FGF Family Signaling Pathways
Degradation
Phosphatase
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
(Inactive)
Differentiation
Factor
Factor
Factor
Inhibitors
| • FGF-1 subfamily members: FGF-1 and FGF-2. |
| • Both lack a classical secretory signal peptide and are secreted independently of the traditional ER-Golgi secretory pathway. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • FGF-1 and FGF-2 are found in the nucleus of some cells. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-1 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-4 subfamily members: FGF-4, FGF-5, and FGF-6. |
| • Have a cleavable N-terminal signal peptide. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-4 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-7 subfamily members: FGF-3, FGF-7, FGF-10, and FGF-22. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-7 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-8 subfamily members: FGF-8, FGF-17, and FGF-18. |
| • Have a cleavable N-terminal signal peptide. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • Alternative splicing of FGF8 gives rise to four potential isoforms in human (FGF-8a, FGF-8b, FGF-8e, FGF-8f) and eight in mouse (FGF-8a-h). |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-8 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-9 subfamily members: FGF-9, FGF-16, and FGF-20. |
| • Lack a classical N-terminal signal peptide, but have an internal hydrophobic sequence that functions as a signal for their transport into the ER and secretion. |
| • Utilize heparin/HS as a co-factor to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-9 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-11 subfamily members: FGF-11, FGF-12, FGF-13, and FGF-14. |
| • Also known as FGF homologous factors (FHFs), FGF-11 subfamily members have high sequence identity and structural homology with the FGF family, but are not secreted and do not activate FGF receptors. |
| • As intracellular FGFs, FGF-11 subfamily members interact with the cytosolic carboxy-terminal tail of voltage-gated sodium channels. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-11 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
| • FGF-19 subfamily members: FGF-19 (human)/FGF-15 (mouse), FGF-21, and FGF-23. |
| • Bind to heparin/HS with very low affinity, facilitating their release from the ECM and their function as endocrine factors. |
| • Require Klotho proteins as co-factors to bind to FGF receptors. |
| • FGF-15 is the mouse orthologue of human FGF-19. |
| • See the table below the pathway for additional information on the FGF-19 subfamily members including their suggested physiological functions and reported receptor binding specificities. |
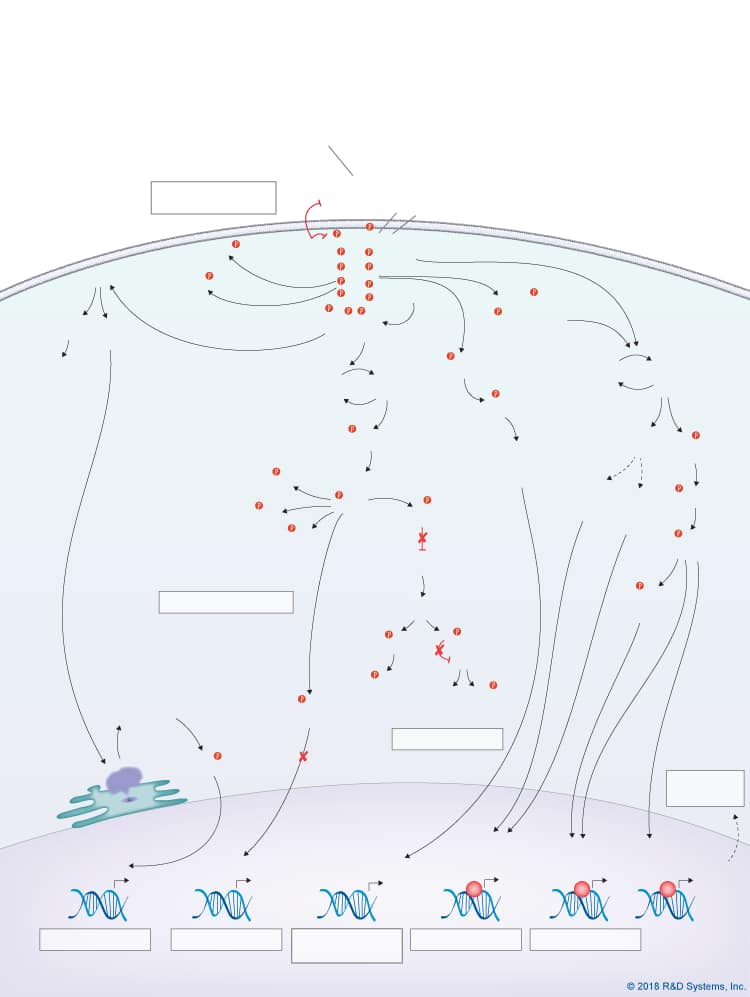
Overview of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Family Signaling Pathways
The mammalian Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) superfamily consists of eighteen secreted proteins (FGF-1 – FGF-10 and FGF-16 – FGF-23) and four intracellular FGFs (FGF-11 – FGF-14), known as FGF homologous factors. The secreted FGFs belong to one of six subfamilies (FGF-1, FGF-4, FGF-7, FGF-8, FGF-9, and FGF-19) based on sequence homology, biological functions, and evolutionary relationships, while the intracellular FGFs make up the FGF-11 subfamily. Secreted FGFs are typically sequestered by heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) that are tethered to the cell surface and/or associated with the extracellular matrix, causing their effects to be localized to nearby cells. Only the FGF-19 subfamily, including FGF-21, FGF-23, and FGF-19 in humans or the mouse FGF-19 equivalent, FGF-15, acts in an endocrine manner. Although these FGFs are also dependent on HSPGs for signaling, they bind to heparin/heparan sulfate (HS) with very low affinity compared to the other FGFs, allowing them to more freely circulate. Unlike the canonical, secreted FGFs, intracellular FGFs (iFGFs) are nonsignaling proteins that interact with the cytosolic carboxy-terminal tail of voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channels. This group of FGFs has been shown to regulate neuronal and myocardial excitability by modulating both the current density and gating properties of NaV channels.
Secreted FGFs bind to one of four transmembrane receptors with intracellular tyrosine kinase domains (FGF R1, FGF R2, FGF R3, and FGF R4) in a 2:2:2 HSPG-FGF-FGF receptor ratio. Ligand binding specificity is determined by the differential expression patterns of the FGFs, FGF receptors, and glycosaminoglycan structures, different receptor binding capacities, the requirement for specific co-factors such as the Klotho family proteins, and alternative splicing of the FGF receptors that results in two different versions of the extracellular Ig-like domain III (b or c). Following HSPG-ligand-binding to the FGF receptor, the receptor homodimerizes, leading to activation of the cytoplasmic intracellular kinase domain of the receptor, and recruitment and docking of adaptor proteins such as FRS2, GRB2, Shb, and Shc. These adaptor proteins subsequently activate multiple downstream signaling pathways including the Ras-MAPK pathway, the Jak-STAT pathway, the PI 3-Kinase-Akt pathway, the PLC gamma pathway, and the p38 and JNK MAPK pathways. Through these signaling pathways, FGFs promote fundamental cellular processes such as survival, proliferation, differentiation, and motility. Secreted FGFs have been shown to be involved in a wide range of biological processes during normal physiological development including cell differentiation in the early embryo, pattern formation, branching morphogenesis, limb development, and organogenesis, including heart and brain development. Additionally, they contribute to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis, repair, and metabolism in adult organisms. Gain or loss of function mutations in FGFs are associated with a variety of developmental defects and pathological conditions including cancer.
To learn more, please visit our FGF Family Research Area page
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-1 | FGF-1 | FGF acidic; HBGF-1 | Not established | • FGF1 amplification - ovarian cancer | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| FGF-2 | FGF basic; HBGF-2 | Wound healing | • FGF2 overexpression - bladder cancer, prostate cancer, small cell lung carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-4 | FGF-4 | K-FGF; HBGF-4; HST-1 | Limb bud and heart development | • FGF4 amplication - breast cancer | X | X | X | X | |||
| FGF-5 | HBGF-5 | Hair follicle development and growth cycle regulation | • FGF5 overexpression - glioblastoma | X | X | X | |||||
| FGF-6 | HBGF-6; HST-2 | Muscle development and regeneration | • FGF6 overexpression - prostate cancer | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-7 | FGF-3 | HBGF-3; INT2 | Inner ear development | • FGF3 haploinsufficiency - Otodental syndrome • FGF3 missense/frameshift mutation - Michel aplasia, LAMM syndrome • FGF3 amplification - breast cancer | X | X | |||||
| FGF-7 | KGF; HBGF-7 | Branching morphogenesis | • FGF7 polymorphism - COPD • FGF7 overexpression - lung adenocarcinoma | X | |||||||
| FGF-10 | KGF-2 | Branching morphogenesis; Inner ear development | • FGF10 nonsense mutation - Aplasia of the lacrimal and salivary glands (ALSG), Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital (LADD) syndrome • FGF10 polymorphism - severe myopia • FGF10 overexpression - breast cancer, prostate cancer | X | X | ||||||
| FGF-22 | Presynapitc neural organizer | X | X | ||||||||
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-8 | FGF-8a | AIGF; HBGF-8 | Brain, eye, ear, heart, kidney, and limb bud development | • FGF8 nonsense mutation - Familial hypogonadotropic hypogonadism • FGF8 missense mutation - cleft lip and palate, holoprosencephaly, craniofacial defects, hypothalamo-pituitary dysfunction | |||||||
| FGF-8b | AIGF; HBGF-8 | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| FGF-8e | AIGF; HBGF-8 | X | X | ||||||||
| FGF-8f | AIGF; HBGF-8 | X | X | X | |||||||
| FGF-17 | FGF-13 | Brain development | • FGF17 missense mutation - Familial hypogonadotropic hypogonadism • FGF17 overexpression - hepatocellular carcinoma, prostate cancer | X | X | X | X | ||||
| FGF-18 | ZFGF5 | Bone development; Lung alveolar development | • FGF18 polymorphism - nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate • FGF18 overexpression - hepatocellular carcinoma | X | X | ||||||
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-9 | FGF-9 | GAF; HBGF-9 | Organogenesis; Gonad development; Inner ear development | • FGF9 missense mutation - Multiple synostosis syndrome (SYNS) • FGF9 promoter mutation - Sertoli cell-only syndrome (SCOS) • FGF9 frameshift/missense/nonsense mutations - colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer • FGF9 overexpression - non-small cell lung cancer | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| FGF-16 | MF4 | Heart development | • FGF16 nonsense mutation - metacarpal 4-5 fusion • FGF16 overexpression - ovarian cancer | X | X | X | X | ||||
| FGF-20 | RHDA2 | Neurotrophic factor | • FGF20 polymorphism - risk of Parkinson's disease • FGF20 frameshift mutation - bilateral renal agenesis | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-11 | FGF-11 | FHF-3 | |||||||||
| FGF-12 | FHF-1 | • FGF12 missense mutation - Brugada syndrome | |||||||||
| FGF-13 | FHF-2 | Neuronal migration; Learning and memory | • FGF13 nonsense mutation - Borjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome (BFLS) • Low FGF13 expression - X-linked congenital generalized hypertrichosis | ||||||||
| FGF-14 | FHF-4 | Neuronal firing; Movement and coordination; Learning and memory | • FGF14 missense/deletion/translocation mutations - Spinocerebellar ataxia 27 (SCA27) | ||||||||
| Subfamily | Human Ligands | Alternate Name | Physiological Function (Based on the knockout mouse phenotype) | Pathologies Associated with FGF Mutations | Reported Receptor Binding Specificity | ||||||
| R1b | R1c | R2b | R2c | R3b | R3c | R4 | |||||
| FGF-19 | FGF-19 | FGF-15 (mouse) | Bile acid metabolism; lipolysis; gall bladder filling | • FGF19 overexpression - prostate cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma | X | X | X | X | |||
| FGF-21 | Energy/lipid metabolism | • FGF21 polymorphism - increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes | X | X | X | X | |||||
| FGF-23 | ADHR; HPDR2; HYPF | Phosphate and vitamin D homeostasis; Middle ear development | • FGF23 missense mutation - Autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets (ADHR), Familial tumoral calcinosis (FTC) • FGF23 polymorphism - cardiac abnormalities in Kawasaki syndrome, increased risk of prostate cancer | X | X | X | X | ||||

