VEGFR
External Information | Products | Related Information | Gene Data
Vascular endothelial growth factor is a signaling protein involved in the regulation of angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. VEGF binds to and activates a receptor tyrosine kinase, VEGFR, through transphosphorylation. Three VEGFR isoforms have been identified in humans.
Whilst multiple receptors and ligands are involved in angiogenesis, VEGF signaling is one of the most important, rate-limiting steps of the process. VEGF is diffusible and selective for vascular endothelial cells, and possesses the ability to promote the growth and survival of these cells in vitro. Hypoxic conditions activate hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), resulting in increased VEGF mRNA expression. Other growth factors such as EGF, TGF-β and PDGF may also upregulate VEGF expression. The increased expression levels of VEGF in solid tumors, hematological malignancies, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetes mellitus and various inflammatory disorders has placed great emphasis on developing VEGF inhibitors.
VEGF binds to and activates the receptor tyrosine kinase, VEGFR. Three VEGFR isoforms have been identified in humans: VEGFR-1 (Flt-1), VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk-1) and VEGFR-3 (Flt-4). VEGFR-2 mediates the majority of cellular responses to VEGF, in particular its mitogenic and angiogenic effects. VEGFR-1 is thought to modulate VEGFR-2 signaling or to act as a dummy/decoy receptor to sequester VEGF away from VEGFR-2. The expression of VEGFR-1 is also up-regulated by hypoxia, in a similar mechanism to VEGF, via HIF-1; its functions may vary depending on cell type and developmental stage.
External Information for VEGFR
VEGFR Inhibitors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Activity |
| 5318 | AEE 788 | Potent VEGFR and EGFR inhibitor |
| 4274 | AP 24534 | Potent multi-kinase and pan-Bcr-Abl inhibitor |
| 4350 | Axitinib | Potent VEGFR-1, -2 and -3 inhibitor |
| 7454 | Cediranib | Potent inhibitor of VEGFR, PDGFR and FGFR |
| 2542 | Ki 8751 | Potent, selective VEGFR-2 inhibitor |
| 7743 | Linifanib | Potent inhibitor of PDGFRβ, KDR, FLT3 and CSF-1R |
| 7049 | Nintedanib | Potent VEGFR, PDGFR and FGFR inhibitor |
| 6814 | Sorafenib | VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 inhibitor; also inhibits Raf-1, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 and cKIT |
| 3300 | SU 5402 | Potent VEGFR and FGFR inhibitor |
| 3037 | SU 5416 | VEGFR inhibitor. Also inhibits KIT, RET, MET and FLT3 |
| 3768 | Sunitinib malate | Potent VEGFR, PDGFRβ and KIT inhibitor |
| 7497 | Vandetanib | Potent VEGFR-2 inhibitor, also inhibits EGFR and RET oncoproteins activity |
| 5680 | Vatalanib succinate | Potent VEGFR inhibitor; also aromatase inhibitor |
| 5422 | XL 184 | Potent VEGFR inhibitor; also inhibits other RTKs |
| 2475 | ZM 323881 hydrochloride | Potent, selective inhibitor of VEGFR-2 |
Other | ||
| 6986 | EG 00229 trifluoroacetate | Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) receptor antagonist; inhibits VEGFA binding to NRP1 |
Related Products
Soluble VEGF R2: Controlling Lymphangiogenesis

Read about how VEGF and its receptors regulate angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis during embryonic development, pregnancy, and would healing.
VEGF - VEGF R2 Signaling Pathways
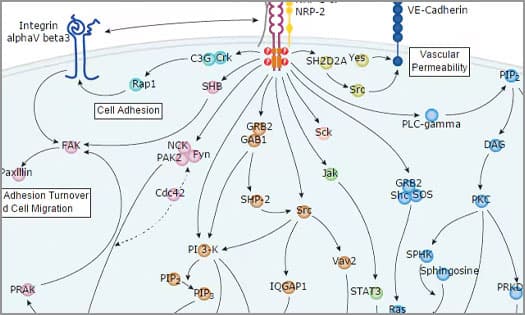
VEGF signaling pathway is involved in embryonic vascular development (vasculogenesis) and in the formation of new blood vessel (angiogenesis). It also induces cell migration, proliferation and survival.
