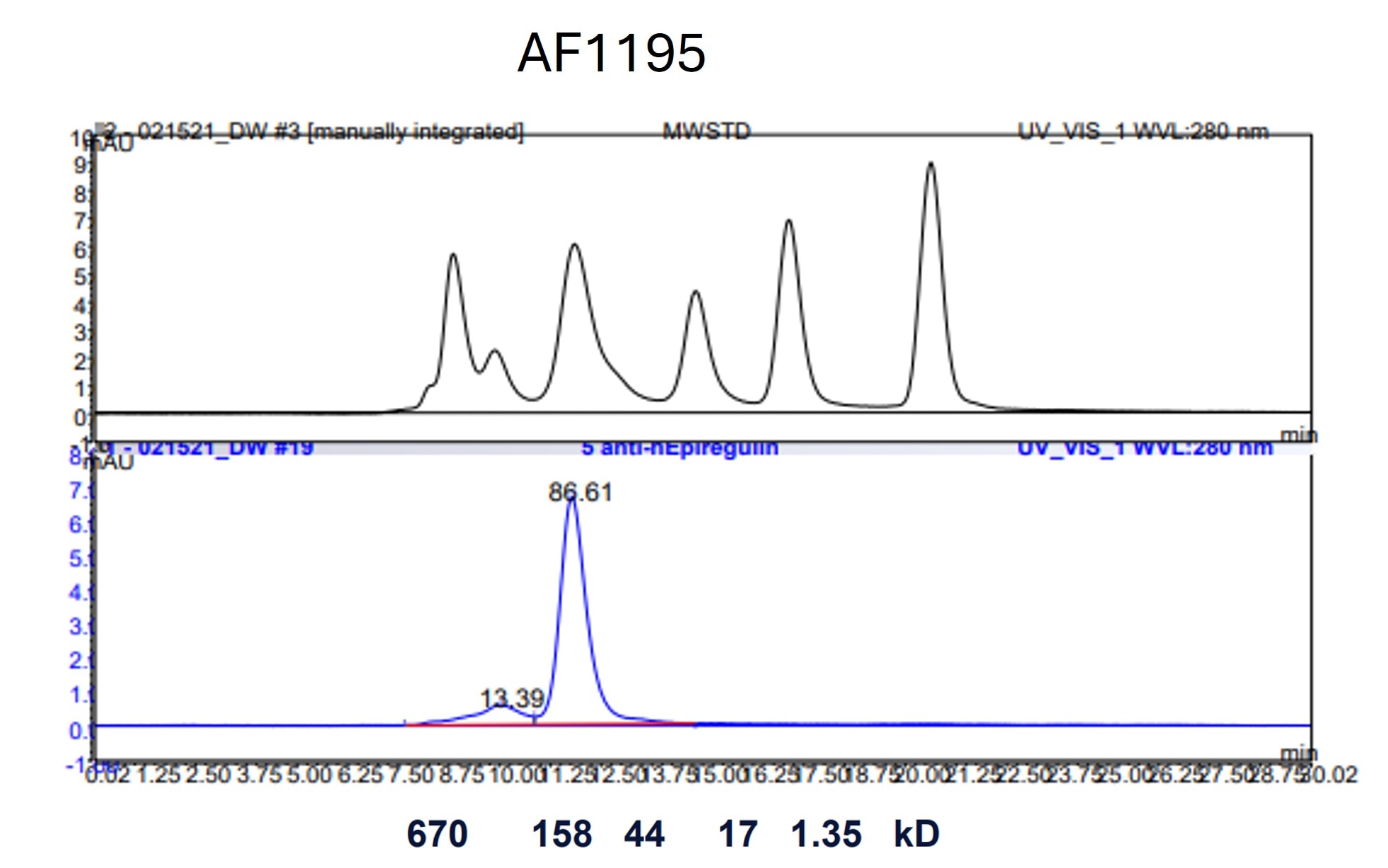
Human Epiregulin Antibody Summary
Val63-Leu108
Accession # O14944
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Applications
This antibody functions as an ELISA detection antibody when paired with Rat Anti-Human Epiregulin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB14252).
This product is intended for assay development on various assay platforms requiring antibody pairs. We recommend the Human Epiregulin DuoSet ELISA Kit (Catalog # DY1195-05) for convenient development of a sandwich ELISA.
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Scientific Data
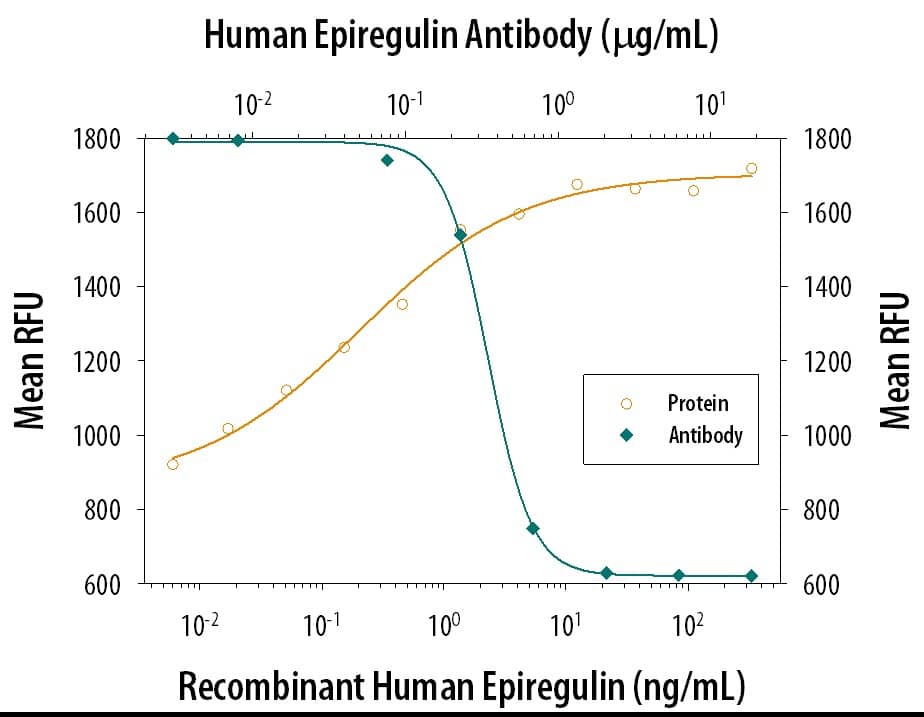 View Larger
View Larger
Cell Proliferation Induced by Epiregulin and Neutralization by Human Epiregulin Antibody. Recombinant Human Epiregulin (Catalog # 1195-EP) stimulates proliferation in the Balb/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Human Epiregulin is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Human Epiregulin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1195). The ND50 is typically ≤1.5 µg/mL.
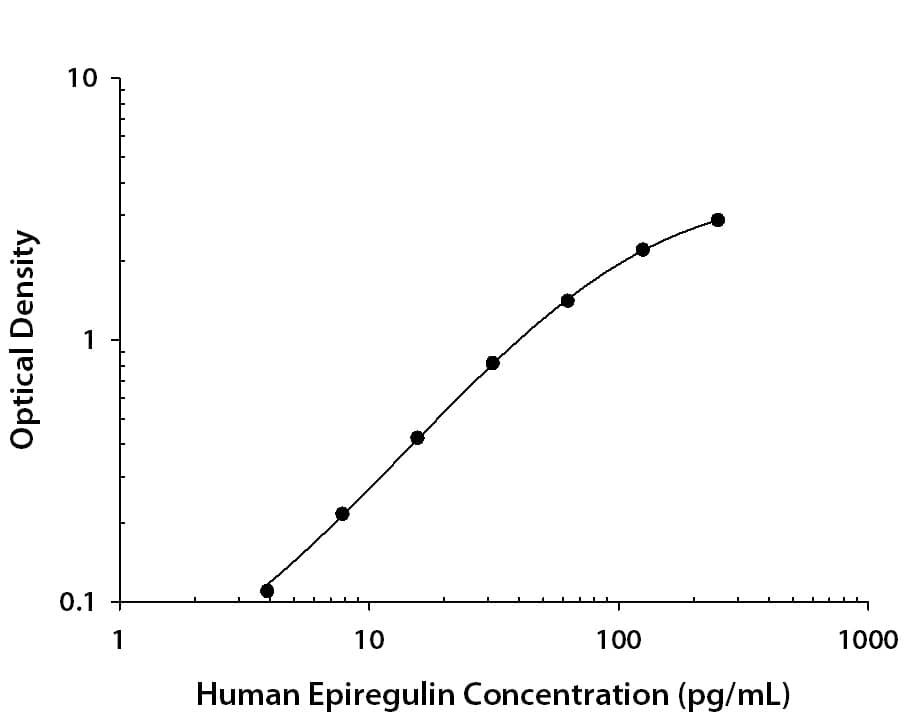 View Larger
View Larger
Human Epiregulin ELISA Standard Curve. Recombinant Human Epiregulin protein was serially diluted 2-fold and captured by Rat Anti-Human Epiregulin Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB14252) coated on a Clear Polystyrene Microplate (Catalog # DY990). Goat Anti-Human Epiregulin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1195) was biotinylated and incubated with the protein captured on the plate. Detection of the standard curve was achieved by incubating Streptavidin-HRP (Catalog # DY998) followed by Substrate Solution (Catalog # DY999) and stopping the enzymatic reaction with Stop Solution (Catalog # DY994).
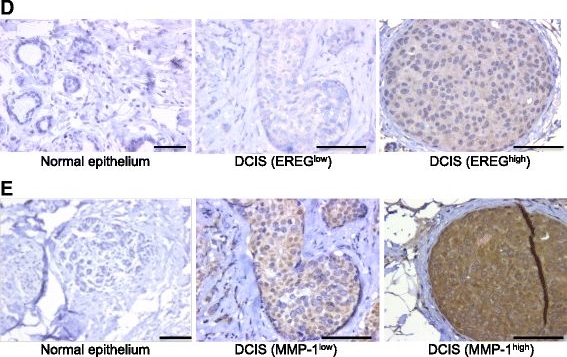 View Larger
View Larger
Detection of Human Epiregulin by Immunohistochemistry EREG expression correlates with MMP-1 levels in human DCIS lesions. a qRT-PCR analysis of MMP-1 gene expression in MCF10A and MCF10DCIS cells. Expression levels of MMP-1 are normalized to CYBP. b Immunoblot analysis of MMP-1 in conditioned media obtained from MCF10A and MCF10DCIS cells. Loading was assessed by Coomassie staining (Additional file 1: Figure S1C). c qRT-PCR analysis of MMP-1 gene expression in MCF10DCIS cells expressing either NT or EREG shRNA constructs. Expression levels of MMP-1 are normalized to CYBP. d Immunohistochemistry of normal breast tissue and DCIS stained with an anti-EREG antibody. Scale bars represent 50 μm. e Normal and DCIS human samples were stained with an anti-MMP-1 antibody. Representative images of normal and varying levels of MMP-1 staining in DCIS lesions are shown. f Quantification of the percent of samples staining positive for EREG. g Quantification of the percent of samples staining positive for MMP-1. Scale bars represent 50 μm. *p < 0.05. ***p < 0.0001 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26215578), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
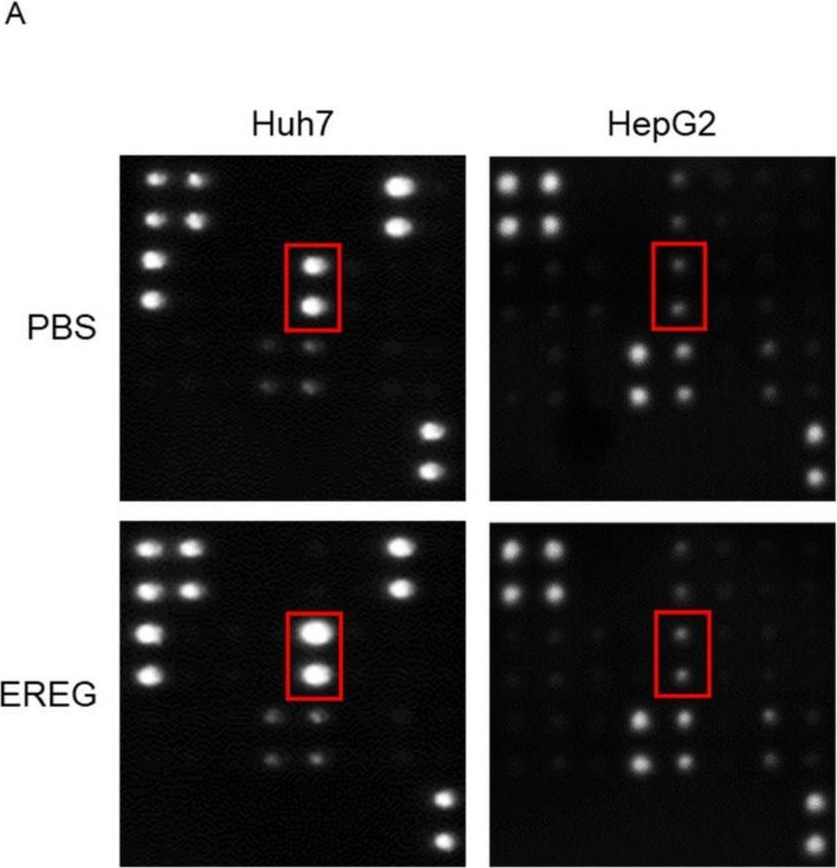
Detection of Epiregulin by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence EREG increased IL-8 production from cancer cells through EGFR signaling to induce tumor neovascularization. (A) Representative images of the change in angiogenic factors in both Huh7 and HepG2 cells with/without stimulation with EREG. IL-8 levels in Huh7 cells only increased during stimulation with rEREG. Red box showed the expression of IL-8. The graph for the intensity of IL-8 in the angiogenesis array kit in the untreated and EREG-treated groups (B) in Huh7 and (C) in HepG2. The graph for the expression level of IL-8 by RT-PCR in the untreated and EREG-treated groups (D) in Huh7 and (E) in HepG2. (F) The expression level of IL-8 in Huh7 cells in the monoculture group (left graph) and the group co-cultured with LX-2 (right graph) under the LPS stimulation. (G) Change in IL-8 expression levels when treated with/without anti-EREG antibodies under LPS present. (H) Representative images of the change in angiogenic factors in LX-2 with/without stimulation with LPS. (I) The graph for the intensity of IL-8 measured by the angiogenesis array kit in the untreated and LPS-treated groups in LX-2. Significance was determined using a one-way analysis of variance for group comparisons. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001, ns; not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/8/4405), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
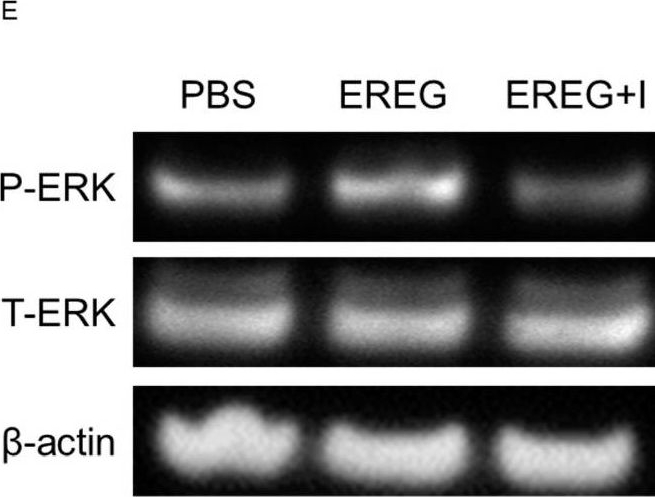
Detection of Epiregulin by Western Blot EREG promoted cell proliferation and migration/invasion activity of liver cancer cells expressing EGFR in vitro. (A) Expression levels of EGFR in each HCC line (Huh7, JHH, and HepG2). EGFR was expressed in Huh7 and JHH cells but not in HepG2 cells. Cell proliferation of (B) Huh7 cells and (C) HepG2 cells was stimulated with different concentrations of EREG (0, 1, 10, 50, and 100 ng/mL). (D) Cell proliferation of Huh7 co-cultured with LX-2 was measured by the WST-1 assay when stimulated with 100 and 1000 ng/mL of LPS. (E) Change in the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in Huh7 stimulated with EREG and in combination with EREG and EGFR inhibitors (AG1478; 100 ng/mL). (F) Cell proliferation of Huh7 co-cultured with LX-2 with LPS stimulation and a combination of LPS and anti-EREG antibodies. Significance was determined using a one-way analysis of variance for group comparisons. *; p < 0.05, **; p < 0.01. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/8/4405), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View Larger
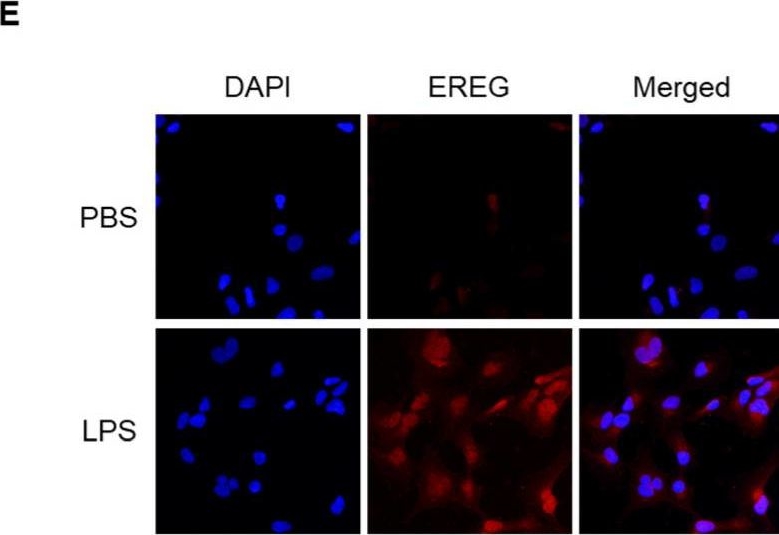
Detection of Epiregulin by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence Change in EREG expression and production in LX-2 cells by LPS stimulation. (A) Expression level of EREG in LX-2 stimulated with different concentrations of LPS (0, 1, 10, and 100 ng/mL) measured by RT-PCR. (B) Expression of EREG in LX-2 cells measured by RT-PCR and (C) production of EREG protein level by enzyme-linked immuno-sorbent assay (ELISA) in the supernatant with LX-2 cells cultured with/without 100 ng/mL of LPS for 24 h. (D) EREG expression in LX-2 cells stimulated with/without recombinant human EREG protein (100 ng/mL) by RT-PCR. (E) Representative images of immunostaining for EREG in LX-2 cells compared between the conditions stimulated with/without LPS stimulation. Magnification, 60×. (F) Gene expression levels of other members in the EGF family in LX-2 cells with/without LPS stimulation. Graphs showed the mean ± SEM. *; p < 0.05, ***; p < 0.001, ns; not significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/8/4405), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Reconstitution Calculator
Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Epiregulin
Epiregulin is a member of the EGF family of growth factors which includes, among others, epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha, amphiregulin (ARG), HB (heparin-binding)-EGF, betacellulin, and the various heregulins. All EGF family members are synthesized as transmembrane precursors and are converted to soluble forms by proteolytic cleavage. Epiregulin was originally purified from the mouse fibroblast-derived tumor cell line NIH3T3/T7. The human epiregulin cDNA encodes a 169 amino acid (aa) residues transmembrane precursor with a 29 aa signal peptide, a 21 aa transmembrane domain and a 21 aa cytoplasmic domain. The putative soluble mature Epiregulin comprising the EGF-like domain (aa residues 64-104) is formed by proteolytic removal of the propeptide regions. There is 85% aa sequence homology between human and mouse epiregulins. Epiregulin is expressed primarily in the placenta and macrophages. High level expression has also been detected in various carcinomas. Epiregulin specifically binds EGF R (ErbB1) and ErbB4 but not ErbB2 and ErbB3. It activates the homodimers of both ErbB1 and ErbB4. In addition, epiregulin can also activate all possible heteromeric combinations of the four ErbB family members. Epiregulin stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and hepatocytes. It has been shown to be an autocrine growth factor for epidermal keratinocytes as well as mesangial cells. Epiregulin has also been shown to inhibit growth of several epithelial tumor cells. In addition, Epiregulin has been implicated in the implantation process during pregnancy.
Product Datasheets
Citations for Human Epiregulin Antibody
R&D Systems personnel manually curate a database that contains references using R&D Systems products. The data collected includes not only links to publications in PubMed, but also provides information about sample types, species, and experimental conditions.
13
Citations: Showing 1 - 10
Filter your results:
Filter by:
-
Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulin-mediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Authors: Boudot C, Henaut L, Thiem U et al.
Oncotarget
-
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Biomarkers Linked to Lung Metastatic Potential and Cell Stemness
Authors: Ruiz de Garibay G, Herranz C, Llorente A et al.
PLoS ONE.
-
EREG-driven oncogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma exhibits higher sensitivity to Erlotinib therapy
Authors: S Liu, Y Wang, Y Han, W Xia, L Zhang, S Xu, H Ju, X Zhang, G Ren, L Liu, W Ye, Z Zhang, J Hu
Theranostics, 2020-08-25;10(23):10589-10605.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC -
Epiregulin (EREG) is upregulated through an IL‐1 beta autocrine loop in Caco‐2 epithelial cells with reduced CFTR function
Authors: Macarena Massip‐Copiz, Mariángeles Clauzure, Ángel G. Valdivieso, Tomás A. Santa‐Coloma
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry
-
Tumor endothelial cells promote metastasis and cancer stem cell-like phenotype through elevated Epiregulin in esophageal cancer
Am J Cancer Res, 2016-10-01;6(10):2277-2288.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Lysates, Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P, Western Blot -
Epiregulin contributes to breast tumorigenesis through regulating matrix metalloproteinase 1 and promoting cell survival
Authors: Mariya Farooqui, Laura R. Bohrer, Nicholas J. Brady, Pavlina Chuntova, Sarah E. Kemp, C. Taylor Wardwell et al.
Molecular Cancer
Species: Mouse
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
Proteins of the VEGFR and EGFR pathway as predictive markers for adjuvant treatment in patients with stage II/III colorectal cancer: results of the FOGT-4 trial
Authors: Thomas Thomaidis, Annett Maderer, Andrea Formentini, Susanne Bauer, Mario Trautmann, Michael Schwarz et al.
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
-
High epiregulin expression in human U87 glioma cells relies on IRE1alpha and promotes autocrine growth through EGF receptor.
Authors: Auf G, Jabouille A, Delugin M, Guerit S, Pineau R, North S, Platonova N, Maitre M, Favereaux A, Vajkoczy P, Seno M, Bikfalvi A, Minchenko D, Minchenko O, Moenner M
BMC Cancer, 2013-12-13;13(0):597.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernates
Applications: ELISA Development -
Epiregulin as a marker for the initial steps of ovarian cancer development.
Authors: Amsterdam A, Shezen E, Raanan C
Int. J. Oncol., 2011-07-14;39(5):1165-72.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
The complete family of epidermal growth factor receptors and their ligands are co-ordinately expressed in breast cancer
Authors: Emmet McIntyre, Edith Blackburn, Philip J. Brown, Colin G. Johnson, William J. Gullick
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: Immunohistochemistry -
HER family receptor abnormalities in lung cancer brain metastases and corresponding primary tumors.
Authors: Sun M, Behrens C, Feng L, Ozburn N, Tang X, Yin G, Komaki R, Varella-Garcia M, Hong WK, Aldape KD, Wistuba II
Clin. Cancer Res., 2009-07-21;15(15):4829-37.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Tissue
Applications: IHC-P -
Human trophoblast survival at low oxygen concentrations requires metalloproteinase-mediated shedding of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor.
Authors: Armant DR, Kilburn BA, Petkova A, Edwin SS, Duniec-Dmuchowski ZM, Edwards HJ, Romero R, Leach RE
Development, 2006-01-11;133(4):751-9.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: ICC -
Autocrine extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in normal human keratinocytes: metalloproteinase-mediated release of amphiregulin triggers signaling from ErbB1 to ERK.
Authors: Kansra S, Johnson JL
Mol. Biol. Cell, 2004-07-14;15(9):4299-309.
Species: Human
Sample Types: Whole Cells
Applications: Neutralization
FAQs
No product specific FAQs exist for this product, however you may
View all Antibody FAQsReviews for Human Epiregulin Antibody
Average Rating: 4 (Based on 1 Review)
Have you used Human Epiregulin Antibody?
Submit a review and receive an Amazon gift card.
$25/€18/£15/$25CAN/¥75 Yuan/¥2500 Yen for a review with an image
$10/€7/£6/$10 CAD/¥70 Yuan/¥1110 Yen for a review without an image
Filter by: