Avi-tag and Amine-Labeled Biotinylated Proteins
R&D Systems offers a wide assortment of biotinylated proteins allowing researchers to take the guesswork out of protein biotinylation. In addition to amine-labeled biotinylated proteins, we have a growing list of Avi-tag biotinylated proteins. Each biotinylated protein is held to the same industry-leading quality standards as their unlabeled counterpart while also limiting batch-to-batch variability. Also, the R&D Systems Custom Protein Development Team can work with you to create a customized protein solution to meet your specific research needs.
Advantages of Avi-tag Biotinylated Recombinant Proteins
- 1. Consistent labeling. Biotinylation only occurs on the single lysine residue in the Avi-tag.
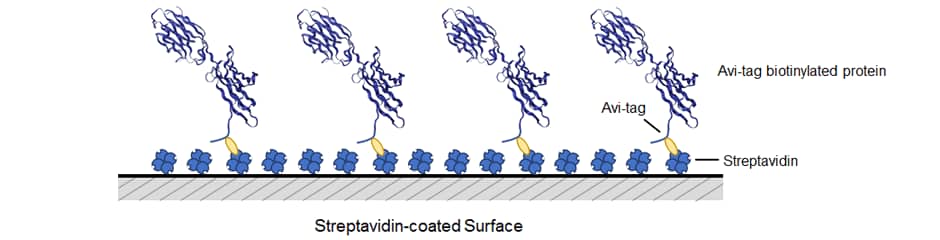
- 2. Uniform orientation of protein. When bound to a streptavidin-coated surface, the avitagged protein orientation will be uniform due to the precise control over biotinylation.
- 3. Equivalent bioactivity. Because biotinylation is restricted to the Avi-tag, the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein’s bioactivity.
- 4. Lot-to-lot consistency. Each new lot is tested side-by-side with previous lots and with a master lot to ensure high lot-to-lot consistency.
Looking for an Avi-tag protein that we don’t have? We want to hear from you!
Click the link to contact us.
Avi-tag Biotinylated Proteins – Products by Molecule
Advantages of Amine-labeled and Sugar-labeled Biotinylated Proteins
- 1. High signal strength. Proteins typically average multiple biotins per molecule making them an excellent choice when high signal strength is important.
- 2. Equivalent bioactivity. Biotinylated proteins are rigorously tested to ensure that they exhibit the same level of bioactivity as the unlabeled protein.
- 3. Lot-to-lot consistency. Each new lot is tested side-by-side with previous lots and with a master lot to ensure high lot-to-lot consistency.
Amine-labeled and Sugar-labeled Biotinylated Proteins – Products by Molecule

Custom Services
If you can't find what the protein that need on our website, contact us. From scratch protein development to customizing a protein from our catalog, our custom services team will create the protein that fits with your experimental needs.
Contact our team
Biotinylated protein features: Equivalent Bioactivity
Consistent bioactivity between biotinylated and non-biotinylated proteins

Both Biotinylated Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Avi-tag and unlabeled Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 inhibit anti-CD3 antibody-induced IL-2 secretion in human T lymphocytes. The similarity in activity highlights that the biotinylated Avi-tag protein is fully functional.

Both Biotinylated Recombinant Human VEGF 165 (Catalog # BT293) and unlabeled Recombinant Human VEGF 165 (Catalog # 293-VE) stimulate HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation. The ED50 for this effect is 1-6 ng/mL. The similarity in activity highlights that the biotinylated protein is fully functional.

Both Biotinylated Recombinant Human TNF-alpha (Catalog # BT210) and unlabeled Recombinant Human TNF-alpha (Catalog # 210-TA) promotes cytotoxicity in L‑929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D. The ED50 for this effect is 25-100 pg/mL. The similarity in activity highlights that the biotinylated protein is fully functional.
Binding activity

When 500 ng/mL of Biotinylated Recombinant Human PD-1 His-tag Avi-tag protein is immobilized onto Streptavidin coated plate (Catalog # CP004), it binds to Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 156-B7) with an ED50 of 1.2-7.2 ng/mL.

When Recombinant Human APRIL/TNFSF13 (Catalog # 5860-AP) is immobilized at 0.1 µg/mL, Recombinant Human BCMA/TNFRSF17 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI193) binds with an ED50 of 0.3-1.8 ng/mL.

When Recombinant Human VSIG3 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 9229-VS) is coated at 5 μg/mL, Biotinylated Recombinant Human VISTA/B7-H5/PD-1H Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI7126) binds with an ED50 of 0.5-3 μg/mL.
Lot-to-lot consistency

Three independent lots of B7-H1/PD-L1 have near identical bioactivity. When Recombinant Human PD-1 (Catalog #1086-PD) is coated at1 μg/mL, Biotinylated Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI156) binds with an ED50 of 8-48 ng/mL.
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)

Immobilized CD155/PVR-Fc Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI9174) bound to streptavidin CM5 chip binds to TIGIT-Fc (Catalog # 7898-TGB) with an affinity constant of 25.4 nM. For more information on using Avi-tag proteins in SPR, download the application note.
About Biotinylated Proteins
Biotinylated proteins are powerful tools used in a wide variety of assay formats, including immunoprecipitation, flow cytometry, immunoassays, biopanning, and surface plasmon resonance. Historically, individual labs have made their own biotinylated proteins in small batches. However, often times researchers encounter protein-specific technical challenges and high variability leading to inconsistent results.
What is Avi-tag?
Avi-tag Biotinylated Proteins are proteins that feature biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 amino acid peptide. The DNA sequence coding for the Avi-tag is inserted during cloning and contained in the final expression vector construct. Biotinylation of the Avi-tag is enzymatically added by the E. coli biotin ligase BirA. This results in a single biotin molecule covalently attached to the lysine residue within the Avi-tag. The Avi-tag sequence is Gly-Leu-Asn-Asp-Ile-Phe-Glu-Ala-Gln-Lys-Ile-Glu-Trp-His-Glu.
