Platelet Activation Overview
Click on one of the choices in the Explore Pathways box to view a different Platelet pathway.
Extracellular Matrix
ProductsClose
Collagen
ProductsClose
Fibronectin
ProductsClose
Laminin
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
Vitronectin
ProductsClose
Vascular Endothelium
Endothelial
Injury
Injury
Healthy Endothelium
Integrins
ProductsClose
Integrin alpha 2b
beta 3
beta 3
ProductsClose
activation
ProductsClose
We currently do not offer products for this molecule. Use our Product Suggestion form to enter a request. You will be notified once it becomes available.
ProductsClose
Integrin alpha 2b
beta 3
beta 3
ProductsClose
Rap1
RIAM
ProductsClose
LAT
PI 3-K
ProductsClose
PI 3-Kinase Activators
PI 3-Kinase C2 beta
PI 3-Kinase Inhibitors
PI 3-Kinase p55 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p85 alpha
PI 3-Kinase p110 beta
PI 3-Kinase p110 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p110 delta
PI 3-Kinase p85 beta
Other PI 3-Kinase Products
Kinase Assay Kits
Kinase Substrates
Other Kinase Activators
Other Kinase Inhibitors
Other Kinase Libraries
PI 3-Kinase C2 beta
PI 3-Kinase Inhibitors
PI 3-Kinase p55 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p85 alpha
PI 3-Kinase p110 beta
PI 3-Kinase p110 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p110 delta
PI 3-Kinase p85 beta
Other PI 3-Kinase Products
Kinase Assay Kits
Kinase Substrates
Other Kinase Activators
Other Kinase Inhibitors
Other Kinase Libraries
PKC
ProductsClose
Src
ProductsClose
GP Adhesion
Proteins
Proteins
GPIb,IX,V
GPVI
eNOS
ProductsClose
LAT
PI 3-K
ProductsClose
PI 3-Kinase Activators
PI 3-Kinase C2 beta
PI 3-Kinase Inhibitors
PI 3-Kinase p55 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p85 alpha
PI 3-Kinase p110 beta
PI 3-Kinase p110 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p110 delta
PI 3-Kinase p85 beta
Other PI 3-Kinase Products
Kinase Assay Kits
Kinase Substrates
Other Kinase Activators
Other Kinase Inhibitors
Other Kinase Libraries
PI 3-Kinase C2 beta
PI 3-Kinase Inhibitors
PI 3-Kinase p55 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p85 alpha
PI 3-Kinase p110 beta
PI 3-Kinase p110 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p110 delta
PI 3-Kinase p85 beta
Other PI 3-Kinase Products
Kinase Assay Kits
Kinase Substrates
Other Kinase Activators
Other Kinase Inhibitors
Other Kinase Libraries
PKC
ProductsClose
Rap1
RIAM
ProductsClose
Src
ProductsClose
G Protein
Coupled Receptors
Coupled Receptors
P2Y1,12
ProductsClose
PAR1,3,4
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
5-HT2A
5-HT2A Receptor Agonists
5-HT2A Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Additional Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Products
5-HT4
5-HT4 Receptor Agonists
5-HT4 Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Antagonists
Additional 5-HT-Related Compounds
5-HT2A Receptor Agonists
5-HT2A Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Additional Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Products
5-HT4
5-HT4 Receptor Agonists
5-HT4 Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Antagonists
Additional 5-HT-Related Compounds
5-HT2A,4
ProductsClose
5-HT2A
5-HT2A Receptor Agonists
5-HT2A Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Additional Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Products
5-HT4
5-HT4 Receptor Agonists
5-HT4 Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Antagonists
Additional 5-HT-Related Compounds
5-HT2A Receptor Agonists
5-HT2A Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Additional Non-selective 5-HT2 Receptor Products
5-HT4
5-HT4 Receptor Agonists
5-HT4 Receptor Antagonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Agonists
Non-selective 5-HT Receptor Antagonists
Additional 5-HT-Related Compounds
ProductsClose
Thromboxane A2 R
ProductsClose
PI 3K
ProductsClose
PI 3-Kinase Activators
PI 3-Kinase C2 beta
PI 3-Kinase Inhibitors
PI 3-Kinase p55 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p85 alpha
PI 3-Kinase p110 beta
PI 3-Kinase p110 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p110 delta
PI 3-Kinase p85 beta
Other PI 3-Kinase Products
Kinase Assay Kits
Kinase Substrates
Other Kinase Activators
Other Kinase Inhibitors
Other Kinase Libraries
PI 3-Kinase C2 beta
PI 3-Kinase Inhibitors
PI 3-Kinase p55 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p85 alpha
PI 3-Kinase p110 beta
PI 3-Kinase p110 gamma
PI 3-Kinase p110 delta
PI 3-Kinase p85 beta
Other PI 3-Kinase Products
Kinase Assay Kits
Kinase Substrates
Other Kinase Activators
Other Kinase Inhibitors
Other Kinase Libraries
PKC
ProductsClose
PLC
Rap1
RIAM
ProductsClose
Src
ProductsClose
Inhibitory
Receptors
Receptors
ProductsClose
CD31/PECAM-1
ProductsClose
G6b
ProductsClose
PTGIR
ProductsClose
PKA
ProductsClose
PKG
ProductsClose
Immune
Receptors
Receptors
ProductsClose
CCR1,2,3,4
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
CX3CR1
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
CXCR4,6
ProductsClose
ProductsClose
CD40 Ligand
ProductsClose
Fc gamma RIIA
ProductsClose
IGF-I R
ProductsClose
PDGF R alpha
PDGF R beta
P-Selectin
RAGE
ProductsClose
TLR1,2,4,6
ProductsClose
Alpha Granule
Dense Granule
Lysosome
Coagulation regulators
Inflammatory mediators
Wound healing factors
Bioactive amines
Polyphosphates
Purines
Glycosidases
Proteases
Calcium release
Integrin activation
Granule release
Thromboxane A2 production
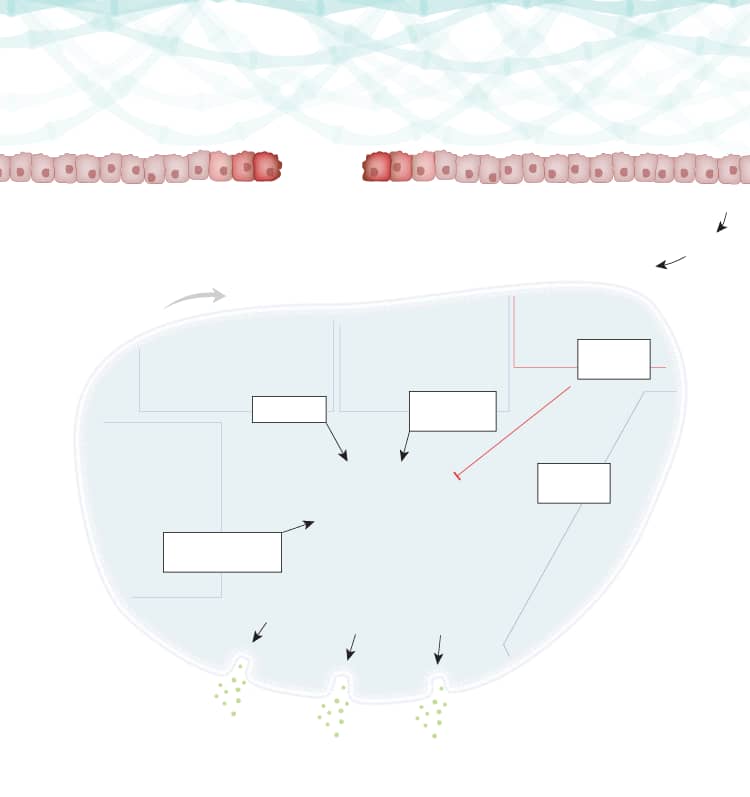
Overview of Platelet Activation
Platelet activation encompasses a complex and very rapid series of processes that are critical for hemostasis and inflammation. Resting platelets express many cell surface receptors which respond to ligands generated or exposed during inflammation and damage to the vascular endothelium. Activated platelets promote clot formation (thrombosis), broaden inflammatory responses, and contribute to wound healing. Impaired platelet activation can lead to uncontrolled bleeding. Pathological activation of platelets is characteristic of several diseases (e.g. atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension, and deep vein thrombosis) and is a common target of anti-thrombotic treatment for these patients.

