Platelet Activation Inhibitory Signaling
Click on one of the choices in the Explore Pathways box to view a different Platelet pathway.
ProductsClose
Integrin alpha 2b beta 3
GPVI
CLEC-2
GPVI
CLEC-2
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Src
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Csk
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Lyn
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Fyn
ProductsClose
SHIP
ProductsClose
CD31/
PECAM-1
PECAM-1
ProductsClose
G6b
Shp1,2
ProductsClose
PI 3-Kinase
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
PLC-gamma
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
alpha-2 Adrenergic R
alpha-2A Adrenergic R/ADRA2A
alpha-2B Adrenergic R/ADRA2B
alpha-2C Adrenergic R/ADRA2C
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Antagonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligand Sets
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligands
Adrenergic Receptor Ligand Sets
Additional Adrenergic Receptor-related Compounds
Adrenergic Related Compound Inhibitors
P2Y12
P2Y12/P2RY12
P2Y Receptor Agonists
P2Y Receptor Antagonists
PTGER3
PTGER3
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
alpha-2A Adrenergic R/ADRA2A
alpha-2B Adrenergic R/ADRA2B
alpha-2C Adrenergic R/ADRA2C
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Antagonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligand Sets
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligands
Adrenergic Receptor Ligand Sets
Additional Adrenergic Receptor-related Compounds
Adrenergic Related Compound Inhibitors
P2Y12
P2Y12/P2RY12
P2Y Receptor Agonists
P2Y Receptor Antagonists
PTGER3
PTGER3
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
alpha-2 Adrenergic R
P2Y12
PTGER3
P2Y12
PTGER3
ProductsClose
alpha-2 Adrenergic R
alpha-2A Adrenergic R/ADRA2A
alpha-2B Adrenergic R/ADRA2B
alpha-2C Adrenergic R/ADRA2C
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Antagonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligand Sets
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligands
Adrenergic Receptor Ligand Sets
Additional Adrenergic Receptor-related Compounds
Adrenergic Related Compound Inhibitors
P2Y12
P2Y12/P2RY12
P2Y Receptor Agonists
P2Y Receptor Antagonists
PTGER3
PTGER3
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
alpha-2A Adrenergic R/ADRA2A
alpha-2B Adrenergic R/ADRA2B
alpha-2C Adrenergic R/ADRA2C
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Antagonists
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligand Sets
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Ligands
Adrenergic Receptor Ligand Sets
Additional Adrenergic Receptor-related Compounds
Adrenergic Related Compound Inhibitors
P2Y12
P2Y12/P2RY12
P2Y Receptor Agonists
P2Y Receptor Antagonists
PTGER3
PTGER3
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
ProductsClose
G alpha i
ProductsClose
PTGER2,4
PTGIR
Adenosine A2a,A2b R
VIP R1/VPAC1
PTGIR
Adenosine A2a,A2b R
VIP R1/VPAC1
ProductsClose
PTGER2,4
PTGER2
PTGER4/EP4
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
PTGIR
PTGIR
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
Prostacyclin
Adenosine A2a,A2b R
Adenosine A2a R
Adenosine A2a Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2a Receptor Antagonists
Adenosine A2b R
Adenosine A2b Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2b Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Agonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Antagonists
Other Adenosine Inhibitors
Additional Adenosine Products
AVIP R1/VPAC1
VIP R1/VPAC1
VIP Receptor Agonists
VIP Receptor Antagonists
PTGER2
PTGER4/EP4
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
PTGIR
PTGIR
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
Prostacyclin
Adenosine A2a,A2b R
Adenosine A2a R
Adenosine A2a Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2a Receptor Antagonists
Adenosine A2b R
Adenosine A2b Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2b Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Agonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Antagonists
Other Adenosine Inhibitors
Additional Adenosine Products
AVIP R1/VPAC1
VIP R1/VPAC1
VIP Receptor Agonists
VIP Receptor Antagonists
ProductsClose
PTGER2,4
PTGER2
PTGER4/EP4
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
PTGIR
PTGIR
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
Prostacyclin
Adenosine A2a,A2b R
Adenosine A2a R
Adenosine A2a Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2a Receptor Antagonists
Adenosine A2b R
Adenosine A2b Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2b Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Agonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Antagonists
Other Adenosine Inhibitors
Additional Adenosine Products
AVIP R1/VPAC1
VIP R1/VPAC1
VIP Receptor Agonists
VIP Receptor Antagonists
PTGER2
PTGER4/EP4
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
PTGIR
PTGIR
Prostanoid Receptor Agonists
Prostanoid Receptor Antagonists
Additional Prostanoid Receptor Compounds
Prostacyclin
Adenosine A2a,A2b R
Adenosine A2a R
Adenosine A2a Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2a Receptor Antagonists
Adenosine A2b R
Adenosine A2b Receptor Agonists
Adenosine A2b Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Agonists
Non-selective Adenosine Receptor Antagonists
Other Adenosine Inhibitors
Additional Adenosine Products
AVIP R1/VPAC1
VIP R1/VPAC1
VIP Receptor Agonists
VIP Receptor Antagonists
ProductsClose
G alpha s
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
PTGER3
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
G alpha z
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Adenylyl Cyclase
ProductsClose
cAMP
ProductsClose
AMP
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
PKA
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Phosphodiesterase 2,3
ProductsClose
Caldesmon
ProductsClose
Filamin A
ProductsClose
G alpha 13
ProductsClose
GPIb
ProductsClose
HSP27
IP3 Receptor
ProductsClose
LASP
ProductsClose
MAPK
ProductsClose
Phosphodiesterase 3A
ProductsClose
Rap1
Rap1GAP2
ProductsClose
TRPC6
ProductsClose
VASP
ProductsClose
Nitric Oxide
ProductsClose
L-Arginine
ProductsClose
We currently do not offer products for this molecule. Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request. You will be notified once it becomes available.
eNOS
Citrulline
ProductsClose
Nitric Oxide
ProductsClose
Soluble
Guanylyl
Cyclase
Guanylyl
Cyclase
cGMP
GMP
ProductsClose
We currently do not offer products for this molecule. Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request. You will be notified once it becomes available.
ProductsClose
Phosphodiesterase 5A
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
PKG
ProductsClose
HSP27
IP3 Receptor
ProductsClose
LASP
ProductsClose
Myosin Light
Chain Kinase
Chain Kinase
ProductsClose
MAPK
ProductsClose
PI 3-Kinase
ProductsClose
Phosphodiesterase 5A
ProductsClose
Rap1
Rap1GAP2
ProductsClose
Thromboxane A2 R
ProductsClose
TRPC6
ProductsClose
VASP
ProductsClose
Inhibition of
Granule Release
Calcium Release
Integrin Activation
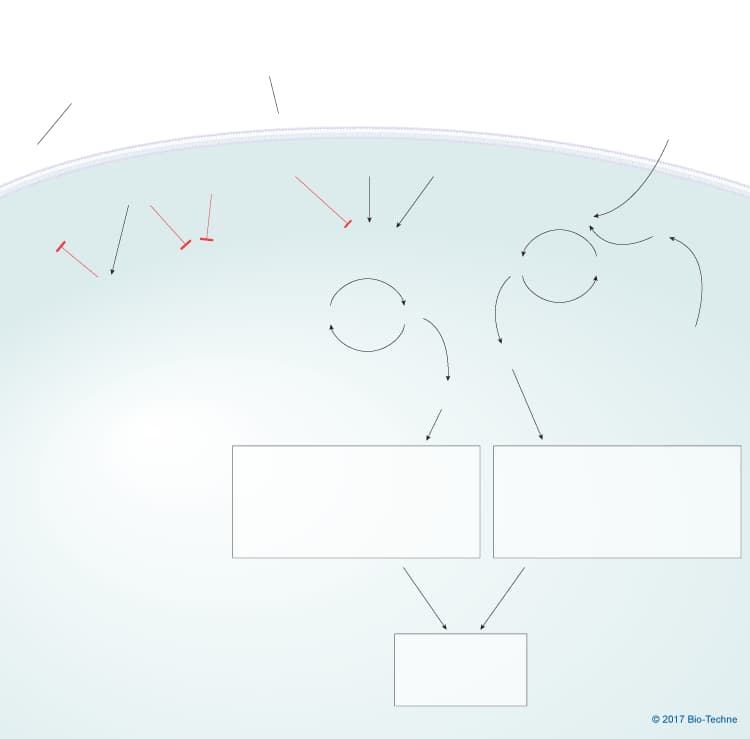
Overview of Inhibitory Signaling in Platelets
Unrestricted platelet activation can lead to life threatening thrombosis. In order to maintain control of this process, multiple steps in the platelet activation are regulated by cell surface receptors that block activation signals and by receptors that induce both activating and inhibitory signaling. Healthy vascular endothelial cells release nitric oxide and prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) into the blood where they maintain platelet quiescence by blocking granule release and integrin activation.

