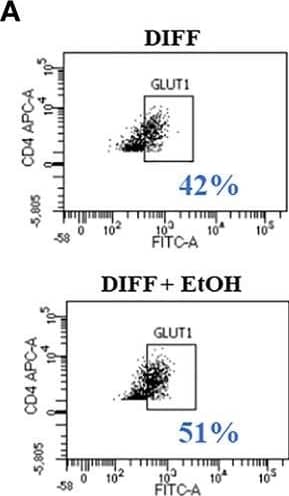 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Glut1 by Flow Cytometry Effect of ethanol on CD4+ T cell glucose metabolism. (A) Representative FACS plots of GLUT1 expression in DIFF and DIFF + EtOH CD4+ T cells. (B) Ethanol increased CD4+ T cell GLUT1 expression. (C) Representative FACS histograms of 2-NBDG uptake in DIFF and DIFF + EtOH CD4+ T cells. (D) Ethanol increased glucose uptake within differentiated CD4+ T cells. (E) All experimental groups were analyzed using the Glycolytic Stress test. Ethanol increased glycolysis (F) and glycolytic capacity (G) within differentiated groups. MFI = mean fluorescent intensity, 2-NBDG = 2-Deoxy-2-[(7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl)amino]-D-glucose, ECAR = extracellular acidification rate, Naïve = undifferentiated and no ethanol treatment, EtOH = undifferentiated and ethanol-treated, DIFF = differentiated and no ethanol treatment, and DIFF + EtOH = differentiated and ethanol-treated. Data represents average values using CD4+ T cells from 6 donors expressed as mean ± SEM. Significant differences (p<0.05) were determined by repeated measures 2-way ANOVA. *p ≤ 0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35634279), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Glut1
Glut1 belongs to the facilitative glucose transport protein family that comprises 13 members. It is an integral membrane protein with 12 transmembrane domains and is expressed at variable levels in many tissues including brain endothelial cells, CD8+ T cells, and erythrocytes (1‑4). Glut1 is a major glucose transporter that mediates glucose transport across the mammalian blood‑brain barrier.
- Mueckler, M. et al. 1994, Eur. J. Biochem. 219:713.
- Meuckler, M. et al. 1985, Science 229:941.
- Jones, K.S. et al. 2006, J. Virol. 8291.
- Takenouchi, N. et al. 2007, J. Virol. 1506.
- Kinet, S. et al. 2007, Retrovirology 4:31.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Glut1 Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
32
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Induction of HIF-1? by HIV-1 Infection in CD4+ T Cells Promotes Viral Replication and Drives Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Inflammation
Authors: G Duette, P Pereyra Ge, J Rubione, PS Perez, AL Landay, SM Crowe, Z Liao, KW Witwer, MP Holgado, J Salido, J Geffner, O Sued, CS Palmer, M Ostrowski
MBio, 2018-09-11;9(5):.
-
Assessment of metabolic and mitochondrial dynamics in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in virologically suppressed HIV-positive individuals on combination antiretroviral therapy
Authors: JJR Masson, AJ Murphy, MKS Lee, M Ostrowski, SM Crowe, CS Palmer
PLoS ONE, 2017-08-30;12(8):e0183931.
-
Immunometabolic and Lipidomic Markers Associated With the Frailty Index and Quality of Life in Aging HIV+ Men on Antiretroviral Therapy
Authors: HL Yeoh, AC Cheng, CL Cherry, JM Weir, PJ Meikle, JF Hoy, SM Crowe, CS Palmer
EBioMedicine, 2017-07-18;0(0):.
-
Polymorphism rs1385129 Within Glut1 Gene SLC2A1 Is Linked to Poor CD4+ T Cell Recovery in Antiretroviral-Treated HIV+ Individuals
Authors: Jesse J. R. Masson, Catherine L. Cherry, Nicholas M. Murphy, Isabel Sada-Ovalle, Tabinda Hussain, Riya Palchaudhuri et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Alcohol Impairs Immunometabolism and Promotes Na�ve T Cell Differentiation to Pro-Inflammatory Th1 CD4(+) T Cells
Authors: McTernan PM, Levitt DE, Welsh DA et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
CD28 Superagonistic Activation of T Cells Induces a Tumor Cell-Like Metabolic Program
Authors: Thilipan Thaventhiran, Wai Wong, Ahmad F. Alghanem, Naif Alhumeed, Mohammad A. Aljasir, Simeon Ramsey et al.
Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy
-
High rates of glucose utilization in the gas gland of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) are supported by GLUT1 and HK1b
Authors: Kathy A. Clow, Connie E. Short, Jennifer R. Hall, Robert L. Gendron, Hélène Paradis, Ankur Ralhan et al.
Journal of Experimental Biology
-
Glucose Metabolism in T Cells and Monocytes: New Perspectives in HIV Pathogenesis
Authors: Clovis S. Palmer, Catherine L. Cherry, Isabel Sada-Ovalle, Amit Singh, Suzanne M. Crowe
EBioMedicine
-
Chronic stimulation desensitizes ?2-adrenergic receptor responses in natural killer cells
Authors: Jürgens, M;Claus, M;Wingert, S;Niemann, JA;Picard, LK;Hennes, E;Haasler, I;Hellwig, B;Overbeck, N;Reinders, J;Rahnenführer, J;Schedel, M;Capellino, S;Watzl, C;
European journal of immunology
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Visualizing inflammation with an M1 macrophage selective probe via GLUT1 as the gating target
Authors: H Cho, HY Kwon, A Sharma, SH Lee, X Liu, N Miyamoto, JJ Kim, SH Im, NY Kang, YT Chang
Nature Communications, 2022-10-10;13(1):5974.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Alcohol Impairs Immunometabolism and Promotes Na�ve T Cell Differentiation to Pro-Inflammatory Th1 CD4(+) T Cells
Authors: McTernan PM, Levitt DE, Welsh DA et al.
Frontiers in Immunology
-
Tumor-derived exosomes drive immunosuppressive macrophages in a pre-metastatic niche through glycolytic dominant metabolic reprogramming
Authors: Samantha M. Morrissey, Fan Zhang, Chuanlin Ding, Diego Elias Montoya-Durango, Xiaoling Hu, Chenghui Yang et al.
Cell Metabolism
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Cell Lysates
Applications: Western Blot -
Single Cell Mass Cytometry of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Reveals Complexity of In vivo And Three-Dimensional Models over the Petri-dish
Authors: R Alföldi, JÁ Balog, N Faragó, M Halmai, E Kotogány, P Neuperger, LI Nagy, LZ Fehér, GJ Szebeni, LG Puskás
Cells, 2019-09-16;8(9):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
CD28 Superagonistic Activation of T Cells Induces a Tumor Cell-Like Metabolic Program
Authors: Thilipan Thaventhiran, Wai Wong, Ahmad F. Alghanem, Naif Alhumeed, Mohammad A. Aljasir, Simeon Ramsey et al.
Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Rhinovirus induces an anabolic reprogramming in host cell metabolism essential for viral replication
Authors: GA Gualdoni, KA Mayer, AM Kapsch, K Kreuzberg, A Puck, P Kienzl, F Oberndorfe, K Frühwirth, S Winkler, D Blaas, GJ Zlabinger, J Stöckl
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2018-07-09;115(30):E7158-E7165.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Detection and Characterization of CD8+ Autoreactive Memory Stem T Cells in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Authors: D Vignali, E Cantarelli, C Bordignon, A Canu, A Citro, A Annoni, L Piemonti, P Monti
Diabetes, 2018-03-05;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Blood
Applications: IHC -
Metabolically active CD4+ T cells expressing Glut1 and OX40 preferentially harbor HIV during in vitro infection
Authors: Clovis S. Palmer, Gabriel A. Duette, Marc C. E. Wagner, Darren C. Henstridge, Suah Saleh, Candida Pereira et al.
FEBS Letters
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Manipulating Glucose Metabolism during Different Stages of Viral Pathogenesis Can Have either Detrimental or Beneficial Effects
Authors: SK Varanasi, D Donohoe, U Jaggi, BT Rouse
J. Immunol., 2017-08-02;0(0):.
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Emerging Role and Characterization of Immunometabolism: Relevance to HIV Pathogenesis, Serious Non-AIDS Events, and a Cure
J Immunol, 2016-06-01;196(11):4437-44.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
High rates of glucose utilization in the gas gland of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) are supported by GLUT1 and HK1b
Authors: Kathy A. Clow, Connie E. Short, Jennifer R. Hall, Robert L. Gendron, Hélène Paradis, Ankur Ralhan et al.
Journal of Experimental Biology
Species: Fish
Sample Types: Tissue Homogenates
Applications: Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot -
Foxp3-mediated inhibition of Akt inhibits Glut1 (glucose transporter 1) expression in human T regulatory cells.
Authors: Basu S, Hubbard B, Shevach E
J Leukoc Biol, 2014-12-09;97(2):279-83.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Increased glucose metabolic activity is associated with CD4+ T-cell activation and depletion during chronic HIV infection.
Authors: Palmer C, Ostrowski M, Gouillou M, Tsai L, Yu D, Zhou J, Henstridge D, Maisa A, Hearps A, Lewin S, Landay A, Jaworowski A, McCune J, Crowe S
AIDS, 2014-01-28;28(3):297-309.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
The chemokine CCL5 regulates glucose uptake and AMP kinase signaling in activated T cells to facilitate chemotaxis.
Authors: Chan O, Burke J, Gao D, Fish E
J Biol Chem, 2012-07-10;287(35):29406-16.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Entry of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 is augmented by heparin sulfate proteoglycans bearing short heparin-like structures.
Authors: Tanaka A, Jinno-Oue A, Shimizu N
J. Virol., 2012-01-11;86(6):2959-69.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Role of FDG-PET as a biological marker for predicting the hypoxic status of tongue cancer.
Authors: Han M, Lee H, Cho K, Kim J, Roh J, Choi S, Nam S, Kim S
Head Neck, 2011-11-03;34(10):1395-402.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
DC-SIGN mediates cell-free infection and transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 by dendritic cells.
Authors: Jain P, Manuel SL, Khan ZK, Ahuja J, Quann K, Wigdahl B
J. Virol., 2009-08-19;83(21):10908-21.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Antiparallel segregation of notch components in the immunological synapse directs reciprocal signaling in allogeneic Th:DC conjugates.
Authors: Luty WH, Rodeberg D, Parness J, Vyas YM
J. Immunol., 2007-07-15;179(2):819-29.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Analysis of the Single-Cell Heterogeneity of Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines and the Investigation of Intratumor Heterogeneity Reveals the Expression of Transmembrane Protein 45A (TMEM45A) in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cancer Patients
Authors: Patrícia Neuperger, József Á. Balog, László Tiszlavicz, József Furák, Nikolett Gémes, Edit Kotogány et al.
Cancers (Basel)
-
Surfaceome analyses uncover CD98hc as an antibody drug-conjugate target in triple negative breast cancer
Authors: Juan Carlos Montero, Elisa Calvo-Jiménez, Sofía del Carmen, Mar Abad, Alberto Ocaña, Atanasio Pandiella
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
-
Metabolically active CD4+ T cells expressing Glut1 and OX40 preferentially harbor HIV during in vitro infection
Authors: Clovis S. Palmer, Gabriel A. Duette, Marc C. E. Wagner, Darren C. Henstridge, Suah Saleh, Candida Pereira et al.
FEBS Letters
-
Tumor-derived exosomes drive immunosuppressive macrophages in a pre-metastatic niche through glycolytic dominant metabolic reprogramming
Authors: Samantha M. Morrissey, Fan Zhang, Chuanlin Ding, Diego Elias Montoya-Durango, Xiaoling Hu, Chenghui Yang et al.
Cell Metabolism
-
Isolation of Stem Cells, Endothelial Cells and Pericytes from Human Infantile Hemangioma
Authors: Lan Huang, Joyce Bischoff
BIO-PROTOCOL
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Glut1 Antibody
There are currently no reviews for this product. Be the first to review Human Glut1 Antibody and earn rewards!
Have you used Human Glut1 Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image