Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody Summary
Glu25-Thr932
Accession # P08581
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of HGF R/c‑MET in MDA‑MB‑231 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry. MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line was stained with Human HGF R/c-MET Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3582, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG F(ab')2Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0101B).
 View Larger
View Larger
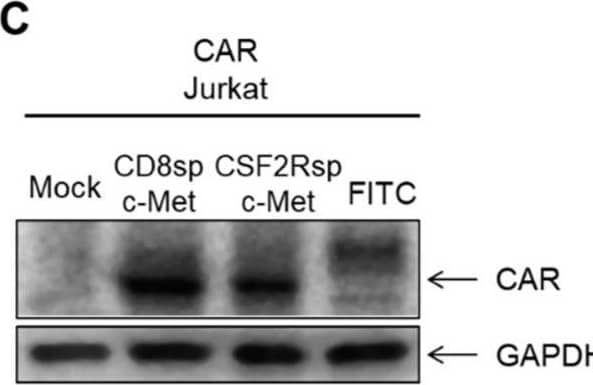
Detection of HGFR/c-MET by Western Blot Generation of CARs and analysis of IL-2 secretion by c-Met CAR Jurkat cell. (A) Schematic representation of c-Met CAR and FITC CAR construct. (B) c-Met gene (pCMV3-Met) was transduced by electroporation into K562, and Western blot was performed. (C) After transducing the mock CD8sp-c-Met CAR, CSF2Rsp-c-Met CAR, or FITC CAR construct into Jurkat, expressions of CAR were confirmed through Western blot. (D) The mock CD8sp-c-Met CAR, CSF2Rsp-c-Met CAR, or FITC CAR Jurkat were co-cultured with K562 or c-Met-K562 at an E:T ratio of 15:1. After overnight incubation, supernatants were collected and ELISA was performed to measure IL-2 level. (The whole western blots figure see Figure S1). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34830894), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
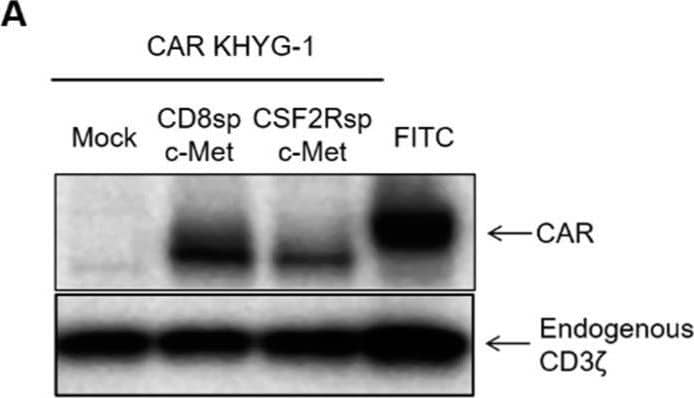
Detection of HGFR/c-MET by Western Blot c-Met CAR KHYG-1 specifically lyses the c-Met positive GC cells. (A) Western blot with the cell lysates of mock CD8sp-c-Met, CSF2Rsp-c-Met, or FITC KHYG-1 cells to see the CAR expression (B) The mock CD8sp-c-Met CAR, CSF2Rsp-c-Met CAR, or FITC CAR KHYG-1 were co-incubated with MKN-45, SNU-5, SNU-1, and SNU-484 at E:T ratio of 5:1 or 10:1 for 5 h. The cytotoxicity of CAR KHYG-1 was measured by the Bright-Glo (luciferase) assay system. (The whole western blots figure see Figure S1). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34830894), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: HGFR/c-MET
HGF R, also known as Met (from N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced), is a glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in epithelial morphogenesis and cancer development. HGF R is synthesized as a single chain precursor which undergoes cotranslational proteolytic cleavage. This generates a mature HGF R that is a disulfide-linked dimer composed of a 50 kDa extracellular alpha chain and a 145 kDa transmembrane beta chain (1, 2). The extracellular domain (ECD) contains a seven bladed beta -propeller sema domain, a cysteine-rich PSI/MRS, and four Ig-like E-set domains, while the cytoplasmic region includes the tyrosine kinase domain (3, 4). Proteolysis and alternate splicing generate additional forms of human HGF R which either lack of the kinase domain, consist of secreted extracellular domains, or are deficient in proteolytic separation of the alpha and beta chains (5-7). The sema domain, which is formed by both the alpha and beta chains of HGF R, mediates both ligand binding and receptor dimerization (3, 8). Ligand-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in the cytoplasmic region activates the kinase domain and provides docking sites for multiple SH2-containing molecules (9, 10). HGF stimulation induces HGF R downregulation via internalization and proteasome-dependent degradation (11). In the absence of ligand, HGF R forms non-covalent complexes with a variety of membrane proteins including CD44v6, CD151, EGF R, Fas, Integrin alpha 6/ beta 4, Plexins B1, 2, 3, and MSP R/Ron (12-19). Ligation of one complex component triggers activation of the other, followed by cooperative signaling effects (12-19). Formation of some of these heteromeric complexes is a requirement for epithelial cell morphogenesis and tumor cell invasion (12, 16, 17). Paracrine induction of epithelial cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis results from the stimulation of HGF R on undifferentiated epithelium by HGF released from neighboring mesenchymal cells (20). Genetic polymorphisms, chromosomal translocation, over-expression, and additional splicing and proteolytic cleavage of HGF R have been described in a wide range of cancers (1). Within the ECD, human HGF R shares 86-88% amino acid sequence identity with canine, mouse, and rat HGF R.
- Birchmeier, C. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:915.
- Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
- Gherardi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:12039.
- Park, M. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:6379.
- Crepaldi, T. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1750.
- Prat, M. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:5954.
- Rodrigues, G.A. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:2962.
- Kong-Beltran, M. et al. (2004) Cancer Cell 6:75.
- Naldini, L. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1793.
- Ponzetto, C. et al. (1994) Cell 77:261.
- Jeffers, M. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:799.
- Orian-Rousseau, V. et al. (2002) Genes Dev. 16:3074.
- Klosek, S.K. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336:408.
- Jo, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:8806.
- Wang, X. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell 9:411.
- Trusolino, L. et al. (2001) Cell 107:643.
- Giordano, S. et al. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4:720.
- Conrotto, P. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:5131.
- Follenzi, A. et al. (2000) Oncogene 19:3041.
- Sonnenberg, E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 123:223.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
14
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
c-Met-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Demonstrate Anti-Tumor Effect in c-Met Positive Gastric Cancer
Authors: CH Kang, Y Kim, DY Lee, SU Choi, HK Lee, CH Park
Cancers, 2021-11-16;13(22):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Aberrant Expression of and Cell Death Induction by Engagement of the MHC-II Chaperone CD74 in Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)
Authors: KD Wurster, M Costanza, S Kreher, S Glaser, B Lamprecht, N Schleussne, I Anagnostop, M Hummel, K Jöhrens, H Stein, A Molina, A Diepstra, B Gillissen, K Köchert, R Siebert, O Merkel, L Kenner, M Janz, S Mathas
Cancers, 2021-10-07;13(19):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Adipose stem cell niche reprograms the colorectal cancer stem cell metastatic machinery
Authors: S Di Franco, P Bianca, DS Sardina, A Turdo, M Gaggianesi, V Veschi, A Nicotra, LR Mangiapane, M Lo Iacono, I Pillitteri, S van Hooff, F Martorana, G Motta, E Gulotta, VL Lentini, E Martorana, ME Fiori, S Vieni, MR Bongiorno, G Giannone, D Giuffrida, L Memeo, L Colarossi, M Mare, P Vigneri, M Todaro, R De Maria, JP Medema, G Stassi
Nature Communications, 2021-08-18;12(1):5006.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: ICC -
ERBB3 overexpression due to miR-205 inactivation confers sensitivity to FGF, metabolic activation, and liability to ERBB3 targeting in glioblastoma
Authors: F De Bacco, F Orzan, J Erriquez, E Casanova, L Barault, R Albano, A D'Ambrosio, V Bigatto, G Reato, M Patanè, B Pollo, G Kuesters, C Dell'Aglio, L Casorzo, S Pellegatta, G Finocchiar, PM Comoglio, C Boccaccio
Cell Reports, 2021-07-27;36(4):109455.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Synergistic activity of agents targeting growth factor receptors, CDKs and downstream signaling molecules in a panel of pancreatic cancer cell lines and the identification of antagonistic combinations: Implications for future clinical trials in pancreatic cancer
Authors: T Khan, AM Seddon, AG Dalgleish, S Khelwatty, N Ioannou, S Mudan, H Modjtahedi
Oncol Rep, 2020-10-22;0(0):.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
A reference collection of patient-derived cell line and xenograft models of proneural, classical and mesenchymal glioblastoma
Authors: BW Stringer, BW Day, RCJ D'Souza, PR Jamieson, KS Ensbey, ZC Bruce, YC Lim, K Goasdoué, C Offenhäuse, S Akgül, S Allan, T Robertson, P Lucas, G Tollesson, S Campbell, C Winter, H Do, A Dobrovic, PL Inglis, RL Jeffree, TG Johns, AW Boyd
Sci Rep, 2019-03-20;9(1):4902.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
TGF beta 1 regulates HGF ‐induced cell migration and hepatocyte growth factor receptor MET expression via C‐ets‐1 and miR‐128‐3p in basal‐like breast cancer
Authors: Christian Breunig, Nese Erdem, Alexander Bott, Julia F. Greiwe, Eileen Reinz, Stephan Bernhardt et al.
Molecular Oncology
-
Necrosis- and apoptosis-related Met cleavages have divergent functional consequences
Authors: R Montagne, M Berbon, L Doublet, N Debreuck, A Baranzelli, H Drobecq et al.
Cell Death & Disease
-
Necrotic cell-derived high mobility group box 1 attracts antigen-presenting cells but inhibits hepatocyte growth factor-mediated tropism of mesenchymal stem cells for apoptotic cell death.
Authors: Vogel S, Borger V, Peters C, Forster M, Liebfried P, Metzger K, Meisel R, Daubener W, Trapp T, Fischer J, Gawaz M, Sorg R
Cell Death Differ, 2015-01-09;22(7):1219-30.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
beta1 integrin targeting potentiates antiangiogenic therapy and inhibits the growth of bevacizumab-resistant glioblastoma.
Authors: Carbonell W, DeLay M, Jahangiri A, Park C, Aghi M
Cancer Res, 2013-05-03;73(10):3145-54.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Expression of growth factor receptors and targeting of EGFR in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines
Authors: Ling Xu, Martin Hausmann, Wolfgang Dietmaier, Silvia Kellermeier, Theresa Pesch, Manuela Stieber-Gunckel et al.
BMC Cancer
-
Down-regulation of the met receptor tyrosine kinase by presenilin-dependent regulated intramembrane proteolysis.
Authors: Foveau B, Ancot F, Leroy C, Petrelli A, Reiss K, Vingtdeux V, Giordano S, Fafeur V, Tulasne D
Mol. Biol. Cell, 2009-03-18;20(9):2495-507.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
Resistance of acute myeloid leukemic cells to the triterpenoid CDDO-Imidazolide is associated with low caspase-8 and FADD levels.
Authors: Riccioni R, Senese M, Diverio D, Riti V, Mariani G, Boe A, LoCoco F, Foa R, Peschle C, Sporn M, Testa U
Leuk. Res., 2008-03-04;32(8):1244-58.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Flow Cytometry -
H1/pHGFK1 nanoparticles exert anti-tumoural and radiosensitising effects by inhibition of MET in glioblastoma
Authors: W Zhang, R Duan, J Zhang, WKC Cheung, X Gao, R Zhang, Q Zhang, M Wei, G Wang, Q Zhang, PJ Mei, HL Chen, H Kung, MC Lin, Z Shen, J Zheng, L Zhang, H Yao
Br. J. Cancer, 2018-01-18;0(0):.
FAQs
-
Does Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody, Catalog # MAB3582, bind to the alpha chain or beta chain of HGFR/c-MET?
The immunogen for MAB3582 (Recombinant human HGF R/cMET, aa Glu25-Thr932) spans both the alpha and beta chain regions of Human HGFR and we do not epitope map our antibodies. However, staining in flow cytometry detects a surface epitope. Since only the alpha chain is extracellular in location and the beta chain is transmembrane in location, the antibody likley binds the alpha chain of this protein.
Reviews for Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 4 Reviews)
Have you used Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by:
Detection of human HGFR/c-MET on epidermoid carcinoma cell line A-431. A-431 cells were treated with 100 nM of the human HGFR/c-MET antibody (catalog # MAB3582) or mouse IgG1 isotype control, followed by a secondary antibody goat a-mouse IgG Fc APC. Isotype control (RED), human HGFR/c-MET antibody (BLUE).
Antibody was printed on custom arrays and incubated with fluorescently labeled human EDTA plasma







