LIF Signaling Pathways
Cell Proliferation
(Inactive)
(Unknown)
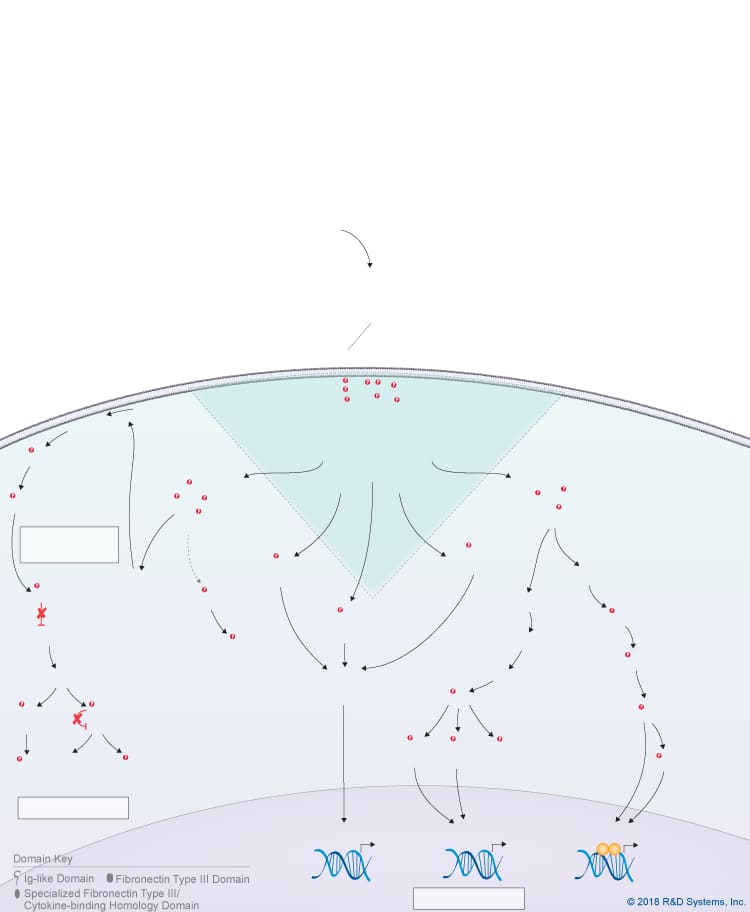
Overview of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) Signaling Pathways
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) is a member of the IL-6 cytokine family, which also includes IL-6, IL-11, IL-27 p28/IL-30, IL-31, Oncostatin M (OSM), Cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), and Neuropoietin. Like other IL-6 family cytokines, LIF is a four alpha-helix bundle cytokine that signals through a receptor complex containing the gp130 receptor subunit. LIF binds with high affinity to both LIF R and gp130, which form a heterodimeric receptor complex. Both LIF R and gp130 are signal-transducing receptor subunits that associate with the Jak family of tyrosine kinases through their intracellular domains. Activation of Jak family kinases leads to the phosphorylation of STAT family proteins, primarily STAT3 and to a lesser extent STAT1, which dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, where they regulate gene expression. In addition to Jak-STAT signaling, LIF also activates the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt signaling pathway, and the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways.
LIF is produced by numerous different cell types and plays a critical role in regulating nervous system development, stem cell pluripotency, differentiation, bone metabolism, and inflammation. It was originally identified and purified based on its ability to induce mouse myeloid leukemia M1 cell differentiation and has subsequently been shown to be involved in maintaining the pluripotency and self-renewal capacity of embryonic stem cells and increasing the self-renewal capabilities of neural stem cells. In addition, LIF has been found to have effects on the nervous, reproductive, skeletal, muscular, and endocrine systems. It has been shown to stimulate the production and survival of neurons and oligodendrocytes, facilitate successful embryo implantation, regulate bone formation and remodeling, regulate myoblast survival and differentiation, promote the differentiation of both cardiac smooth muscle cells and adipocytes, and regulate adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion. Besides these activities, LIF has also been reported to regulate inflammation, promote regulatory T cell differentiation, and induce the acute phase response in hepatocytes.
To learn more, please visit our IL-6 Family Research Area page.
| Primary LIF-Expressing Cells | Primary Biological Effects of LIF |
| Astrocytes | Induces the differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells |
| Bone marrow stromal cells | Maintains the pluripotency and self-renewal capacity of embryonic stem cells |
| Cardiac myoblasts | Increases the self-renewal of neural stem cells and stimulates the production and survival of neurons and oligodendrocytes |
| Chondrocytes | Facilitates successful endometrial implantation of an embryo |
| Epithelial cells | Regulates myoblast differentiation and promotes their survival |
| Fibroblasts | Promotes the differentiation of cardiac smooth cells and adipocytes |
| Keratinocytes | Induces cardiomyocte hypertrophy |
| Monocytes/macrophages | Regulates bone formation and remodeling |
| Osteoblasts | Regulates the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| Synoviocytes | Induces the production of acute phase proteins by hepatocytes |
| T cells | Promotes Treg differentiation and inhibits Th17 cell differentiation |
| Reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increases the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines |

